|
Chronic Bee Paralysis Virus
Chronic bee paralysis virus (CBPV) commonly affects adult Apis mellifera cypria, ''Apis mellifera'' honey bees and causes a chronic paralysis that can easily spread to other members of a colony. Bees infected with CBPV begin to show symptoms after 5 days and die a few days after. Chronic bee paralysis virus infection is a factor that can contribute to or cause the sudden collapse of honeybee colonies. Since honeybees serve a vital role in ecological resilience, it is important to understand factors and diseases that threaten them. Although CBPV infects mainly adult bees, the virus can also infect bees in earlier developmental stages, though developing bees typically have significantly lower viral loads compared to their adult counterparts. Death as a result of CBPV infection in developing bees or brood losses due to viral infection are low or nonexistent. Bees that have been infected with CBPV may harbor millions of viral particles, with half of them concentrated in the head reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abeille Infectée Par Le Virus De La Maladie Noire (CBPV)
Abeille may refer to: Ships *HMS Abeille (1796), HMS ''Abeille'' (1796), a ship of the Royal Navy *''Abeille Bourbon'', a high sea tow vessel *''Abeille Flandre'', a high sea tug of the French navy *''Abeille Liberté'', a salvage tug *''Abeille Provence'', a salvage tug, later the ''Ryan Leet'' *ST Abeille No 7, a tug, originally the ''Empire Helen'' *ST Abeille No 8, a tug, originally the ''Empire Simon'' *ST Abeille No 22, a tug, originally the ''Empire Alfred'' *ST Abeille No 23, a tug, originally the ''Empire Sprite'' People * Abeille de Perrin (1843–1910), full name Elzéar Emmanuel Arène Abeille de Perrin, French entomologist * Scipion Abeille (died 1697), French physician * Gaspard Abeille (1648–1718), French poet * Pierre-César Abeille (1674 – after 1733), French composer * Guy Abeille, French economist * Jacques Abeille (1942–2022), French writer * Louis Paul Abeille (1719–1807), French economist * Ludwig Abeille (1761–1838), German pianist and composer * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research
Research is creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge. It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectivity
In epidemiology, infectivity is the ability of a pathogen In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ... to establish an infection. More specifically, infectivity is the extent to which the pathogen can enter, survive, and multiply in a host. It is measured by the ratio of the number of people who become infected to the total number exposed to the pathogen. Infectivity has been shown to positively correlate with virulence, in plants. This means that as a pathogen's ability to infect a greater number of hosts increases, so does the level of harm it brings to the host. A pathogen's infectivity is different from its transmissibility, which refers to a pathogen's capacity to pass from one organism to another. See also * Basic reproduction number (basic reproductive rate, basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclinical Infection
A subclinical infection—sometimes called a preinfection or inapparent infection—is an infection by a pathogen that causes few or no signs or symptoms of infection in the host. Subclinical infections can occur in both humans and animals. Depending on the pathogen, which can be a virus or intestinal parasite, the host may be infectious and able to transmit the pathogen without ever developing symptoms; such a host is called an asymptomatic carrier. Many pathogens, including HIV, typhoid fever, and coronaviruses such as COVID-19 spread in their host populations through subclinical infection. Not all hosts of asymptomatic subclinical infections will become asymptomatic carriers. For example, hosts of ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' bacteria will only develop active tuberculosis in approximately one-tenth of cases; the majority of those infected by ''Mtb'' bacteria have latent tuberculosis, a non-infectious type of tuberculosis that does not produce symptoms in individuals w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Bee
A queen bee is typically an adult, mated female ( gyne) that lives in a colony or hive of honey bees. With fully developed reproductive organs, the queen is usually the mother of most, if not all, of the bees in the beehive. Queens are developed from larvae selected by worker bees and specially fed in order to become sexually mature. There is normally only one adult, mated queen in a hive, in which case the bees will usually follow and fiercely protect her. The term "queen bee" can be more generally applied to any dominant reproductive female in a colony of a eusocial bee species other than honey bees. However, as in the Brazilian stingless bee ('' Schwarziana quadripunctata''), a single nest may have multiple queens or even dwarf queens, ready to replace a dominant queen in case of a sudden death. Development During the warm parts of the year, female "worker" bees leave the hive every day to collect nectar and pollen. While male bees serve no architectural or pollinating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(+)ssRNA
Positive-strand RNA viruses (+ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome. Positive-strand RNA viruses are divided between the phyla ''Kitrinoviricota'', ''Lenarviricota'', and ''Pisuviricota'' (specifically classes ''Pisoniviricetes'' and '' Stelpavirictes'') all of which are in the kingdom ''Orthornavirae'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are monophyletic and descended from a common RNA virus ancestor. In the Baltimore classification system, +ssRNA viruses belong to Group IV. Positive-sense RNA viruses include pathogens su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
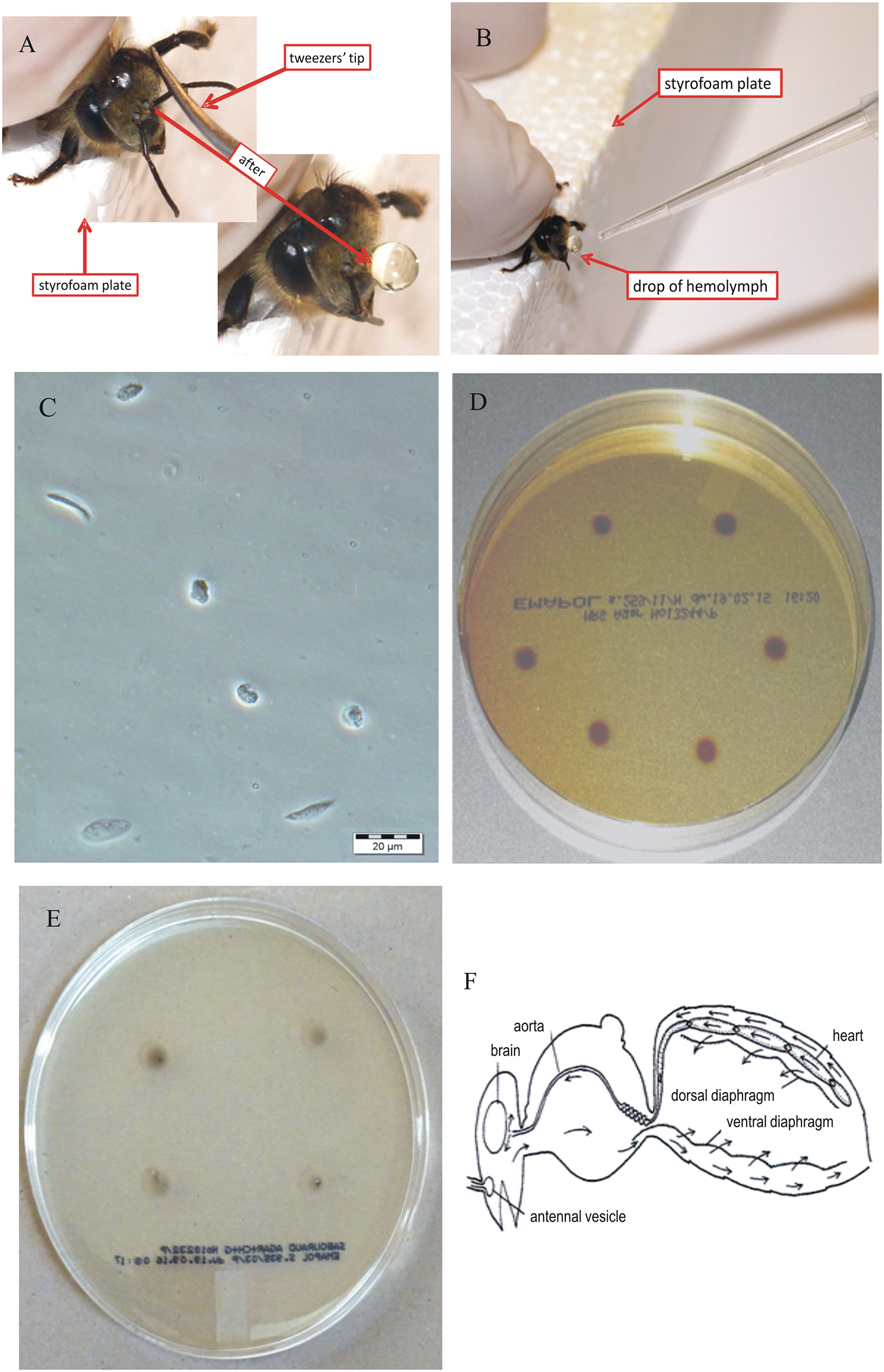
Hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, similar to the blood in invertebrates, that circulates in the inside of the arthropod's body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are dispersed. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods (for example, arachnids, crustaceans and insects). In addition, some non-arthropods such as mollusks possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system. Oxygen-transport systems were long thought unnecessary in insects, but ancestral and functional hemocyanin has been found in the hemolymph. Insect "blood" generally does not carry hemoglobin, although hemoglobin may be present in the tracheal system instead and play some role in respiration. Method of transport In the grasshopper, the closed portion of the system consists of tubular hearts and an ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varroa Destructor
''Varroa destructor'', the Varroa mite, is an ectoparasite, external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on honey bees and is one of the most damaging honey bee pests in the world. A significant mite infestation leads to the death of a honey bee colony, usually in the late autumn through early spring. Without management for Varroa mite, honey bee colonies typically collapse within 2 to 3 years in temperate climates. These mites can infest ''Apis mellifera'', the western honey bee, and ''Apis cerana'', the Asian honey bee. Due to very similar physical characteristics, this species was thought to be the closely related ''Varroa jacobsoni'' prior to 2000, but they were found to be two separate species after DNA analysis. Parasitism of bees by mites in the genus ''Varroa'' is called varroosis. The Varroa mite can reproduce only in a honey bee colony. It attaches to the body of the bee and weakens the bee. The species is a vector for at least five debilitating bee viruses, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |