|
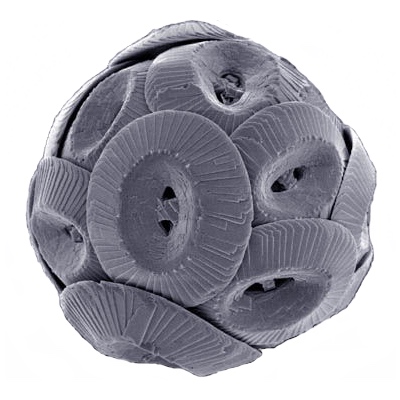
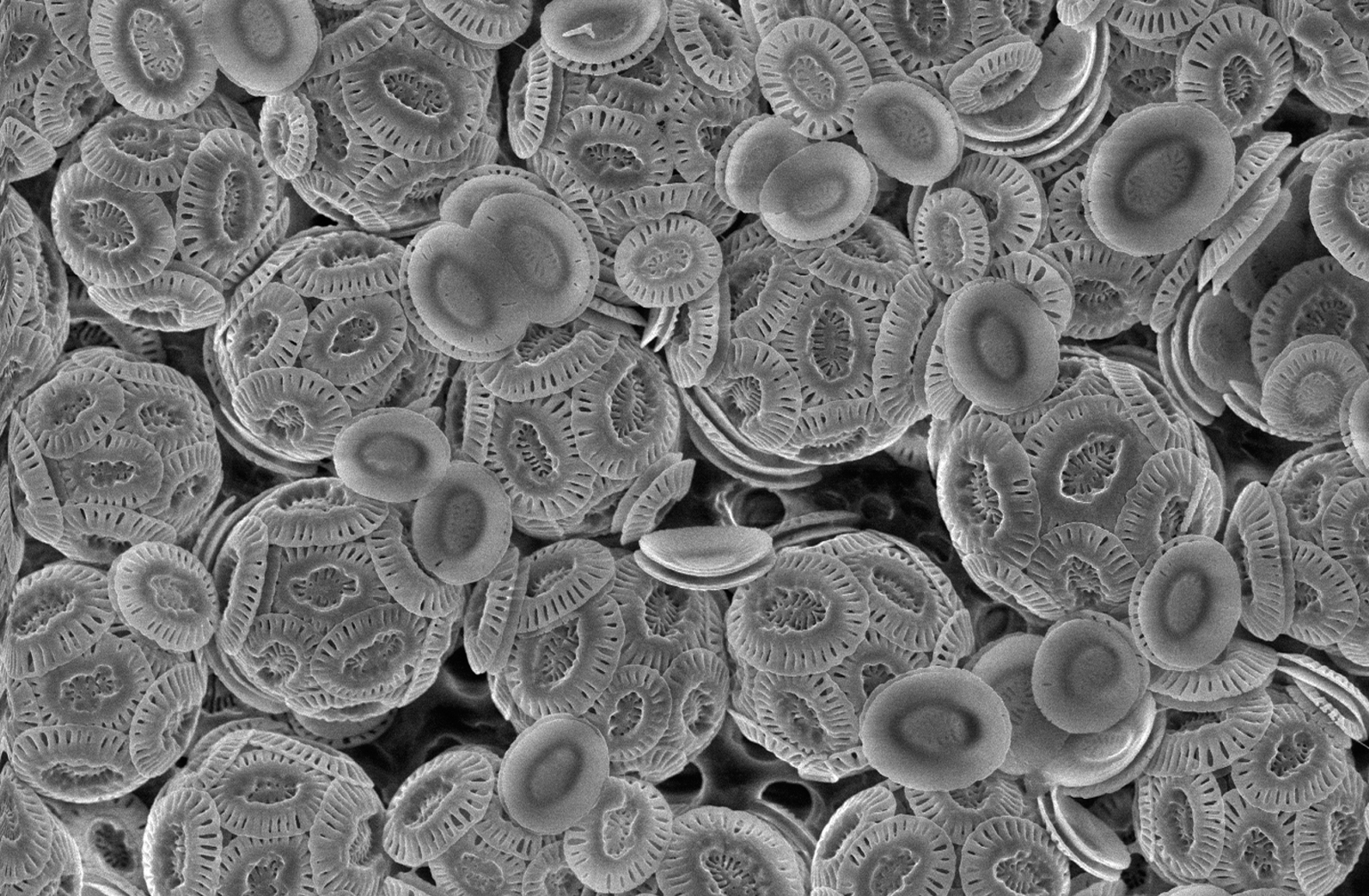
Coccoliths
Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores (single-celled phytoplankton such as ''Emiliania huxleyi'') and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a ''coccosphere''. Overview Coccoliths, which are about 2-25 micrometres across, enclose coccolithophores, which are spherical cells about 5-100 micrometres across. Coccolithophores are an important group of about 200 marine phytoplankton species which cover themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a "coccosphere". They are ecologically and biogeochemically important but the reason why they calcify remains elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one of the main causes of phytoplankton death in the ocean. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License File:Cross section of a coccolithophore with coc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker (ecologist), Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division (botany), division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively Marine (ocean), marine, are photosynthesis, photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the Photic zone, sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccosphere
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively marine, are photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a '' coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that the coccosphere offers protection against microzooplankton predation, which is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccolithophore Shells
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker (ecologist), Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division (botany), division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively Marine (ocean), marine, are photosynthesis, photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the Photic zone, sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emiliania Huxleyi
''Gephyrocapsa huxleyi'', also called ''Emiliania huxleyi'', is the most abundant species of coccolithophore in modern oceans found in almost all ecosystems from the equator to sub-polar regions, and from nutrient rich upwelling zones to nutrient poor oligotrophic waters. It is one of thousands of different photosynthetic plankton that freely drift in the photic zone of the ocean, forming the basis of virtually all marine food webs. It is studied for the extensive blooms it forms in nutrient-depleted waters after the reformation of the summer thermocline. Like other coccolithophores, ''G. huxleyi'' is a single-celled phytoplankton covered with uniquely ornamented calcite disks called coccoliths. Individual coccoliths are abundant in marine sediments although complete coccospheres are more unusual. In the case of ''G. huxleyi'', not only the shell, but also the soft part of the organism may be recorded in sediments. It produces a group of chemical compounds that are very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
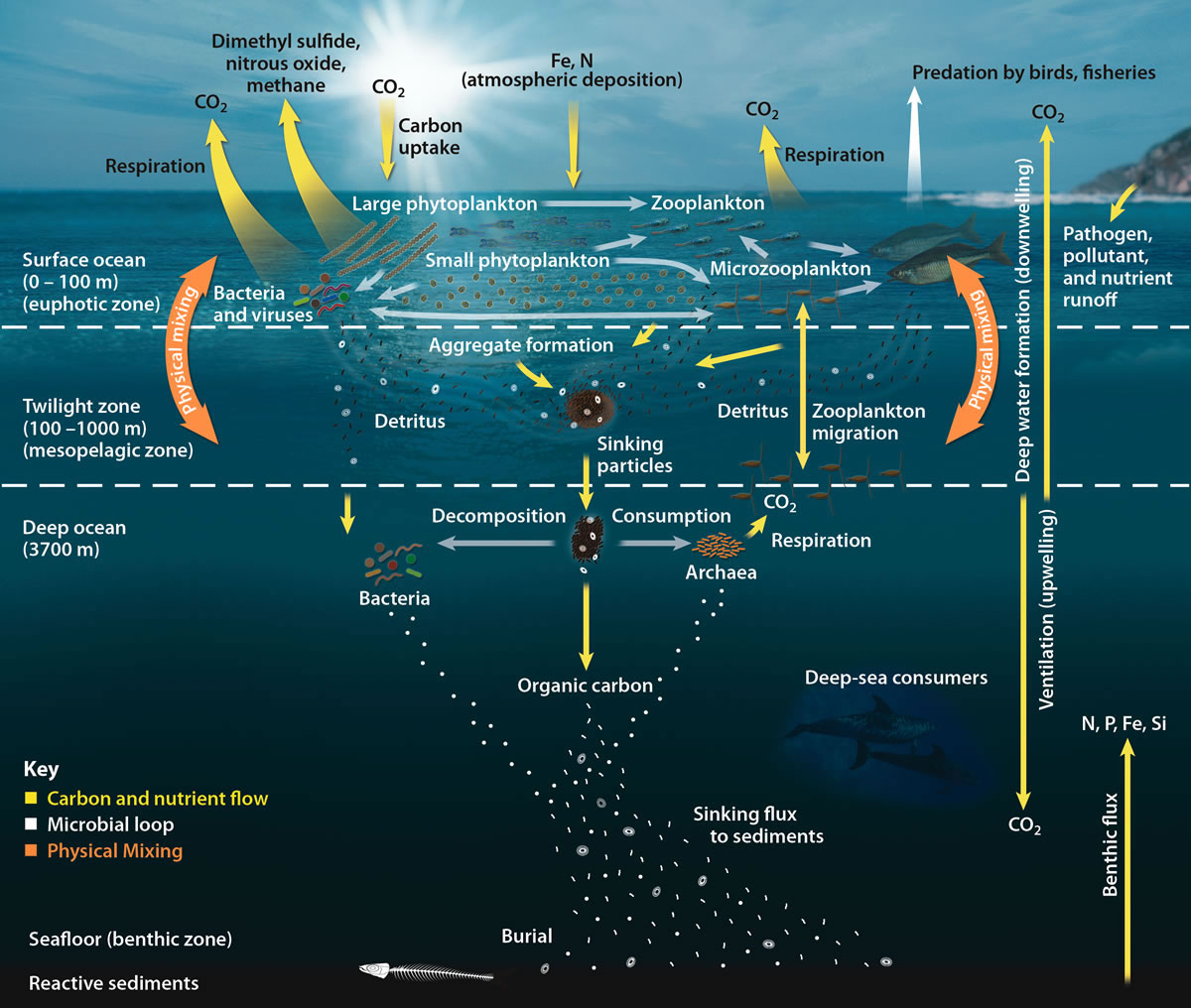
Ballast Minerals
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated process which results in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calculations of the biolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Cliffs Of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover are the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, deposited during the Late Cretaceous. The cliffs, on both sides of the town of Dover in Kent, stretch for . The White Cliffs of Dover form part of the North Downs. A section of coastline encompassing the cliffs was purchased by the National Trust in 2016. The cliffs are part of the Dover to Kingsdown Cliffs Site of Special Scientific Interest and Special Area of Conservation. The point where Great Britain is closest to continental Europe, on a clear day the cliffs are visible from France, approximately away. A celebrated UK landmark, the cliffs have featured on commemorative postage stamps issued by the Royal Mail, including in their British coastline series in 2002 and UK A-Z series in 2012. Location The cliffs are part of the coas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Carbon Pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven Carbon sequestration, sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated process which results in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calcul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroups, such as Archaeplastida ( photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and " Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, including extreme habitats. Their diversity, larger than for all other eukaryotes, has only been discovered in rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in water (or air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish, and baleen whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa, microscopic fungi, and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in lakes and rivers. Mostly, plankton just drift where currents take them, though some, like jellyfish, swim slowly but not fast enough to generally overcome the influence of currents. Although plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, there are also airborne versions that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These ''aeroplankton'' include plant spor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
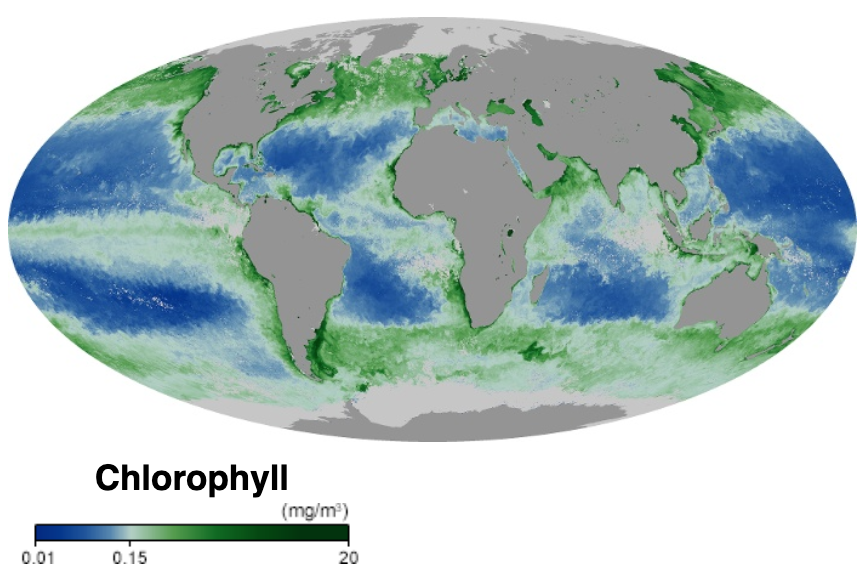
Marine Primary Production
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotrophs. Most marine primary production is generated by a diverse collection of marine microorganisms called algae and cyanobacteria. Together these form the principal primary producers at the base of the ocean food chain and produce half of the world's oxygen. Marine primary producers underpin almost all marine animal life by generating nearly all of the oxygen and food marine animals need to exist. Some marine primary producers are also ecosystem eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccolithus Pelagicus
''Coccolithus'' is a genus of unicellular haptophytes. Species The species in this genus include: *'' Coccolithus oceanicus'' *'' Coccolithus pelagicus'' *'' Coccolithus pliopelagicus'' References Haptophyte genera {{Haptophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |