|
Clustal
Clustal is a computer program used for multiple sequence alignment in bioinformatics. The software and its algorithms have gone through several iterations, with ClustalΩ (Omega) being the latest version . It is available as standalone software, via a Clustal#External links, web interface, and through a server hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute. Clustal has been an important bioinformatic software, with two of its academic publications amongst the top 100 papers cited of all time, according to Nature (journal), Nature in 2014. History Version history * Clustal: The original software for multiple sequence alignments, created by Desmond G. Higgins, Des Higgins in 1988, was based on deriving a guide tree from pairwise sequences of Amino acid, amino acids or Nucleotide, nucleotides. * ClustalV: The second generation of Clustal, released in 1992. It introduced the ability to create new alignments from existing alignments in a process known as phylogenetic tree re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Bioinformatics Institute
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is an intergovernmental organization (IGO) which, as part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) family, focuses on research and services in bioinformatics. It is located on the Wellcome Genome Campus in Hinxton near Cambridge, and employs over 600 full-time equivalent (FTE) staff. Further, the EMBL-EBI hosts training programs that teach scientists the fundamentals of the work with biological data and promote the plethora of bioinformatic tools available for their research, both EMBL-EBI-based and not so. Bioinformatic services One of the roles of the EMBL-EBI is to index and maintain biological data in a set of databases, including Ensembl (housing whole genome sequence data), UniProt (protein sequence and annotation database) and Protein Data Bank (protein and nucleic acid tertiary structure database). A variety of online services and tools is provided, such as Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) or Clust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sequence Alignment
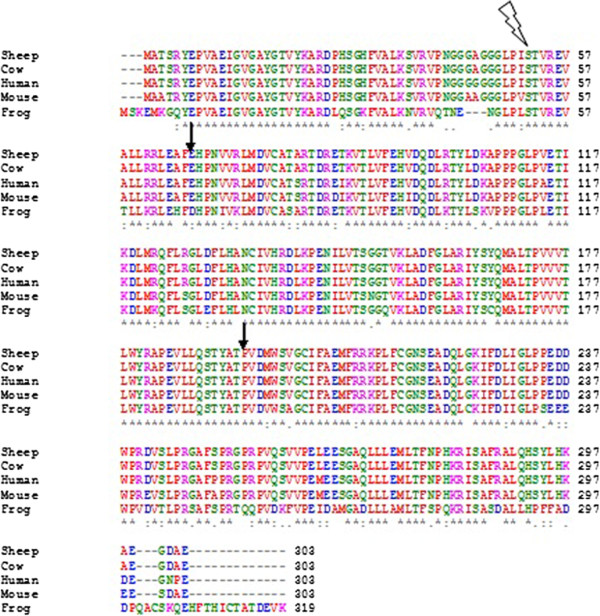
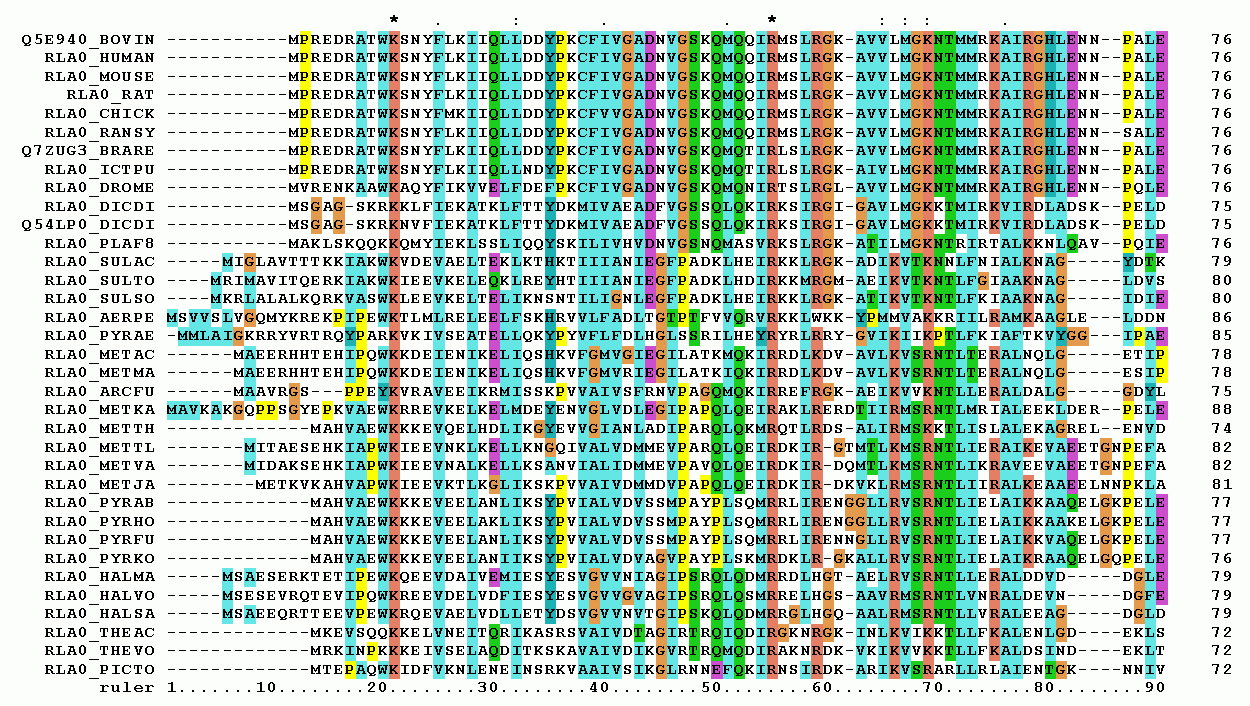
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis and can highlight homologous features between sequences. Alignments highlight mutation events such as point mutations (single amino acid or nucleotide changes), insertion mutations and deletion mutations, and alignments are used to assess sequence conservation and infer the presence and activity of protein domains, tertiary structures, secondary structures, and individual amino acids or nucleotides. Multiple sequence alignments require more sophisticated methodologies than pairwise alignments, as they are more computationally complex. Most multiple sequence alignment programs use heuristic methods rather than global optimization because identifying the optimal alignment between more than a few sequences of moderate length is prohibiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Des Higgins
Desmond Gerard Higgins is a Professor of Bioinformatics at University College Dublin, widely known for CLUSTAL,, Broad Institute a series of computer programs for performing multiple sequence alignment. According to ''Nature'', Higgins' papers describing CLUSTAL are among the top ten most highly cited scientific papers of all time. Education Higgins was educated at Trinity College, Dublin where he was awarded a PhD in 1988 for research on numerical taxonomy of Pterygote insects. Research Research in the Higgins laboratory focuses on developing new bioinformatics and statistical tools for evolutionary biology. The CLUSTAL program for multiple sequence alignment has been developed in the Higgins lab and the T-Coffee software was initially developed in the lab with by Cedric Notredame. Multivariate statistics are used to analyse microarray data sets and molecular evolution such as the evolution of promoters, introns and non-coding RNA.Des Higgins Awards and honours Higgins was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toby Gibson
Toby James Gibson is a group leader and biochemist at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg known for his work on Clustal. According to ''Nature'', Gibson's co-authored papers describing Clustal are among the top ten most highly cited scientific papers of all time. Education Gibson was educated at the University of Edinburgh and went on to his PhD at the University of Cambridge in 1984 on the genome of the Epstein–Barr virus while working in the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB). Career and research Gibson was a postdoctoral research fellow with Sydney Brenner before moving to EMBL in 1986. He was appointed a staff scientist in 1991 and a team leader in 1996 where he has worked since. Gibson’s research interests are in computational biology, bioinformatics, short linear motifs, protein–protein interactions and biological sequence alignment In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmond G
Desmond or Desmond's may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Desmond'' (novel), 1792 novel by Charlotte Turner Smith * '' Desmond's'', 1990s British television sitcom Ireland * Kingdom of Desmond, medieval Irish kingdom * Earl of Desmond, Irish aristocratic title * Desmond Rebellions, Irish rebellions during the 16th century led by the Earl of Desmond Science and technology * DESMOND (diabetes) (Diabetes Education and Self Management for Ongoing and Newly Diagnosed), a UK NHS diabetes education programme * Desmond (software), molecular dynamics simulation software * Storm Desmond, a windstorm in Britain and Ireland in 2015 Other uses * Desmond (name), a common given name and surname * Desmond (horse) (1896–1913), Thoroughbred racehorse * Desmond's (department store), a former US store * Desmond, slang term for the British 2:2 degree classification * Desmond, Western Australia, a former town in the Shire of Ravensthorpe See also * Desman Desmans are aquatic insectivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree (data Structure)
In computer science, a tree is a widely used abstract data type that represents a hierarchical tree structure with a set of connected nodes. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be connected to exactly one parent, except for the ''root'' node, which has no parent (i.e., the root node as the top-most node in the tree hierarchy). These constraints mean there are no cycles or "loops" (no node can be its own ancestor), and also that each child can be treated like the root node of its own subtree, making recursion a useful technique for tree traversal. In contrast to linear data structures, many trees cannot be represented by relationships between neighboring nodes (parent and children nodes of a node under consideration, if they exist) in a single straight line (called edge or link between two adjacent nodes). Binary trees are a commonly used type, which constrain the number of children for each parent to at most two. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighbor Joining
In bioinformatics, neighbor joining is a bottom-up (agglomerative) clustering method for the creation of phylogenetic trees, created by Naruya Saitou and Masatoshi Nei in 1987. Usually based on DNA or protein sequence data, the algorithm requires knowledge of the distance between each pair of taxa (e.g., species or sequences) to create the phylogenetic tree. The algorithm Neighbor joining takes a distance matrix, which specifies the distance between each pair of taxa, as input. The algorithm starts with a completely unresolved tree, whose topology corresponds to that of a star network, and iterates over the following steps, until the tree is completely resolved, and all branch lengths are known: # Based on the current distance matrix, calculate a matrix Q (defined below). # Find the pair of distinct taxa i and j (i.e. with i \neq j) for which Q(i,j) is smallest. Make a new node that joins the taxa i and j, and connect the new node to the central node. For example, in part (B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighting
The process of frequency weighting involves emphasizing the contribution of particular aspects of a phenomenon (or of a set of data) over others to an outcome or result; thereby highlighting those aspects in comparison to others in the analysis. That is, rather than each variable in the data set contributing equally to the final result, some of the data is adjusted to make a greater contribution than others. This is analogous to the practice of adding (extra) weight to one side of a pair of scales in order to favour either the buyer or seller. While weighting may be applied to a set of data, such as epidemiological data, it is more commonly applied to measurements of light, heat, sound, gamma radiation, and in fact any stimulus that is spread over a spectrum A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Similarity (geometry)
In Euclidean geometry, two objects are similar if they have the same shape, or if one has the same shape as the mirror image of the other. More precisely, one can be obtained from the other by uniformly scaling (geometry), scaling (enlarging or reducing), possibly with additional translation (geometry), translation, rotation (mathematics), rotation and reflection (mathematics), reflection. This means that either object can be rescaled, repositioned, and reflected, so as to coincide precisely with the other object. If two objects are similar, each is congruence (geometry), congruent to the result of a particular uniform scaling of the other. For example, all circles are similar to each other, all squares are similar to each other, and all equilateral triangles are similar to each other. On the other hand, ellipses are not all similar to each other, rectangles are not all similar to each other, and isosceles triangles are not all similar to each other. This is because two ellipse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergence (statistics)
In information geometry, a divergence is a kind of statistical distance: a binary function which establishes the separation from one probability distribution to another on a statistical manifold. The simplest divergence is squared Euclidean distance (SED), and divergences can be viewed as generalizations of SED. The other most important divergence is relative entropy (also called Kullback–Leibler divergence), which is central to information theory. There are numerous other specific divergences and classes of divergences, notably ''f''-divergences and Bregman divergences (see ). Definition Given a differentiable manifold M of dimension n, a divergence on M is a C^2-function D: M\times M\to [0, \infty) satisfying: # D(p, q) \geq 0 for all p, q \in M (non-negativity), # D(p, q) = 0 if and only if p=q (positivity), # At every point p\in M, D(p, p+dp) is a positive-definite quadratic form for infinitesimal displacements dp from p. In applications to statistics, the manifold M i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |