|
Coat Of Many Colors
In the Hebrew Bible, the coat of many colors or () is the name for the garment that the Bible, Biblical Joseph (Genesis), Joseph owned; it was given to him by his father Jacob in Vayeshev (Book of Genesis, Genesis 37). Biblical narrative Joseph's father, Jacob (also called Israel), favored him and gave Joseph the coat as a gift; as a result, he was Jealousy, envied by his brothers, who saw the special coat as an indication that Joseph would assume family leadership. His brothers' suspicion grew when Joseph told them of his two dreams (Genesis 37:11) in which all the brothers bowed down to him. The narrative tells that his brothers plotted against him when he was 17, and would have killed him had not the eldest brother Reuben (Bible), Reuben interposed. He persuaded them instead to throw Joseph into a pit and secretly planned to rescue him later. However, while Reuben was absent, the others planned to sell him to a company of Ishmaelites, Ishmaelite merchants. When the passing M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
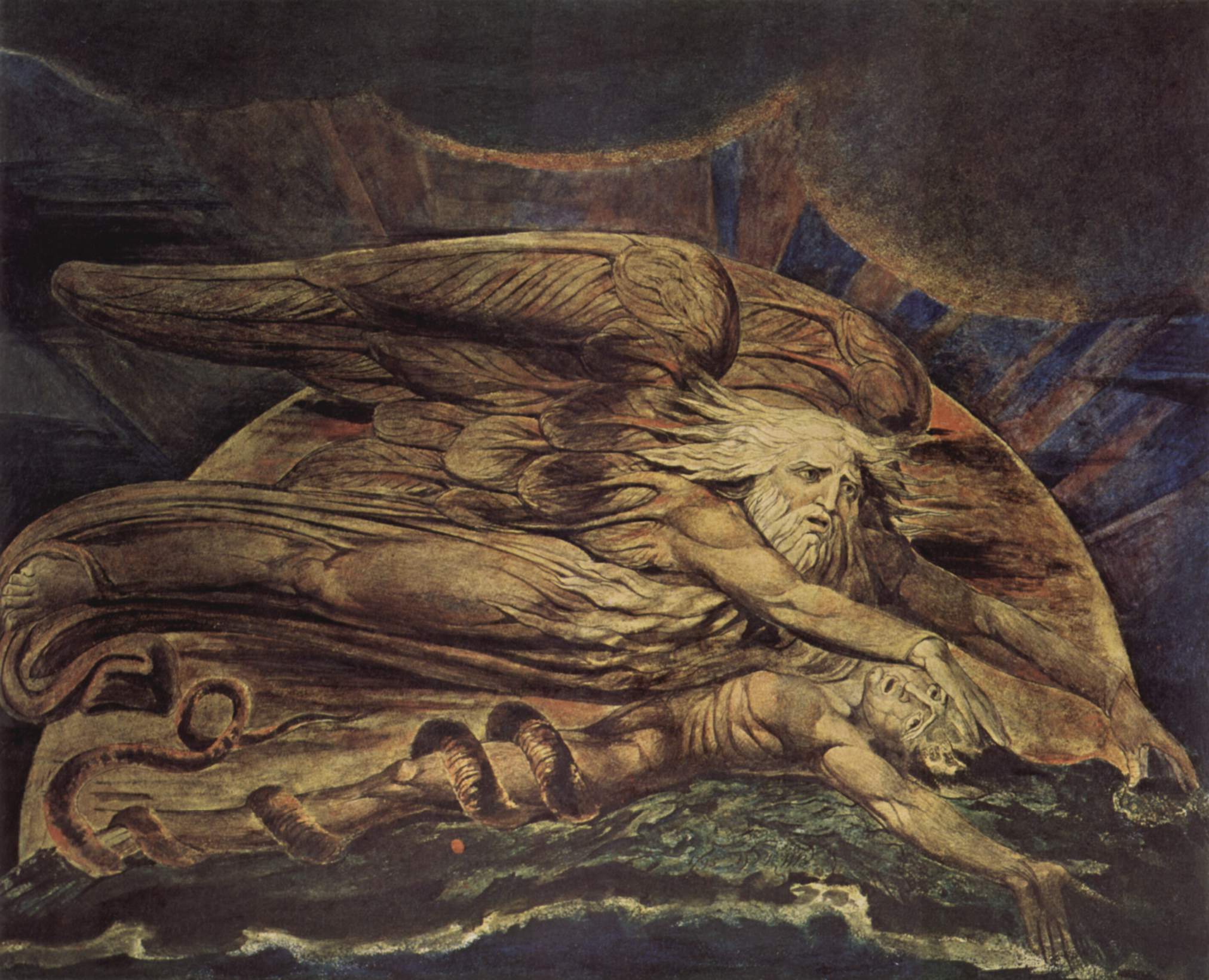
Jacob Blesses Joseph And Gives Him The Coat
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Patriarchs (Bible), Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother Esau, Jacob's paternal grandparents are Abraham and Sarah and his maternal grandfather is Bethuel, whose wife is not mentioned. He is said to have bought Esau's birthright and, with his mother's help, deceived his aging father to bless him instead of Esau. Then, following a severe drought in his homeland Canaan, Jacob and his descendants migrated to neighbouring Biblical Egypt, Egypt through the efforts of his son Joseph (Genesis), Joseph, who had become a confidant of the Pharaohs in the Bible, pharaoh. After dying in Egypt at the age of 147, he is supposed to have been buried in the Cave of Machpelah in Hebron. Per the Hebrew Bible, Jacob's progeny were beget by four women: his wives (and maternal cousins) Leah and Rach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Painting Of Foreign Delegation In The Tomb Of Khnumhotep II Circa 1900 BCE (Detail Mentioning "Abisha The Hyksos" In Hieroglyphs)
Painting is a visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture, narration, and abstraction. Paintings can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Living Torah And Nach
''The Living Torah'' and ''The Living Nach'' are popular, clear and modern English translations of the Tanakh based on traditional Jewish sources, along with extensive notes, maps, illustrations, diagrams, charts, bibliography, and index. A 2006 list, "An Annotated Bibliography Of Translations And Commentaries", placed these volumes in "Texts with Talmudic Translations" in second place, right after ArtScroll. The series is published by Moznaim Publishers. ''The Living Torah'' ''The Living Torah'' is a 1981 translation of the Torah by Rabbi Aryeh Kaplan. It was and remains a highly popular translation, and was reissued in a Hebrew-English version with '' haftarot'' for synagogue use. Kaplan had the following goals for his translation, which were arguably absent from previous English translations: * Make it clear and readable * Keep it close to the basic meaning (''peshat'') of the text in many places, but in other places translated it to be in accord with post-biblical rabbinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aryeh Kaplan
Aryeh Moshe Eliyahu Kaplan (; October 23, 1934 – January 28, 1983) was an American Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox rabbi, author, and translator best known for his The Living Torah and Nach, Living Torah edition of the Torah and extensive Kabbalah, Kabbalistic commentaries. He became well-known as a prolific writer and was lauded as an original thinker. His wide-ranging literary output, inclusive of introductory pamphlets on Jewish beliefs, and Jewish philosophy, philosophy written at the request of NCSY are often regarded as significant factors in the growth of the Baal teshuva movement, ''baal teshuva'' movement. Early life Aryeh Kaplan was born in the Bronx, New York City, to Samuel and Fannie () Kaplan of the Sephardic Jews, Sefardi Menahem Recanati, Recanati family from Salonika, Greece. His mother died on December 31, 1947, when he was 13, and his two younger sisters, Sandra and Barbara, were sent to a foster home. Kaplan was expelled from public school after acting out, leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bereshit (parashah)
Bereshit, Bereishit, Bereshis, Bereishis, or B'reshith (—Hebrew language, Hebrew for "in beginning" or "In the beginning (phrase), in the beginning," the incipit, first word in the parashah) is the first weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Judaism, Jewish cycle of Torah reading. The parashah consists of Book of Genesis, Genesis 1:1–6:8. In the parashah, God in Judaism, God creates the heavens, the world, Adam and Eve, and Sabbath. A Serpents in the Bible#Eden, serpent convinces Eve, who then invites Adam, to eat the forbidden fruit, fruit of the tree of the knowledge of good and evil, which God had forbidden to them. God curses the ground for their sake and expels them from the Garden of Eden. One of their sons, Cain and Abel, Cain, becomes the first murderer, killing his brother Abel out of jealousy. Adam and Eve have other children, whose descendants populate the Earth. Each generation becomes more and more degenerate until God decides to Genesis flood narra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam). According to Christianity, Adam sinned in the Garden of Eden by eating from the tree of the knowledge of good and evil. This action introduced death and sin into the world. This sinful nature infected all his descendants, and led humanity to be expelled from the Garden. Only through the crucifixion of Jesus, humanity can be redeemed. In Islam, Adam is considered '' Khalifa'' (خليفة) (successor) on earth. This is understood to mean either that he is God's deputy, the initiation of a new cycle of sentient life on earth, or both. Similar to the Biblical account, the Quran has Adam placed in a garden where he sins by taking from the Tree of Immortality, so loses his abode in the garden. When Adam repents from his sin, he is forgiven by God. This is seen as a guidan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
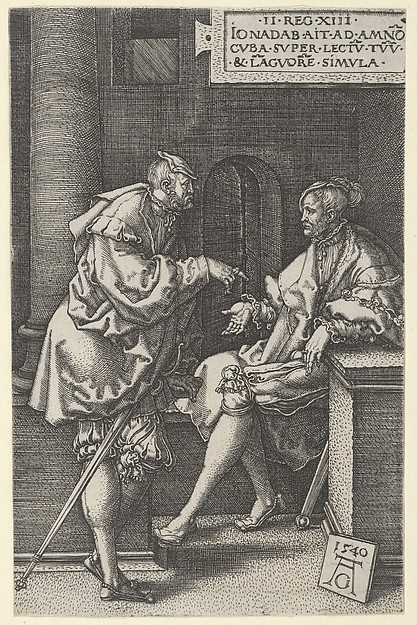
2 Samuel 13
2 Samuel 13 is the thirteenth Chapters and verses of the Bible, chapter of the Second Book of Samuel in the Old Testament of the Christianity, Christian Bible or the second part of Books of Samuel in the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish tradition the book was attributed to the prophet Samuel, with additions by the prophets Gad (prophet), Gad and Nathan (prophet), Nathan, but modern scholars view it as a composition of a number of independent texts of various ages from c. 630–540 BCE. This chapter contains the account of David's reign in Jerusalem. This is within a section comprising 2 Samuel 9–20 and continued to 1 Kings 1–1 Kings 2, 2 which deal with the power struggles among David's sons to succeed David's throne until 'the kingdom was established in the hand of Solomon' (1 Kings 2:46). Text This chapter was originally written in the Biblical Hebrew, Hebrew language. Chapters and verses of the Bible, It is divided into 39 verses. Textual witnesses Some early manuscripts c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tamar (daughter Of David)
Tamar () was an Israelite princess. Born to David and Maacah, who was from Geshur, she was the only full sibling of Absalom. She is described in the Hebrew Bible as being exceptionally beautiful, as is her brother. In the narrative of 2 Samuel 13, she is raped by her paternal half-brother Amnon (born to David and Ahinoam, who was from Jezreel) before fleeing with torn robes to Absalom's house; David is angered by the incident, but does nothing, as Amnon is his heir apparent. Absalom, infuriated by the rape and David's inaction, keeps Tamar in his care and later assassinates Amnon to avenge her, subsequently fleeing to Geshur, which is ruled by his and Tamar's maternal grandfather Talmai. Three years later, he returns to Israel and leads an armed revolt against the House of David, but is killed by David's nephew and army commander Joab during the Battle of the Wood of Ephraim. Tamar is described as being left "a desolate woman in her brother's house" and the sole guard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New International Version
The New International Version (NIV) is a translation of the Bible into contemporary English. Published by Biblica, the complete NIV was released on October 27, 1978, with a minor revision in 1984 and a major revision in 2011. The NIV relies on recently published critical editions of the original Hebrew, Aramaic, and Greek texts. Biblica claims that "the NIV delivers the very best combination of accuracy and readability." As of March 2013, over 450 million printed copies of the translation had been distributed. The NIV is the best-selling translation in the United States. History Beginnings In 1955, businessman Howard Long was convinced of the need for a contemporary English translation of the Bible while sharing the gospel with a business associate. He was unhappy with the King James Version that he used to communicate the gospel and was frustrated with its archaic language. He thought, "Everywhere I go, in Canada, the U.S., anywhere, there are people who would like to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Revised English Bible
The Revised English Bible (REB) is a 1989 English-language translation of the Bible that updates the New English Bible (NEB) of 1970. As with its predecessor, it is published by the publishing houses of both the universities of Oxford and Cambridge. It is not to be confused with the ''Revised English Bible'' of 1877, which was an annotated and slightly emended King James Bible. Translation philosophy The REB is the result of both advances in scholarship and translation made since the 1960s and also a desire to correct what have been seen as some of the NEB's more egregious errors (for examples of changes, see the references). The changes remove many of the most idiosyncratic renderings of the NEB, moving the REB more in the direction of standard translations such as the New Revised Standard Version (NRSV) or the New International Version (NIV). The translation is intended to take account of gender-inclusive usage, though not to the same extent as translations such as the NRSV. Ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Revised Standard Version
The Revised Standard Version (RSV) is an English translation of the Bible published in 1952 by the Division of Christian Education of the National Council of the Churches of Christ in the USA. This translation is a revision of the American Standard Version (ASV) of 1901, and was intended to be a readable and literally accurate modern English translation which aimed to "preserve all that is best in the English Bible as it has been known and used through the years" and "to put the message of the Bible in simple, enduring words that are worthy to stand in the great Tyndale- King James tradition." The RSV was the first translation of the Bible to make use of the Dead Sea Scroll of Isaiah, a development considered "revolutionary" in the academic field of biblical scholarship. The New Testament was first published in 1946, the Old Testament in 1952, and the Apocrypha in 1957; the New Testament was revised in 1971. The original '' Revised Standard Version, Catholic Edition'' (RSV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jewish Publication Society Of America Version
The Jewish Publication Society of America Version (JPS) of the Tanakh (the Hebrew Bible) was the first Bible translation published by the Jewish Publication Society of America and the first translation of the Tanakh into English by a committee of Jews (though there had been earlier solo efforts, such as that of Isaac Leeser). The full publication title is ''The Holy Scriptures According to the Masoretic Text: A New Translation with the Aid of Previous Versions and with Constant Consultation of Jewish Authorities''. Earlier translations The translation, which appeared in 1917, is heavily indebted to the Revised Version and American Standard Version. It differs from them in many passages where Jewish and Christian interpretations differ, notably in Isaiah 7:14, where it has "young woman" as opposed to the word "virgin" which is used in most Christian Bibles. The translation was initiated in 1892 by the Central Conference of American Rabbis, the organization of Reform rabbis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |