 |
Collision Cascade
In condensed-matter physics, a collision cascade (also known as a displacement cascade or a displacement spike) is a set of nearby adjacent energetic (much higher than ordinary thermal energies) collisions of atoms induced by an energetic particle in a solid or liquid. If the maximum atom or ion energies in a collision cascade are higher than the threshold displacement energy of the material (tens of eVs or more), the collisions can permanently displace atoms from their lattice sites and produce defects. The initial energetic atom can be, e.g., an ion from a particle accelerator, an atomic recoil produced by a passing high-energy neutron, electron or photon, or be produced when a radioactive nucleus decays and gives the atom a recoil energy. The nature of collision cascades can vary strongly depending on the energy and mass of the recoil/incoming ion and density of the material (stopping power). Linear cascades When the initial recoil/ion mass is low, and the mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
10kevau Au
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. The journal is considered one of the most prestigious in the field of physics. Over a quarter of Physics Nobel Prize-winning papers between 1995 and 2017 were published in it. ''PRL'' is published both online and as a print journal. Its focus is on short articles ("letters") intended for quick publication. The Lead Editor is Hugues Chaté. The Managing Editor is Robert Garisto. History The journal was created in 1958. Samuel Goudsmit, who was then the editor of '' Physical Review'', the American Physical Society's flagship journal, organized and published ''Letters to the Editor of Physical Review'' into a new standalone journal'','' which became ''Physical Review Letters''. It was the first journal intended for the rapid publication of short articles, a format that eventually became popular in many other fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Maxwell–Boltzmann Distribution
In physics (in particular in statistical mechanics), the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, or Maxwell(ian) distribution, is a particular probability distribution named after James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann. It was first defined and used for describing particle speeds in ideal gas, idealized gases, where the particles move freely inside a stationary container without interacting with one another, except for very brief collisions in which they exchange energy and momentum with each other or with their thermal environment. The term "particle" in this context refers to gaseous particles only (atoms or molecules), and the system of particles is assumed to have reached thermodynamic equilibrium. The energies of such particles follow what is known as Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics, and the statistical distribution of speeds is derived by equating particle energies with kinetic energy. Mathematically, the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution is the chi distribution with three degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Interstitial Defect
In materials science, an interstitial defect is a type of point crystallographic defect where an atom of the same or of a different type, occupies an interstitial site in the crystal structure. When the atom is of the same type as those already present they are known as a self-interstitial defect. Alternatively, small atoms in some crystals may occupy interstitial sites, such as hydrogen in palladium. Interstitials can be produced by bombarding a crystal with elementary particles having energy above the displacement threshold for that crystal, but they may also exist in small concentrations in thermodynamic equilibrium. The presence of interstitial defects can modify the physical and chemical properties of a material. History The idea of interstitial compounds was started in the late 1930s and they are often called Hagg phases after Hägg. Transition metals generally crystallise in either the hexagonal close packed or face centered cubic structures, both of which can be conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Physical Review
''Physical Review'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. The journal was established in 1893 by Edward Nichols. It publishes original research as well as scientific and literature reviews on all aspects of physics. It is published by the American Physical Society (APS). The journal is in its third series, and is split in several sub-journals each covering a particular field of physics. It has a sister journal, '' Physical Review Letters'', which publishes shorter articles of broader interest. History ''Physical Review'' commenced publication in July 1893, organized by Cornell University professor Edward Nichols and helped by the new president of Cornell, J. Gould Schurman. The journal was managed and edited at Cornell in upstate New York from 1893 to 1913 by Nichols, Ernest Merritt, and Frederick Bedell. The 33 volumes published during this time constitute ''Physical Review Series I''. The American Physical Society (APS), founded in 1899, took over its publicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
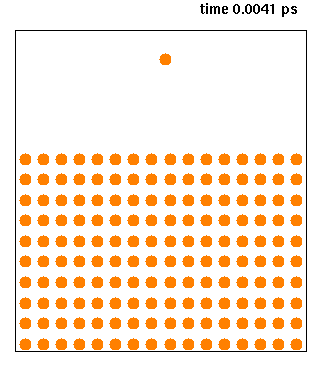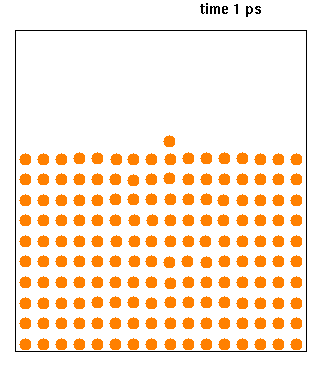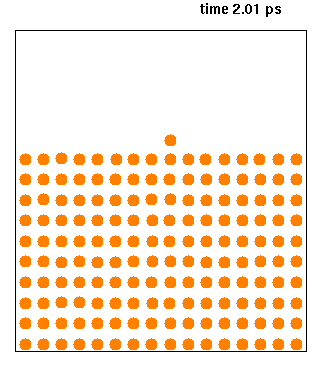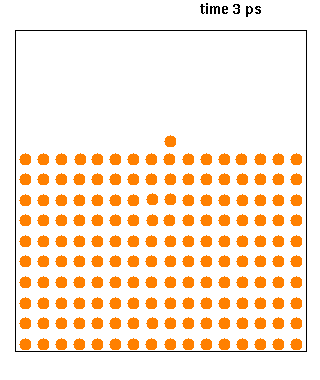 |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Stopping And Range Of Ions In Matter
Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter (SRIM) is a group of computer programs which calculate interactions between stopping power (particle radiation), ions and matter; the core of SRIM is a program called Transport of Ions in Matter (TRIM). SRIM is popular in the ion implantation research and technology community, and also used widely in other branches of radiation material science. History SRIM originated in 1980 as a DOS based program then called TRIM. The DOS version was upgraded until 1998 and is still available for download. It will run on a Unix PC having a DOS emulator. SRIM-2000 requires a computer with any Windows operating system. The program may work with Unix or Macintosh based systems through Wine (software), Wine. The programs were developed by James F. Ziegler and Jochen P. Biersack around 1983 and are being continuously upgraded with the major changes occurring approximately every five years. SRIM is based on a Monte Carlo method, Monte Carlo simulation method, na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |