|
Chronophotographic Gun
The chronophotographic gun is one of the ancestors of the movie camera. It was invented in 1882 by Étienne-Jules Marey, a French scientist and chronophotographer. It could shoot 12 images per second and it was the first invention to capture moving images on the same chronomatographic plate using a metal shutter. History Étienne-Jules Marey developed his chronophotographic gun in 1882, inspired by the photo revolver invented in 1874 by the French astronomer Jules Janssen. Janssen used to record the transit of Venus across the Sun on 9 December 1874. Marey wanted to study how animals, insects and birds moved. The functioning of the chronophotographic gun is very similar to a normal rifle, with grip, canon and rotating drum, except that it does not carry bullets but photographic plates with which it caught the light at high speed. The hammer was made back to the end, which allowed the drum to move where there were the photographic plates. There was also a shutter on the drum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusil Photographique Marey2 , a kind of polytope
{{disambig ...
Fusil may refer to: *Fusil, a light flintlock musket used by a fusilier *Fusil (heraldry), a heraldic ordinary similar to a lozenge *Gerald Fusil, creator of the Raid Gauloises adventure race *Duopyramid In geometry of 4 dimensions or higher, a double pyramid, duopyramid, or fusil is a polytope constructed by 2 orthogonal polytopes with edges connecting all pairs of vertices between the two. The term fusil is used by Norman Johnson as a rhomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shutter Speed
In photography, shutter speed or exposure time is the length of time that the film or digital sensor inside the camera is exposed to light (that is, when the camera's shutter (photography), shutter is open) when taking a photograph. The amount of light that reaches the Photographic film, film or image sensor is proportional to the exposure time. of a second will let half as much light in as . Introduction The camera's shutter speed, the lens's aperture or f-stop, and the scene's luminance together determine the amount of light that reaches the film or sensor (the exposure (photography), exposure). Exposure value (EV) is a quantity that accounts for the shutter speed and the f-number. Once the sensitivity to light of the recording surface (either film or sensor) is set in numbers expressed in "Film speed#ISO, ISOs" (e.g. 200 ISO, 400 ISO), the light emitted by the scene photographed can be controlled through aperture and shutter-speed to match the film or sensor sensitivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Photography
The history of photography began with the discovery of two critical principles: The first is camera obscura image projection; the second is the discovery that some substances are visibly altered by exposure to light. There are no artifacts or descriptions that indicate any attempt to capture images with light sensitive materials prior to the 18th century. Around 1717, Johann Heinrich Schulze used a light-sensitive slurry to capture images of cut-out letters on a bottle. However, he did not pursue making these results permanent. Around 1800, Thomas Wedgwood made the first reliably documented, although unsuccessful attempt at capturing camera images in permanent form. His experiments did produce detailed photograms, but Wedgwood and his associate Humphry Davy found no way to fix these images. In 1826, Nicéphore Niépce first managed to fix an image that was captured with a camera, but at least eight hours or even several days of exposure in the camera were required and the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1882 Introductions
Year 188 (CLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in the Roman Empire as the Year of the Consulship of Fuscianus and Silanus (or, less frequently, year 941 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 188 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Publius Helvius Pertinax becomes pro-consul of Africa from 188 to 189. Japan * Queen Himiko (or Shingi Waō) begins her reign in Japan (until 248). Births * April 4 – Caracalla (or Antoninus), Roman emperor (d. 217) * Lu Ji (or Gongji), Chinese official and politician (d. 219) * Sun Shao, Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 241) Deaths * March 17 – Julian, pope and patriarch of Alexandria * Fa Zhen (or Gaoqing), Chinese scholar (b. AD 100) * Lucius Antistius Burrus, Roman politician (executed) * Ma Xiang, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement which began in Paris. It revolutionized painting and the visual arts, and sparked artistic innovations in music, ballet, literature, and architecture. Cubist subjects are analyzed, broken up, and reassembled in an abstract form. Instead of depicting objects from a single perspective, the artist depicts the subject from multiple perspectives to represent the subject in a greater context. Cubism has been considered the most influential art movement of the 20th century. The term ''cubism'' is broadly associated with a variety of artworks produced in Paris (Montmartre and Montparnasse) or near Paris (Puteaux) during the 1910s and throughout the 1920s. The movement was pioneered in partnership by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, and joined by Jean Metzinger, Albert Gleizes, Robert Delaunay, Henri Le Fauconnier, Juan Gris, and Fernand Léger. One primary influence that led to Cubism was the representation of three-dimensional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nude Descending A Staircase, No
Nudity is the state of being in which a human is without clothing. While estimates vary, for the first 90,000 years of pre-history, anatomically modern humans were naked, having lost their body hair, living in hospitable climates, and not having developed the crafts needed to make clothing. As humans became behaviorally modern, body adornments such as jewelry, tattoos, body paint and scarification became part of non-verbal communications, indicating a person's social and individual characteristics. Indigenous peoples in warm climates used clothing for decorative, symbolic or ceremonial purposes but were often nude, having neither the need to protect the body from the elements nor any conception of nakedness being shameful. In many societies, both ancient and contemporary, children might be naked until the beginning of puberty. Women may not cover their breasts due to the association with nursing babies more than with sexuality. In the ancient civilizations of the Medite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcel Duchamp
Henri-Robert-Marcel Duchamp (, ; ; 28 July 1887 – 2 October 1968) was a French painter, sculptor, chess player, and writer whose work is associated with Cubism, Dada, Futurism and conceptual art. He is commonly regarded, along with Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse, as one of the three artists who helped to define the revolutionary developments in the plastic arts in the opening decades of the 20th century, responsible for significant developments in painting and sculpture. He has had an immense impact on 20th- and 21st-century art, and a seminal influence on the development of conceptual art. By the time of World War I, he had rejected the work of many of his fellow artists (such as Henri Matisse) as "retinal," intended only to please the eye. Instead, he wanted to use art to serve the mind. Duchamp is remembered as a pioneering figure partly because of the two famous scandals he provoked -- his ''Nude Descending a Staircase'' that was the most talked-about work of the landmark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futurism
Futurism ( ) was an Art movement, artistic and social movement that originated in Italy, and to a lesser extent in other countries, in the early 20th century. It emphasized dynamism, speed, technology, youth, violence, and objects such as the car, the airplane, and the industrial city. Its key figures included Italian artists Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Umberto Boccioni, Carlo Carrà, Fortunato Depero, Gino Severini, Giacomo Balla, and Luigi Russolo. Italian Futurism glorified modernity and, according to its doctrine, "aimed to liberate Italy from the weight of its past." Important Futurist works included Marinetti's 1909 ''Manifesto of Futurism'', Boccioni's 1913 sculpture ''Unique Forms of Continuity in Space'', Balla's 1913–1914 painting ''Abstract Speed + Sound'', and Russolo's ''The Art of Noises'' (1913). Although Futurism was largely an Italian phenomenon, parallel movements emerged in Russia, where some Russian Futurism , Russian Futurists would later go on to found gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinematography
Cinematography () is the art of motion picture (and more recently, electronic video camera) photography. Cinematographers use a lens (optics), lens to focus reflected light from objects into a real image that is transferred to some image sensor or Photographic film, light-sensitive material inside the movie camera. These Exposure (photography), exposures are created sequentially and preserved for later processing and viewing as a motion picture. Capturing images with an electronic image sensor produces an Charge-coupled device, electrical charge for each pixel in the image, which is Video processing, electronically processed and stored in a video file for subsequent processing or display. Images captured with photographic emulsion result in a series of invisible latent images on the film stock, which are chemically "Photographic developer, developed" into a Positive (photography), visible image. The images on the film stock are Movie projector, projected for viewing in the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
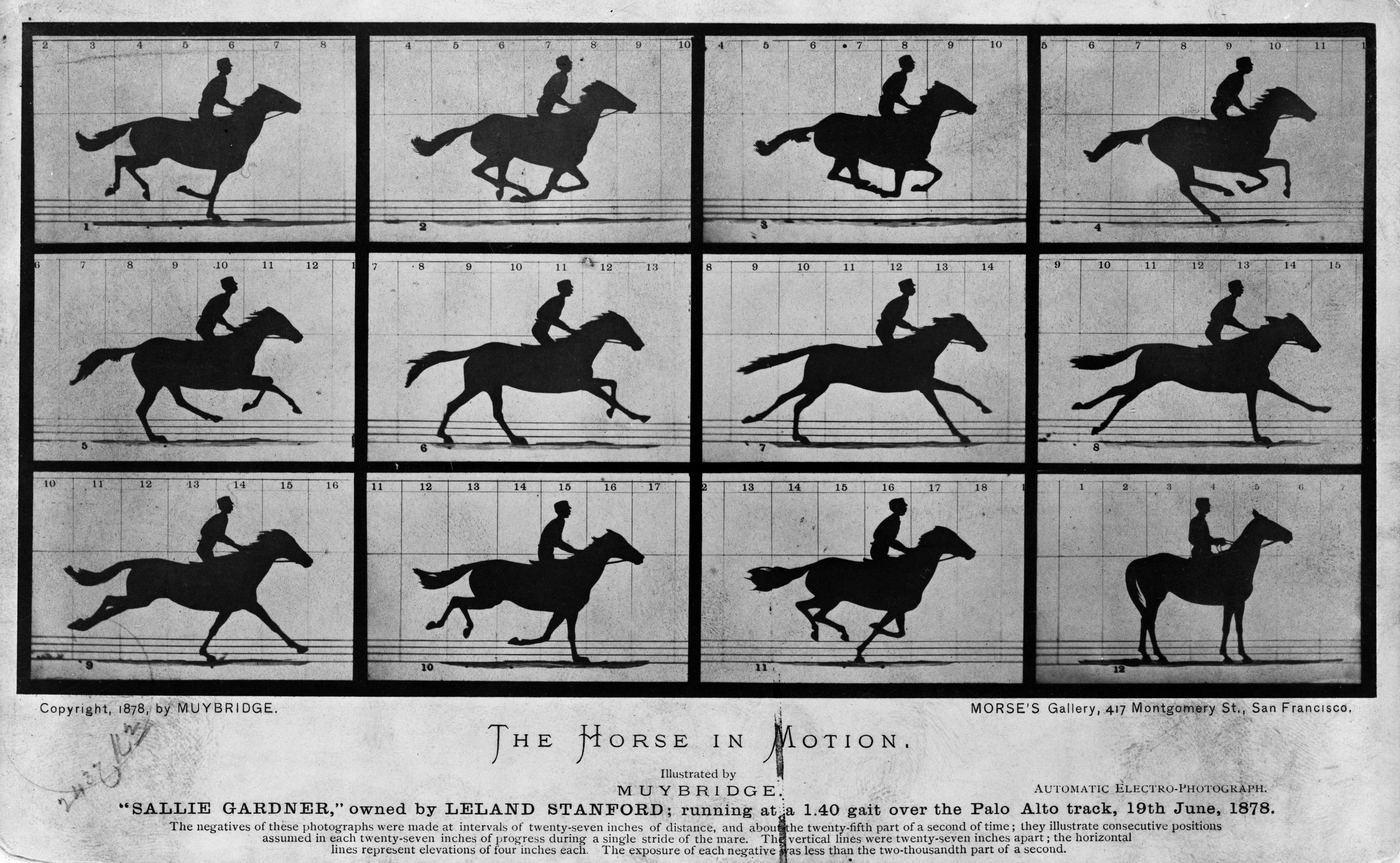
Chronophotography
Chronophotography is a photographic technique from the Victorian era which captures a number of phases of movements. The best known chronophotography works were mostly intended for the scientific study of Animal locomotion, locomotion, to discover practical information for animal handlers and/or as reference material for artists. Although many results were not intended to be exhibited as moving pictures, there is much overlap with the more or less simultaneous quest to register and exhibit photographic motion pictures. Definition Chronophotography is defined as "a set of photographs of a moving object, taken for the purpose of recording and exhibiting successive phases of motion". The term ''chronophotography'' was coined by French physiologist Étienne-Jules Marey to describe photographs of movement from which measurements could be taken and motion could be studied. It is derived from the Greek word χρόνος ''chronos, chrónos'' ("time") combined with ''photography''.The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Locomotion
In ethology, animal locomotion is any of a variety of methods that animals use to move from one place to another. Some modes of locomotion are (initially) self-propelled, e.g., running, swimming, jumping, flight, flying, hopping, soaring and gliding. There are also many animal species that depend on their environment for transportation, a type of mobility called passive locomotion, e.g., sailing (some jellyfish), ballooning (spider), kiting (spiders), rolling (some beetles and spiders) or riding other animals (phoresis). Animals move for a variety of reasons, such as to foraging, find food, a mating system, mate, a suitable microhabitat, or to escape response, escape predators. For many animals, the ability to move is essential for survival and, as a result, natural selection has shaped the locomotion methods and mechanisms used by moving organisms. For example, animal migration, migratory animals that travel vast distances (such as the Arctic tern) typically have a locomotion me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |