|
Chronic Renal Insufficiency
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three months. Early in the course of CKD, patients are usually asymptomatic, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include (in chronological order) high blood pressure (often related to activation of the renin–angiotensin system), bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization. CKD can lead to end-stage kidney failure requiring kidney dialysis or kidney transplantation. Causes of chronic kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney disease. Risk factors inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy ( dialysis and kidney transplantation). The word " renal" is an adjective meaning "relating to the kidneys", and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro-" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" (instead of "nephrology") or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro- as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively. Nephrology also studies systemic conditions that affect the kidneys, such as diabetes and autoimmune disease; and systemic diseases tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
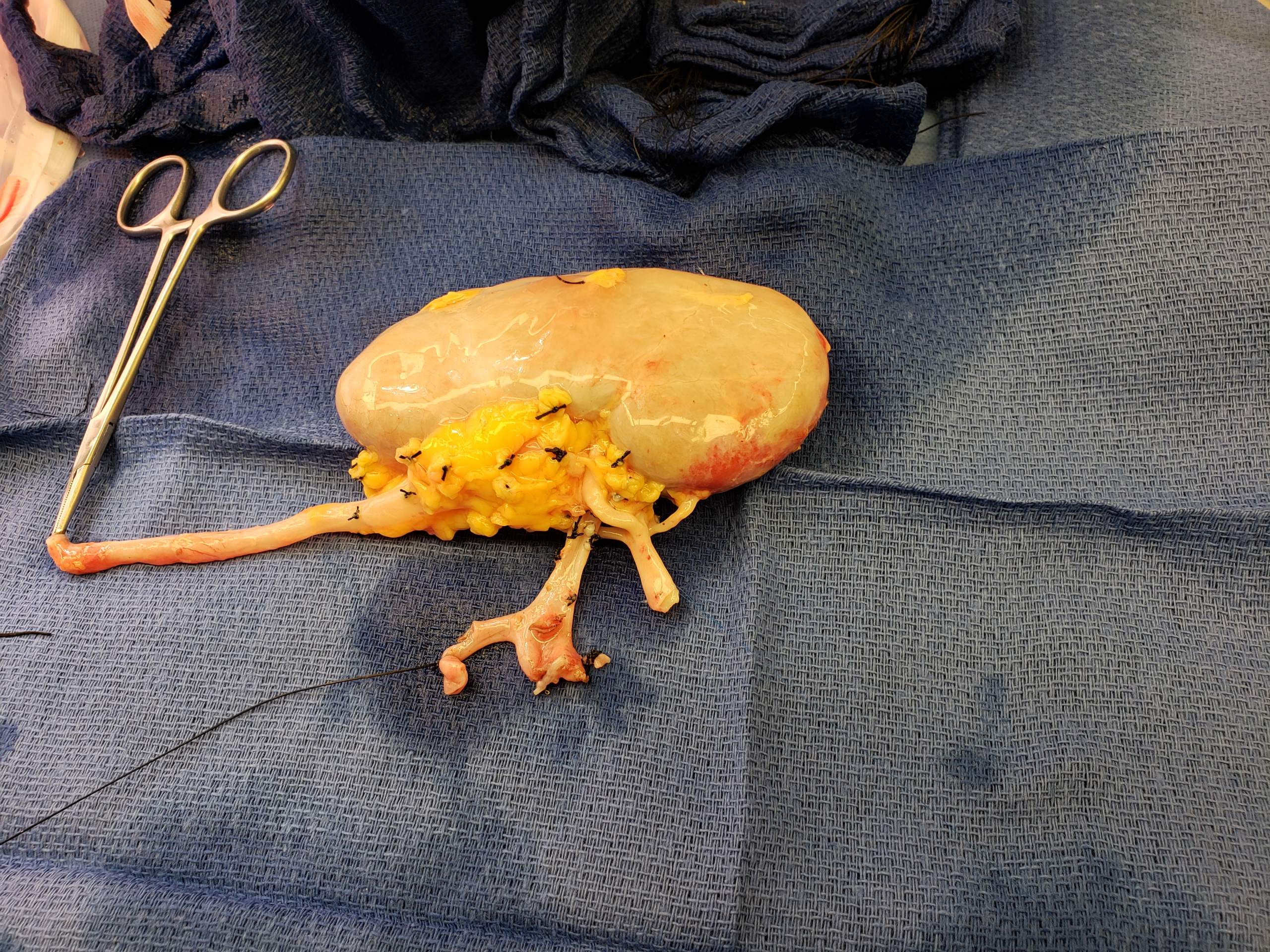
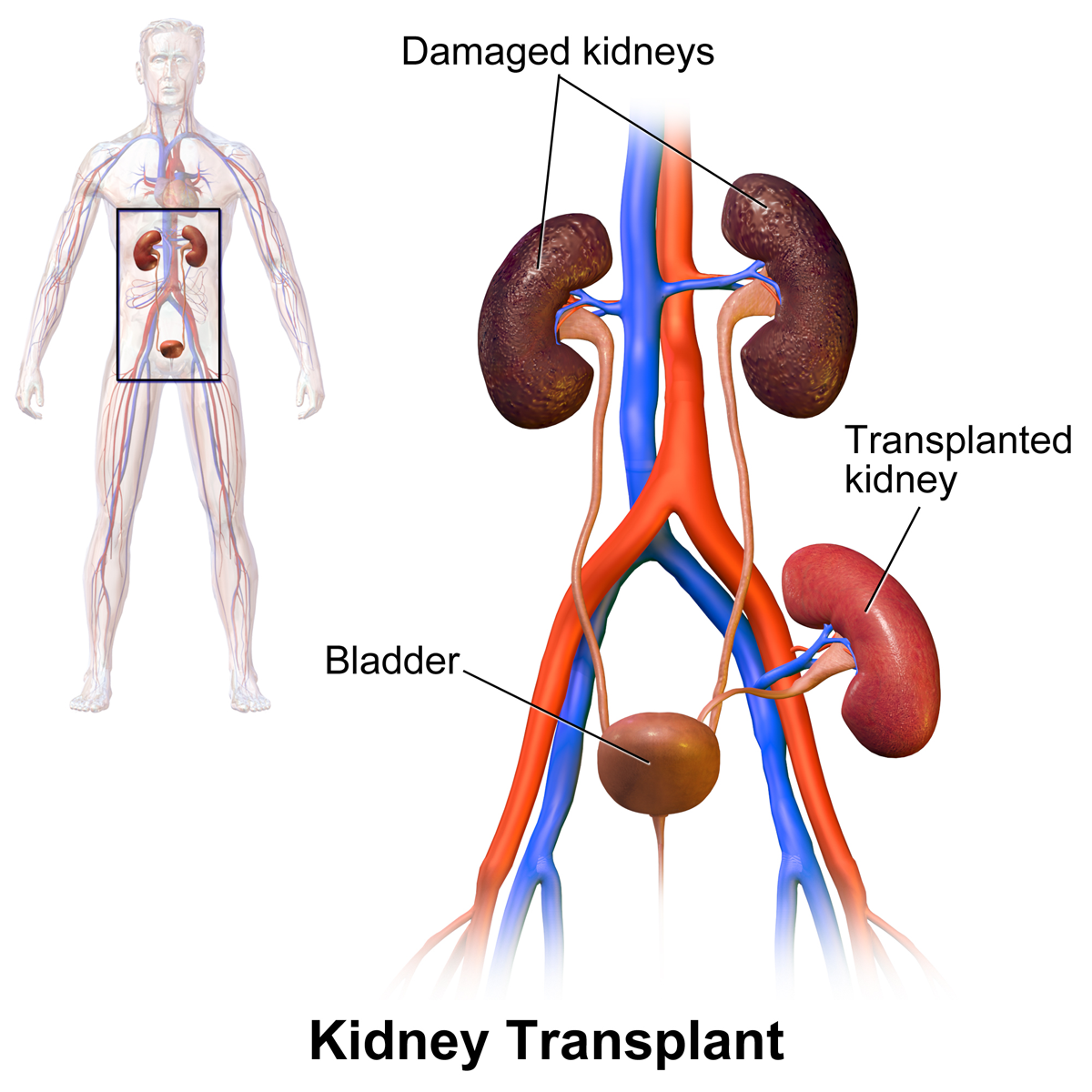
Kidney Transplant
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 by a team including Joseph Murray, the recipient's surgeon, and Hartwell Harrison, surgeon for the donor. Murray was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1990 for this and other work. In 2018, an estimated 95,479 kidney transplants were performed worldwide, 36% of which came from living donors. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called ''albuminoids''. A number of blood transport proteins are evolutionarily related in the albumin family, including serum albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein and afamin. This family is only found in vertebrates. ''Albumins'' in a less strict sense can mean other proteins that coagulate under certain conditions. See ' for lactalbumin, ovalbumin and plant "2S albumin". Function Albumins in general are transport proteins that bind to various ligands and carry them around. Human types include: * Human serum albumin is the main protein of human blood plasma. It m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
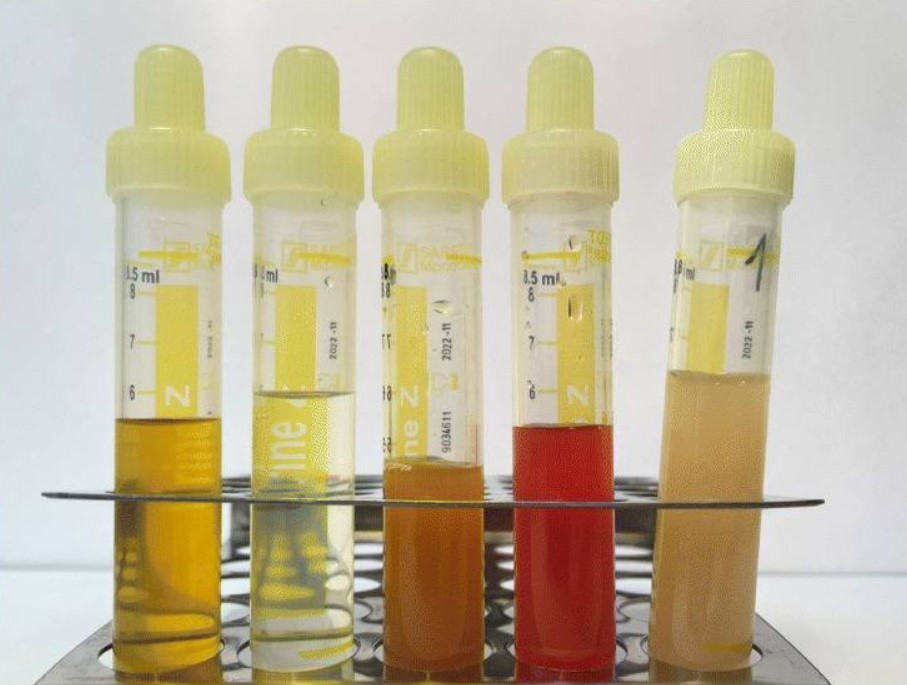
Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, microscopic examination. Macroscopic examination targets parameters such as color, clarity, odor, and specific gravity; urine test strips measure chemical properties such as pH, glucose concentration, and protein levels; and microscopy is performed to identify elements such as Cell (biology), cells, urinary casts, Crystalluria, crystals, and organisms. Background Urine is produced by the filtration of blood in the kidneys. The formation of urine takes place in microscopic structures called nephrons, about one million of which are found in a normal human kidney. Blood enters the kidney though the renal artery and flows through the kidney's vasculature into the Glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus, a tangled knot of capillaries surrounded by Bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance (medicine), clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; production of various hormones, such as erythropoietin; and activation of vitamin D. The kidney has many functions, which a well-functioning kidney realizes by filtering blood in a process known as glomerular filtration. A major measure of kidney function is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). The glomerular filtration rate is the flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney. The creatinine clearance rate (CCr or CrCl) is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine per unit time and is a useful measure for approximating the GFR. Creatinine clearance exceeds GFR due to creatinine secretion, which can be blocked by cimetidine. Both GFR and CCr may be accurately calculated by comparative measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Tests
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholesterol test, are often grouped together into one test panel called a blood panel or blood work. Blood tests are often used in health care to determine physiological and biochemical states, such as disease, mineral content, pharmaceutical drug effectiveness, and organ function. Typical clinical blood panels include a basic metabolic panel or a complete blood count. Blood tests are also used in drug tests to detect drug abuse. Extraction A venipuncture is useful as it is a minimally invasive way to obtain cells and extracellular fluid ( plasma) from the body for analysis. Blood flows throughout the body, acting as a medium that provides oxygen and nutrients to tissues and carries waste products back to the excretory systems f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor kidney transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 by a team including Joseph Murray, the recipient's surgeon, and Hartwell Harrison, surgeon for the donor. Murray was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1990 for this and other work. In 2018, an estimated 95,479 kidney transplants were performed worldwide, 36% of which came from living donors. Before receiving a kidney transplant, a person with ESRD must undergo a thorough medical evaluat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
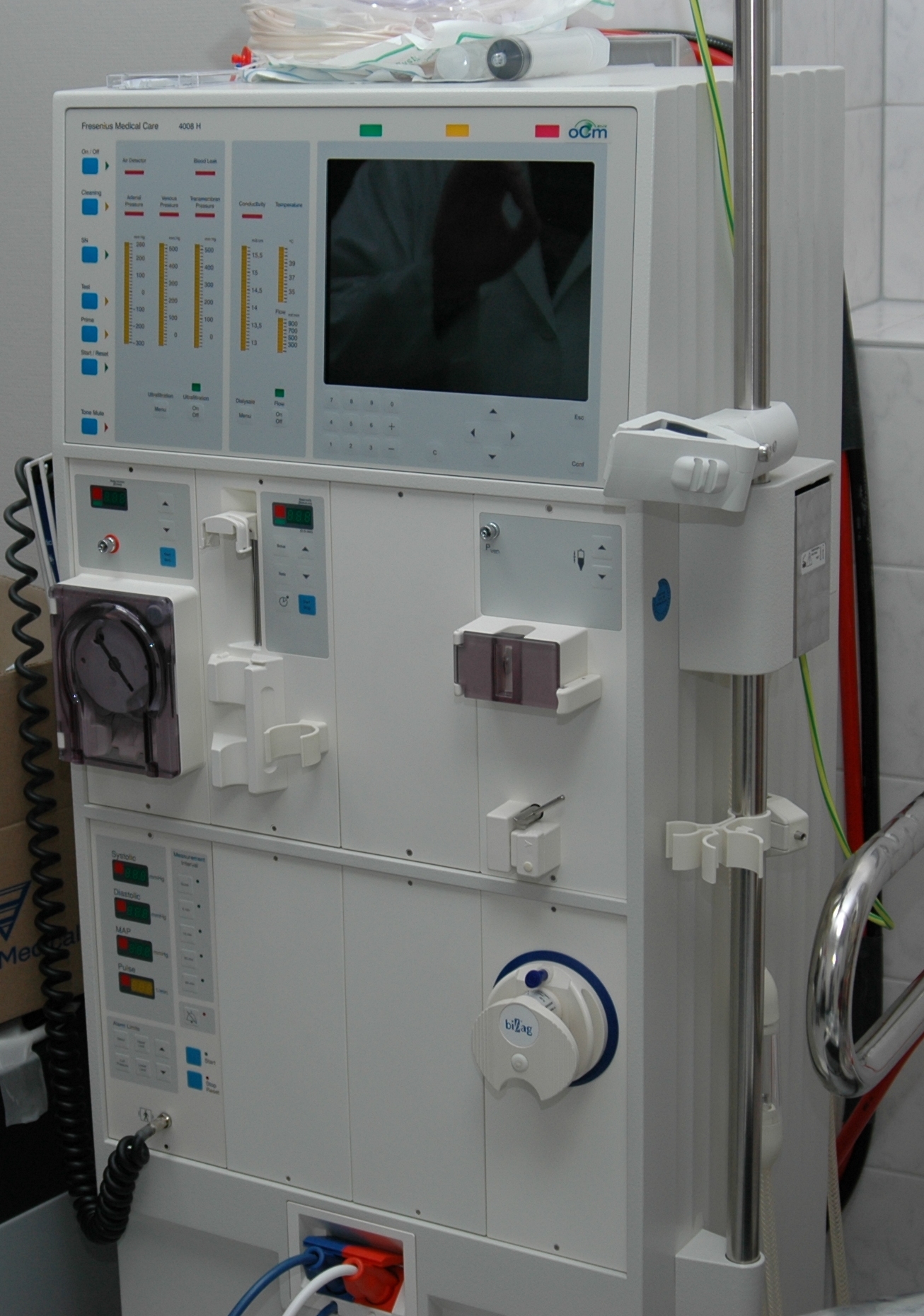
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. Along with kidney transplantation, it is a type of renal replacement therapy. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney failure, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is less than 15% of the normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute, and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not Indication (medicine), indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Singh A, Zawada E. "Initiation of Dialysis". In: ''Handbook of Dialysis''. 4th ed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycystic kidney diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shortly after death. Some organisms, such as '' Turritopsis dohrnii'', are biologically immortal; however, they can still die from means other than aging. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the equivalent for individual components of an organism, such as cells or tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said ''to die'', as a virus is not considered alive in the first place. As of the early 21st century, 56 million people die per year. The most common reason is aging, followed by cardiovascular disease, which is a disease that affects the heart or blood vessels. As of 2022, an estimated total of almost 110 billion humans have died, or rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy is defined as an alteration of bone in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is one measure of the skeletal component of the systemic disorder of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). The term "renal osteodystrophy" was coined in 1943, 60 years after an association was identified between bone disease and kidney failure. The types of renal osteodystrophy have traditionally been defined on the basis of bone turnover and mineralization: 1) mild, slight increase in turnover and normal mineralization; 2) osteitis fibrosa, increased turnover and normal mineralization; 3) osteomalacia, decreased turnover and abnormal mineralization; 4) adynamic, decreased turnover and acellularity; and, 5) mixed, increased turnover with abnormal mineralization.A Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) report has suggested that bone biopsies in patients with CKD should be characterized by determining bone turnover, mineralization, and volume ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renin–angiotensin System
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid, and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance. When renal blood flow is reduced, juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys convert the precursor prorenin (already present in the blood) into renin and secrete it directly into the circulation. Plasma renin then carries out the conversion of angiotensinogen, released by the liver, to angiotensin I, which has no biological function on its own. Angiotensin I is subsequently converted to the active angiotensin II by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) found on the surface of vascular endothelial cells, predominantly those of the lungs. Angiotensin II has a short life of about 1 to 2 minutes. Then, it is rapidly degraded into angiotensin III by angiotensinases which are present in red blood cells and vascular beds in many tissues. Angiotensin III increases blood pressu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |