|
Climate Variability And Change
Climate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more. ''Climate change'' may refer to any time in Earth's history, but the term is now commonly used to describe contemporary climate change, often popularly referred to as global warming. Since the Industrial Revolution, the climate has increasingly been affected by human activities. The climate system receives nearly all of its energy from the sun and radiates energy to outer space. The balance of incoming and outgoing energy and the passage of the energy through the climate system is Earth's energy budget. When the incoming energy is greater than the outgoing energy, Earth's energy budget is positive and the climate system is warming. If more energy goes out, the energy budget is negative and Earth experiences cooling. The energy moving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succeeding the Second Agricultural Revolution. Beginning in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain around 1760, the Industrial Revolution had spread to continental Europe and the United States by about 1840. This transition included going from craft production, hand production methods to machines; new Chemical industry, chemical manufacturing and Puddling (metallurgy), iron production processes; the increasing use of Hydropower, water power and Steam engine, steam power; the development of machine tools; and rise of the mechanisation, mechanised factory system. Output greatly increased, and the result was an unprecedented rise in population and population growth. The textile industry was the first to use modern production methods, and textiles b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny () is a mountain-mountain formation, building process that takes place at a convergent boundary, convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is tectonic uplift, uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation (physics), deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere (crust (geology), crust and uppermost mantle (geology), mantle). A synorogenic (or synkinematic) process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word ''orogeny'' comes . Although it was used before him, the American geologist Grove Karl Gilbert, G. K. Gilbert used the term in 1890 to me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus Hasselmann
Klaus Ferdinand Hasselmann (; born 25 October 1931) is a German oceanographer and climate mathematical model, modeller. He is Professor Emeritus at the University of Hamburg and former Director of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology. He was awarded the 2021 Nobel Prize in Physics jointly with Syukuro Manabe and Giorgio Parisi. Hasselmann grew up in Welwyn Garden City, England and returned to Hamburg in 1949 to attend university. Throughout his career he has mainly been affiliated with the University of Hamburg and the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, which he founded. He also spent five years in the United States as a professor at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, and a year as a visiting professor at the University of Cambridge. He is best known for developing the ''Hasselmann model'' of climate variability, where a system with a long memory (the ocean) integrates stochastic forcing, thereby transforming a white-noi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nobel Laureates In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the 1895 will and testament, will of Alfred Nobel (who died in 1896), awarded for outstanding contributions in physics. As dictated by Nobel's will, the award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death. Each recipient receives a medal, a diploma and a monetary award prize that has varied throughout the years. Statistics The Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to 226 individuals as of 2024. The first prize in physics was awarded in 1901 to Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, of Germany, who received 150,782 Swedish krona, SEK. John Bardeen is the only laureate to win the prize twice—in 1956 and 1972. Lawrence Bragg, Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Resonance
Stochastic resonance (SR) is a behavior of non-linear systems where random (stochastic) fluctuations in the micro state cause deterministic changes in the macro state. This occurs when the non-linear nature of the system amplifies certain (resonant) portions of the fluctuations, while not amplifying other portions of the noise. Information theory In information theory, SR can be used to reveal weak signals. When a signal that is normally too weak to be detected by a sensor can be boosted by adding white noise to the signal, which contains a wide spectrum of frequencies. The frequencies in the white noise corresponding to the original signal's frequencies will resonate with each other, amplifying the original signal while not amplifying the rest of the white noise – thereby increasing the signal-to-noise ratio, which makes the original signal more prominent. Further, the added white noise can be enough to be detectable by the sensor, which can then filter it out to effectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Noise
In science, Brownian noise, also known as Brown noise or red noise, is the type of signal noise produced by Brownian motion, hence its alternative name of random walk noise. The term "Brown noise" does not come from the color, but after Robert Brown, who documented the erratic motion for multiple types of inanimate particles in water. The term "red noise" comes from the "white noise"/"white light" analogy; red noise is strong in longer wavelengths, similar to the red end of the visible spectrum. Explanation The graphic representation of the sound signal mimics a Brownian pattern. Its spectral density is inversely proportional to ''f'' 2, meaning it has higher intensity at lower frequencies, even more so than pink noise. It decreases in intensity by 6 dB per octave (20 dB per decade) and, when heard, has a "damped" or "soft" quality compared to white and pink noise. The sound is a low roar resembling a waterfall or heavy rainfall. See also violet noise, which is a 6&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics, acoustical engineering, telecommunications, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, not to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band. In discrete time, white noise is a discrete signal whose samples are regarded as a sequence of serially uncorrelated random variables with zero mean and finite variance; a single realization of white noise is a random shock. In some contexts, it is also required that the samples be independent and have identical probability distribution (in other words independent and identically distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Inertia
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
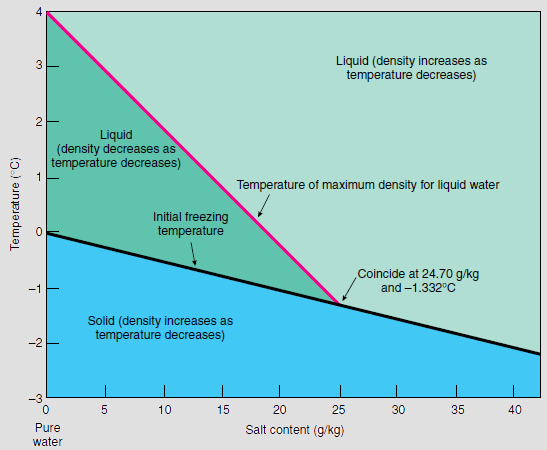
Thermohaline Circulation
Thermohaline circulation (THC) is a part of the large-scale Ocean current, ocean circulation driven by global density gradients formed by surface heat and freshwater fluxes. The name ''thermohaline'' is derived from ''wikt:thermo-, thermo-'', referring to temperature, and ', referring to salinity, salt content—factors which together determine the Water (molecule)#Density of saltwater and ice, density of sea water. Wind-driven surface currents (such as the Gulf Stream) travel Polar regions of Earth, polewards from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean, cooling and sinking en-route to higher latitudes - eventually becoming part of the North Atlantic Deep Water - before flowing into the ocean basins. While the bulk of thermohaline water upwelling, upwells in the Southern Ocean, the oldest waters (with a transit time of approximately 1000 years) upwell in the North Pacific; extensive mixing takes place between the ocean basins, reducing the difference in their densities, forming the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions). Substances usually contract with decreasing temperature (thermal contraction), with rare exceptions within limited temperature ranges ('' negative thermal expansion''). Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. As energy in particles increases, they start moving faster and faster, weakening the intermolecular forces between them and therefore expanding the substance. When a substance is heated, molecules begin to vibrate and move more, usually creating more distance between themselves. The relative expansion (also called strain) divided by the change in temperature is called the material's coefficient of linear thermal expansion and generally varies with temperature. Prediction If an equation of state is available, it can be used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, produced during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer to all explosive eruption products (correctly referred to as '' tephra''), including particles larger than 2 mm. Volcanic ash is formed during explosive volcanic eruptions when dissolved gases in magma expand and escape violently into the atmosphere. The force of the gases shatters the magma and propels it into the atmosphere where it solidifies into fragments of volcanic rock and glass. Ash is also produced when magma comes into contact with water during phreatomagmatic eruptions, causing the water to explosively flash to steam leading to shattering of magma. Once in the air, ash is transported by wind up to thousands of kilometres away. Due to its wide dispersal, ash can have a number of impacts on society, including animal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |