|
Clonal Deletion
In immunology, clonal deletion is the process of removing T and B lymphocytes from the immune system repertoire. The process of clonal deletion helps prevent recognition and destruction of the self host cells, making it a type of Negative selection (immunology), negative selection. Ultimately, clonal deletion plays a role in central tolerance.Jenni., Punt; A., Stranford, Sharon; P., Jones, Patricia; Janis., Kuby (2013-01-01). ''Kuby immunology''. W.H. Freeman. Clonal deletion can help protect individuals against autoimmunity, which is when an organism produces and immune response on its own cells. It is one of many methods used by the body in immune tolerance. Discovery Central tolerance and clonal deletion did not get much attention in the early years of immunology. Macfarlane Burnet, Frank Macfarlane Burnet was the first to suggest the idea of clonal deletion. A couple key findings helped Burnet's in this discovery. In 1936, Erich Traub demonstrated that when a developing m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of biology and medicine that covers the study of Immune system, immune systems in all Organism, organisms. Immunology charts, measures, and contextualizes the Physiology, physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders (such as Autoimmune disease, autoimmune diseases, Hypersensitivity, hypersensitivities, immune deficiency, and transplant rejection); and the physical, chemical, and physiological characteristics of the components of the immune system ''in vitro'', ''In situ#Biology and biomedical engineering, in situ'', and ''in vivo''. Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of medicine, particularly in the fields of organ transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, virology, bacteriology, parasitology, psychiatry, and dermatology. The term was coined by Russian biologist Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov, who advanced studies on immunology and received the Nob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
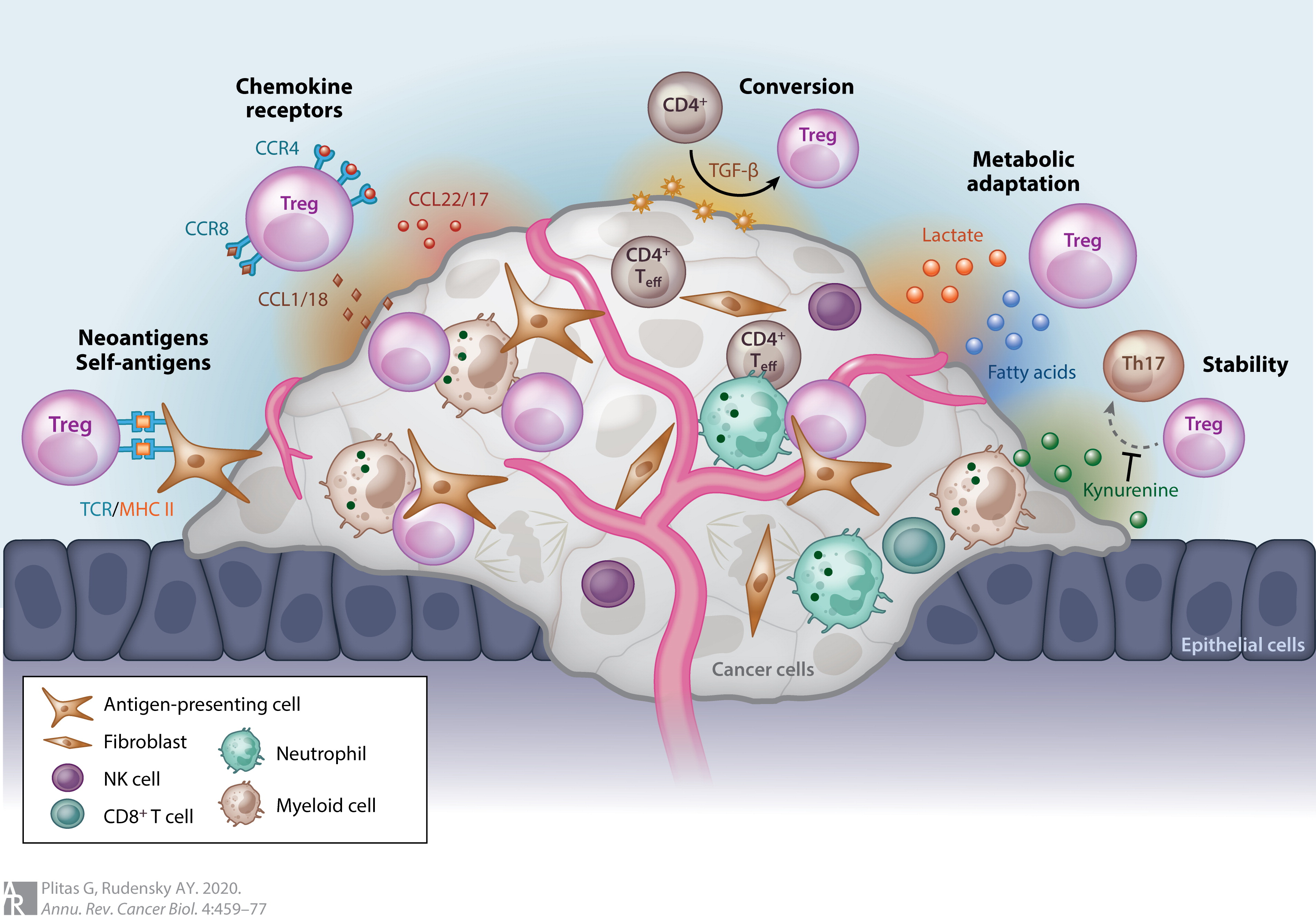
T Regulatory Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
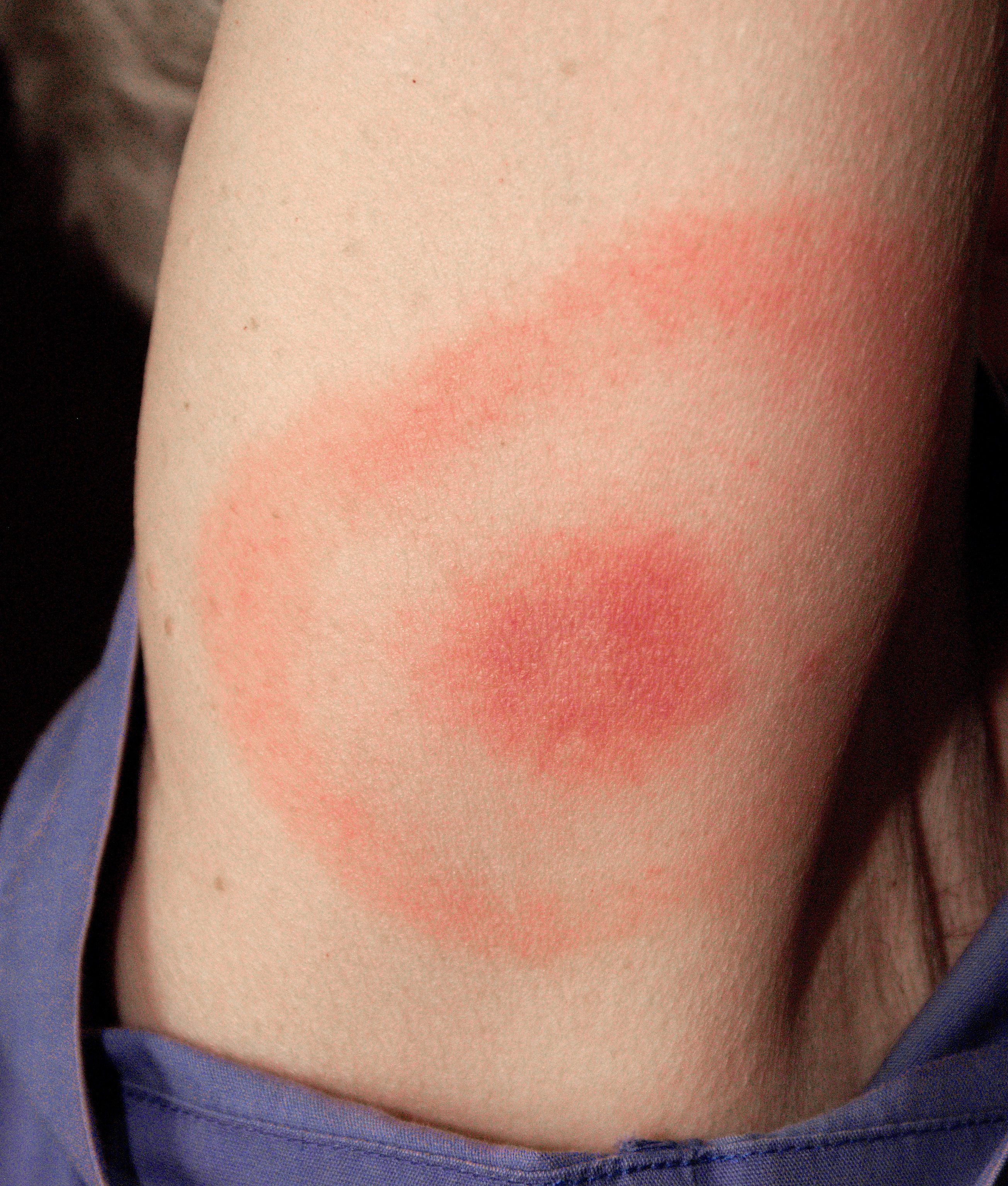
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus '' Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''B. burgdorferi'' are often mistakenly described as Gram negative because of their two external membranes, but they lack lipopolysaccharide and possess many surface lipoproteins, unlike true Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus '' Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berries ( atiniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Mimicry
Molecular mimicry is the theoretical possibility that sequence similarities between foreign and self-peptides are enough to result in the cross-activation of autoreactive T or B cells by pathogen-derived peptides. Despite the prevalence of several peptide sequences which can be both foreign and self in nature, just a few crucial residues can activate a single antibody or TCR ( T cell receptor). This highlights the importance of structural homology in the theory of molecular mimicry. Upon activation, these "peptide mimic" specific T or B cells can cross-react with self-epitopes, thus leading to tissue pathology (autoimmunity). Molecular mimicry is one of several ways in which autoimmunity can be evoked. A molecular mimicking event is more than an epiphenomenon despite its low probability, and these events have serious implications in the onset of many human autoimmune disorders. One possible cause of autoimmunity, the failure to recognize self antigens as "self", is a loss of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incomplete Vs
{{disambigu ...
Incomplete may refer to: * Unfinished creative work * An incomplete formal system, see Completeness (logic) * Gödel's incompleteness theorems, a specification of logic * "Incomplete" (Bad Religion song), 1994 * "Incomplete" (Sisqó song), 1999 * "Incomplete" (Backstreet Boys song), 2005 * "Incomplete" (Hoobastank song), 2013 * ''Incomplete'' (Nembrionic album), or the title track * ''Incomplete'' (Diaura album), 2015 * Incomplete pass, a gridiron football term * Incomplete abortion (or incomplete miscarriage), a medical term * "Incomplete", a song by Alanis Morissette on the 2008 album ''Flavors of Entanglement'' * “Incomplete”, an episode of ''The Good Doctor'' See also * Completeness (other) Complete may refer to: Logic * Completeness (logic) * Completeness of a theory, the property of a theory that every formula in the theory's language or its negation is provable Mathematics * The completeness of the real numbers, which implies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonal Anergy
In immunology, anergy characterizes the absence of a response from the body's defense mechanisms when confronted with foreign substances. This phenomenon involves the direct induction of peripheral lymphocyte tolerance. When an individual is in a state of anergy, it signifies that their immune system is incapable of mounting a typical response against a specific antigen, typically a self-antigen. The term anergy specifically refers to lymphocytes that exhibit an inability to react to their designated antigen. Notably, anergy constitutes one of the essential processes fostering tolerance within the immune system, alongside clonal deletion and immunoregulation. These processes collectively act to modify the immune response, preventing the inadvertent self-destruction that could result from an overactive immune system. Mechanism This phenomenon was first described in B lymphocytes by Gustav Nossal and termed "clonal anergy." The clones of B lymphocytes in this case can still be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain immune tolerance, tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppression, immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulation and upregulation, downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same cell lineage, lineage as naïve T helper cell, CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine Transforming growth factor beta, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. This self-protection method can be contrasted with that employed by Natural killer cell, Natural Killer cells. This process of engulfment and digestion is called phagocytosis; it acts to defend the host against infection and injury. Macrophages are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
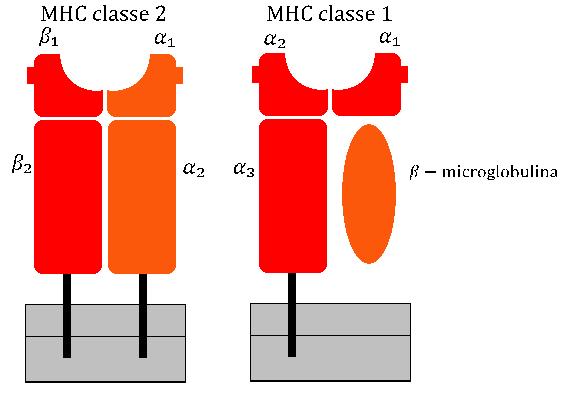
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. Its name comes from its discovery during the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules, which is to bind an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bring the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cell, T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with Major histocompatibility complex, MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is the largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the Thymic involuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |