|
Circulatory Shock
Shock is the state of insufficient blood flow to the tissues of the body as a result of problems with the circulatory system. Initial symptoms of shock may include weakness, tachycardia, hyperventilation, sweating, anxiety, and increased thirst. This may be followed by confusion, unconsciousness, or cardiac arrest, as complications worsen. Shock is divided into four main types based on the underlying cause: hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Hypovolemic shock, also known as low volume shock, may be from bleeding, diarrhea, or vomiting. Cardiogenic shock may be due to a heart attack or cardiac contusion. Obstructive shock may be due to cardiac tamponade or a tension pneumothorax. Distributive shock may be due to sepsis, anaphylaxis, injury to the upper spinal cord, or certain overdoses. The diagnosis is generally based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. A decreased pulse pressure ( systolic blood pressure min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
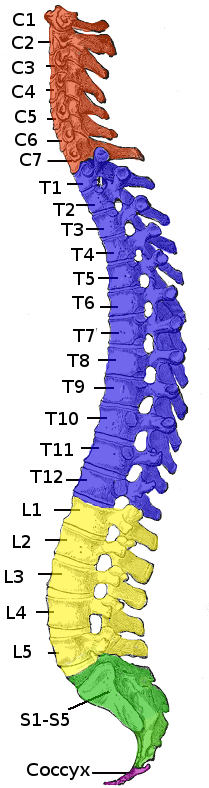
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. It is a destructive neurological and pathological state that causes major motor, sensory and autonomic dysfunctions. Symptoms of spinal cord injury may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. What is diarrhea? How is it caused, treated and prevented? (see also script)The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiogenic Shock
Cardiogenic shock is a medical emergency resulting from inadequate blood flow to the body's organs due to the dysfunction of the heart. Signs of inadequate blood flow include low urine production (<30 mL/hour), cool arms and legs, and decreased level of consciousness. People may also have a severely low blood pressure and heart rate. Causes of cardiogenic shock include cardiomyopathic, arrhythmic, and mechanical. Cardiogenic shock is most commonly precipitated by a heart attack. Treatment of cardiogenic shock depends on the cause with the initial goals to improve blood flow to the body. If cardiogenic shock is due to a heart attack, attempts to open th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypovolemic Shock
Hypovolemic shock is a form of Shock (circulatory), shock caused by severe hypovolemia (insufficient blood volume or extracellular fluid in the body). It can be caused by severe dehydration or blood loss. Hypovolemic shock is a medical emergency; if left untreated, the Ischemia, insufficient blood flow can cause damage to organs, leading to multiple organ failure. In treating hypovolemic shock, it is important to determine the cause of the underlying hypovolemia, which may be the result of hemorrhage, bleeding or other fluid losses. To minimize ischemic damage to tissues, treatment involves quickly replacing lost blood or fluids, with consideration of both rate and the type of fluids used. Tachycardia, a fast heart rate, is typically the first abnormal vital sign. When resulting from blood loss, trauma is the most common root cause, but severe blood loss can also happen in various body systems without clear traumatic injury. The body in hypovolemic shock prioritizes getting oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweating
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals. Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the body and are responsible for secreting the watery, brackish sweat most often triggered by excessive body temperature. Apocrine sweat glands are restricted to the armpits and a few other areas of the body and produce an odorless, oily, opaque secretion which then gains its characteristic odor from bacterial decomposition. In humans, sweating is primarily a means of thermoregulation, which is achieved by the water-rich secretion of the eccrine glands. Maximum sweat rates of an adult can be up to per hour or per day, but is less in children prior to puberty. Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface has a cooling effect due to evaporative cooling. Hence, in hot weather, or when the individual's muscles heat up due to exertion, more sweat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood. The body normally attempts to compensate for this homeostatically, but if this fails or is overridden, the blood pH will rise, leading to respiratory alkalosis. This increases the affinity of oxygen to hemoglobin and makes it harder for oxygen to be released into body tissues from the blood. The symptoms of respiratory alkalosis include dizziness, tingling in the lips, hands, or feet, headache, weakness, fainting, and seizures. In extreme cases, it may cause carpopedal spasms, a flapping and contraction of the hands and feet. Factors that may induce or sustain hyperventilation include: physiological stress, anxiety or panic disorder, high altitude, head injury, stroke, respiratory disorders such as asthma, pneumonia, or hyper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (such as with exercise) or abnormal (such as with electrical problems within the heart). Complications Tachycardia can lead to fainting. When the rate of blood flow becomes too rapid, or fast blood flow passes on damaged endothelium, it increases the friction within vessels resulting in turbulence and other disturbances. According to the Virchow's triad, this is one of the three conditions (along with hypercoagulability and endothelial injury/dysfunction) that can lead to thrombosis (i.e., blood clots within vessels). Causes Some causes of tachycardia include: * Adrenergic storm * Anaemia * Anxiety * Atrial fibrillation * Atrial flutter * Atrial tachycardia * Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia * AV nodal reentrant tachy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue (biology)
In biology, tissue is an assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same embryonic origin that together carry out a specific function. Tissues occupy a Biological organisation#Levels, biological organizational level between cell (biology), cells and a complete organ (biology), organ. Accordingly, organs are formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues. The English word "tissue" Morphological derivation, derives from the French word "", the past participle of the verb tisser, "to weave". The study of tissues is known as histology or, in connection with disease, as histopathology. Xavier Bichat is considered as the "Father of Histology". Plant histology is Studied Space Shuttle designs, studied in both plant anatomy and Plant physiology, physiology. The classical tools for studying tissues are the Microtome#Applications, paraffin block in which tissue is embedded and then sectioned, the staining, histological stain, and the Microscope, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. Blood flow ensures the transportation of nutrients, hormones, metabolic waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide throughout the body to maintain cell-level metabolism, the regulation of the pH, osmotic pressure and temperature of the whole body, and the protection from microbial and mechanical harm. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid, and is most efficiently studied using rheology rather than hydrodynamics. Because blood vessels are not rigid tubes, classic hydrodynamics and fluids mechanics based o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressors
An antihypotensive, also known as a vasopressor, is an agent that raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, thereby increasing systemic vascular resistance. This is different from inotropes which increase the force of cardiac contraction. Some substances do both (e.g. dopamine, dobutamine). If low blood pressure is due to blood loss, then preparations increasing volume of blood circulation—plasma-substituting solutions such as colloid and crystalloid solutions (salt solutions)—will raise the blood pressure without any direct vasopressor activity. Packed red blood cells, plasma or whole blood should not be used solely for volume expansion or to increase oncotic pressure of circulating blood. Blood products should only be used if reduced oxygen carrying capacity or coagulopathy is present. Other causes of either absolute (dehydration, loss of plasma via wound/burns) or relative ( third space losses) vascular volume depletion also respond, although blood products a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |