|
Clofibrate
Clofibrate (trade name Atromid-S) is a lipid-lowering agent used for controlling the high cholesterol and triacylglyceride level in the blood. It belongs to the class of fibrates. It increases lipoprotein lipase activity to promote the conversion of VLDL to LDL, and hence reduce the level of VLDL. It can increase the level of HDL as well. It was patented in 1958 by Imperial Chemical Industries and approved for medical use in 1963. Clofibrate was discontinued in 2002 due to adverse effects. Complications and controversies It can induce SIADH, syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone ADH (vasopressin). Clofibrate can also result in formation of cholesterol stones in the gallbladder. The World Health Organization Cooperative Trial on Primary Prevention of Ischaemic Heart Disease using clofibrate to lower serum cholesterol Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fibrate
In pharmacology, the fibrates are a class of amphipathic carboxylic acids and esters. They are derivatives of fibric acid (phenoxyisobutyric acid). They are used for a range of metabolic disorders, mainly hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol), and are therefore hypolipidemic agents. Medical uses Fibrates improve atherogenic dyslipidemia characterized by high triglyceride and/or low HDL-C levels and elevated concentrations of small dense LDL particles, with or without high LDL-C levels. Fibrates may be compared to statin drugs, which reduce LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) and have only limited effects on other lipid parameters. Clinical trials have shown that the combination of statins and fibrates results in a significantly greater reduction in LDL-C and triglyceride levels and greater increases in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) compared with monotherapy with either drug. Fibrates are used in accessory therapy in many forms of hypercholesterolemia, but the combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Syndrome Of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Hypersecretion
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), also known as the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis (SIAD), is characterized by a physiologically inappropriate release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) either from the posterior pituitary gland, or an ectopic non-pituitary source, such as an ADH-secreting tumor in the lung. Unsuppressed ADH causes a physiologically inappropriate increase in solute-free water being reabsorbed by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulation leading to hypotonic hyponatremia (a low plasma osmolality and low sodium levels). The causes of SIADH are commonly grouped into categories including: central nervous system diseases that directly stimulate the hypothalamus to release ADH, various cancers that synthesize and secrete ectopic ADH, various lung diseases, numerous drugs (carbamazepine, cyclophosphamide, SSRIs) that may stimulate the release of ADH, vasopressin release, desmopressin release, oxytocin, or stimulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile. Biological hydrolysis is the cleavage of Biomolecule, biomolecules where a water molecule is consumed to effect the separation of a larger molecule into component parts. When a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis (e.g., sucrose being broken down into glucose and fructose), this is recognized as saccharification. Hydrolysis reactions can be the reverse of a condensation reaction in which two molecules join into a larger one and eject a water molecule. Thus hydrolysis adds water to break down, whereas condensation builds up by removing water. Types Usually hydrolysis is a chemical process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this addition causes both the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imperial Chemical Industries
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British Chemical industry, chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was listed on the London Stock Exchange and was a constituent of the FT 30 and later the FTSE 100 Index, FTSE 100 indices. ICI was formed in 1926 as a result of the merger of four of Britain's leading chemical companies. From the onset, it was involved in the production of various chemicals, explosives, fertilisers, insecticides, dyestuffs, non-ferrous metals, and paints; the firm soon become involved in plastics and a variety of speciality products, including food ingredients, polymers, electronic materials, fragrances and flavourings. During the Second World War, ICI's subsidiary Nobel Enterprises, ICI Nobel produced munitions for Britain's war effort; the wider company was also involved with Britain's nuclear weapons programme codenamed Tube Alloys. Throughout the 1940s and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils. Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all animal Cell (biology)#Eukaryotic cells, cells and is an essential structural and cholesterol signaling, signaling component of animal cell membranes. In vertebrates, hepatocyte, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
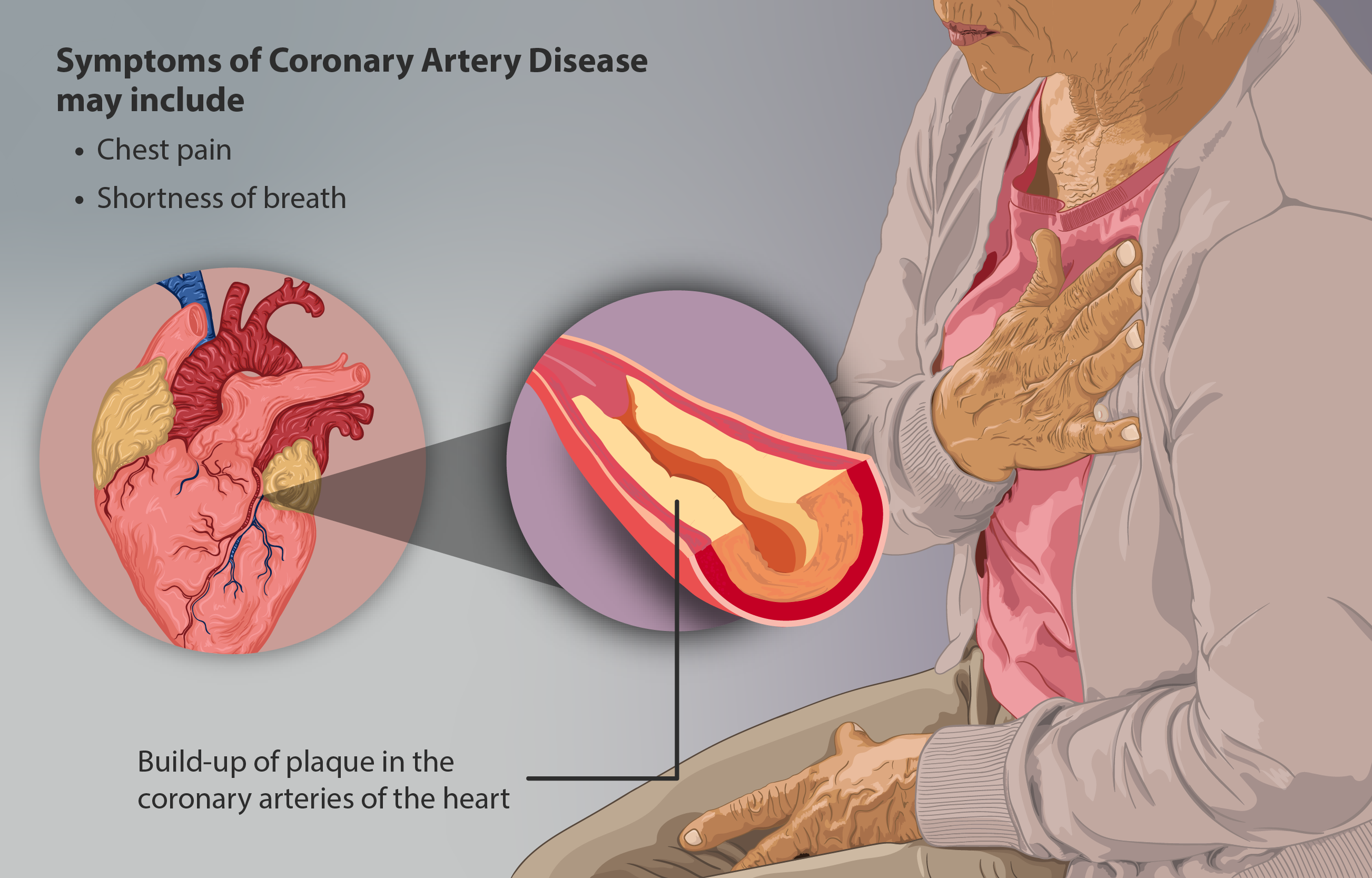
Ischaemic Heart Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of heart disease involving the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an abnormal heartbeat. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vasopressin
Mammalian vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH), arginine vasopressin (AVP) or argipressin, is a hormone synthesized from the ''AVP'' gene as a peptide prohormone in neurons in the hypothalamus, and is converted to AVP. It then travels down the axon terminating in the posterior pituitary, and is released from vesicles into the circulation in response to extracellular fluid hypertonicity ( hyperosmolality). AVP has two primary functions. First, it increases the amount of solute-free water reabsorbed back into the circulation from the filtrate in the kidney tubules of the nephrons. Second, AVP constricts arterioles, which increases peripheral vascular resistance and raises arterial blood pressure. A third function is possible. Some AVP may be released directly into the brain from the hypothalamus, and may play an important role in social behavior, sexual motivation and pair bonding, and maternal responses to stress. Vasopressin induces differentiation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
VLDL
Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver. VLDL is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins (chylomicrons, VLDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein, LDL, low-density lipoprotein, high-density lipoprotein) that enable fats and cholesterol to move within the water-based solution of the bloodstream. VLDL is assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL is converted in the bloodstream to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL). VLDL particles have a diameter of 30–80 nanometers (nm). VLDL transports endogeny, endogenous products, whereas chylomicrons transport exogenous (dietary) products. In the early 2010s both the lipid composition and protein composition of this lipoprotein were characterised in great detail. Physical properties Very-low-density lipoprotein size is variable, with diameters ranging from approximately 35 to 70&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
High Density Lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA). HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. HDL particles are commonly referred to as "good cholesterol", because they transport fat molecules out of artery walls, reduce macrophage accumulation, and thus help prevent or even regress atherosclerosis. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clofibric Acid
Clofibric acid is a biologically active metabolite of the lipid-lowering drugs clofibrate, etofibrate and with the molecular formula C10H11ClO3. It has been found in the environment following use of these drugs, for example in Swiss lakes and the North Sea. Some derivatives of clofibric acid are in a drug class called fibrates In pharmacology, the fibrates are a class of Amphiphile, amphipathic carboxylic acids and esters. They are derivatives of fibric acid (phenoxyisobutyric acid). They are used for a range of metabolism, metabolic disorders, mainly hypercholesterole .... See also * Phenoxy herbicides to which the compound is chemically related References 4-Chlorophenyl compounds 2-Methyl-2-phenoxypropanoic acid derivatives {{Ether-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |