|
Chromaticism
Chromaticism is a compositional technique interspersing the primary diatonic scale, diatonic pitch (music), pitches and chord (music), chords with other pitches of the chromatic scale. In simple terms, within each octave, diatonic music uses only seven different notes, rather than the twelve available on a standard piano keyboard. Music is chromatic when it uses more than just these seven notes. Chromaticism is in contrast or addition to tonality or diatonic and chromatic, diatonicism and modality (music), modality (the major scale, major and minor scale, minor, or "white key", scales). Chromatic elements are considered, "elaborations of or substitutions for diatonic scale members".Matthew Brown; Schenker, "The Diatonic and the Chromatic in Schenker's "Theory of Harmonic Relations", ''Journal of Music Theory'', Vol. 30, No. 1 (Spring 1986), pp. 1–33, citation on p. 1. Development of chromaticism Chromaticism began to develop in the late Renaissance music, Renaissance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatonic And Chromatic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize Scale (music), scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, Musical note, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the Common practice period, common practice music of the period 1600–1900. These terms may mean different things in different contexts. Very often, ''diatonic'' refers to musical elements derived from the modes and transpositions of the "white note scale" C–D–E–F–G–A–B. In some usages it includes all forms of heptatonic scale that are in common use in Western music (the major, and all forms of the minor). ''Chromatic'' most often refers to structures derived from the chromatic scale in 12-tone equal temperament, which consists of all semitones. Historically, however, it had other senses, referring in Ancient Greek mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Notes Diagram
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900. These terms may mean different things in different contexts. Very often, ''diatonic'' refers to musical elements derived from the modes and transpositions of the "white note scale" C–D–E–F–G–A–B. In some usages it includes all forms of heptatonic scale that are in common use in Western music (the major, and all forms of the minor). ''Chromatic'' most often refers to structures derived from the chromatic scale in 12-tone equal temperament, which consists of all semitones. Historically, however, it had other senses, referring in Ancient Greek music theory to a particular tuning of the tetrachord, and to a rhythmic notational conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce the chromatic scale, while other instruments capable of continuously variable pitch, such as the trombone and violin, can also produce microtones, or notes between those available on a piano. Most music uses subsets of the chromatic scale such as diatonic scales. While the chromatic scale is fundamental in western music theory, it is seldom directly used in its entirety in musical compositions or improvisation. Definition The chromatic scale is a musical scale with twelve pitches, each a semitone, also known as a half-step, above or below its adjacent pitches. As a result, in 12-tone equal temperament (the most common tuning in Western music), the chromatic scale covers all 12 of the available pitches. Thus, there is only one chromatic scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the common practice music of the period 1600–1900. These terms may mean different things in different contexts. Very often, ''diatonic'' refers to musical elements derived from the modes and transpositions of the "white note scale" C–D–E–F–G–A–B. In some usages it includes all forms of heptatonic scale that are in common use in Western music (the major, and all forms of the minor). ''Chromatic'' most often refers to structures derived from the chromatic scale in 12-tone equal temperament, which consists of all semitones. Historically, however, it had other senses, referring in Ancient Greek music theory to a particular tuning of the tetrachord, and to a rhythmic notational co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Supertonic Chord
A secondary chord is an analytical label for a specific harmonic device that is prevalent in the tonal idiom of Western music beginning in the common practice period: the use of diatonic functions for tonicization. Secondary chords are a type of altered or borrowed chord, chords that are not part of the music piece's key. They are the most common sort of altered chord in tonal music. Secondary chords are referred to by the function they have and the key or chord in which they function. In Roman numeral analysis, they are written with the notation "''function''/''key''". Thus, one of the most common secondary chords, the dominant of the dominant, is written "V/V" and read as "five of five" or "the dominant of the dominant". The major or minor triad on any diatonic scale degree may have any secondary function applied to it; secondary functions may even be applied to diminished triads in some special circumstances. Secondary chords were not used until the Baroque period and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonality
Tonality is the arrangement of pitch (music), pitches and / or chord (music), chords of a musical work in a hierarchy of perceived ''relations'', ''stabilities'', ''attractions'', and ''directionality''. In this hierarchy, the single pitch or the root (music), root of a triad (music), triad with the greatest ''stability'' in a melody or in its harmony is called the tonic (music), ''tonic''. In this context "stability" approximately means that a pitch occurs frequently in a melody – and usually is the final note – or that the pitch often appears in the harmony, even when it is not the pitch used in the melody. The ''root'' of the tonic triad forms the name given to the key (music), key, so in the key of C major, C major the note C can be both the tonic of the scale (music), scale and the root of the tonic triad. However, the tonic can be a different Musical tone, tone in the same scale, and then the work is said to be in one of the mode (music), ''modes'' of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode Mixture
A borrowed chord (also called mode mixture,Romeo, Sheila (1999). ''Complete Rock Keyboard Method: Mastering Rock Keyboard'', p. 42. . Bouchard, Joe and Romeo, Sheila (2007). ''The Total Rock Keyboardist'', p. 120. Alfred Music. . modal mixture, substituted chord,White, William Alfred (1911). Harmonic Part-writing', p. 42. Silver, Burdett, & Co. . modal interchange, or mutation) is a chord borrowed from the parallel key (minor or major scale with the same tonic). Borrowed chords are typically used as "color chords", providing harmonic variety through contrasting scale forms, which are major scales and the three forms of minor scales.Benward & Saker (2009), p. 71. Chords may also be borrowed from other parallel modes besides the major and minor mode, for example D Dorian with D major. The mixing of the major and minor modes developed in the Baroque period. Borrowed chords are distinguished from modulation by being brief enough that the tonic is not lost or displaced, and may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
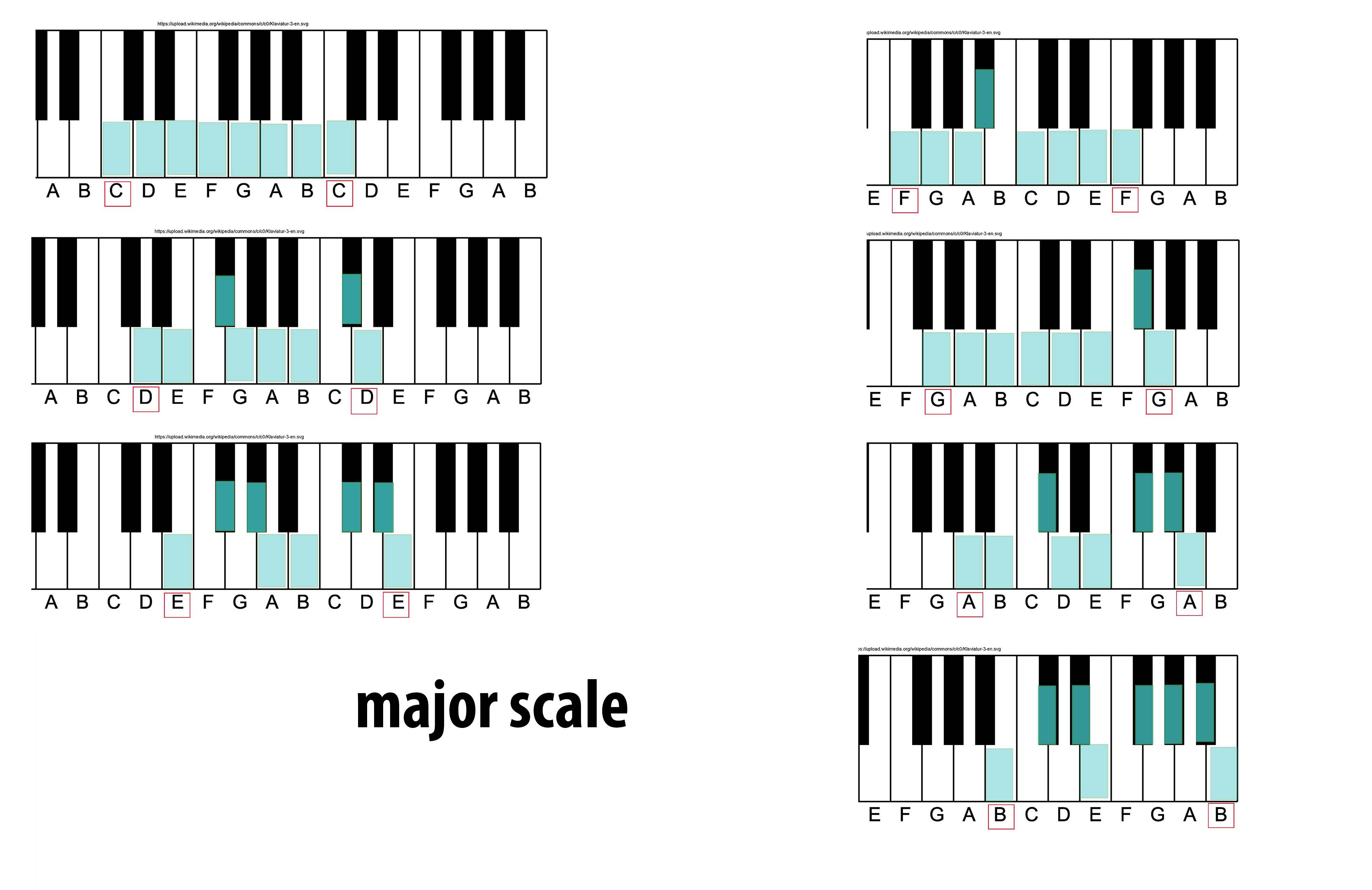
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musica Reservata
In music history, ''musica reservata'' (also ''musica secreta'') is either a style or a performance practice in ''a cappella'' vocal music of the latter half of the 16th century, mainly in Italy and southern Germany, involving refinement, exclusivity, and intense emotional expression of sung text. Definition The exact meaning, which appears in scattered contemporary sources, is a matter of debate among musicologists. While some of the sources are contradictory, four aspects seem clear: # ''musica reservata'' involved the use of chromatic progressions and voice-leading, a manner of composing which became fashionable in the 1550s, both in madrigals and motets; # it involved a style of performance, perhaps with extra ornamentation or other emotive methods; # it used word-painting, i.e. use of specific and recognizable musical figures to illuminate specific words in the text; and # the music was designed to be performed by, and appreciated by, small groups of connoisseurs. Compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lament Bass
In music, the lament bass is a ground bass, built from a descending perfect fourth from tonic to dominant, with each step harmonized.Brover-Lubovsky, Bella (2008). ''Tonal Space in the Music of Antonio Vivaldi'', p.151-52. . The diatonic version is the upper tetrachord from the natural minor scale, known as the Phrygian tetrachord, while the chromatic version, the chromatic fourth, has all semitones filled in. It is often used in music to denote tragedy or sorrow. However, "A common misperception exists that the 'lament bass' of Venetian opera became so prevalent that it immediately swept away all other possible affective associations with this bass pattern...To cite but one example, Peter Holman, writing about Henry Purcell, once characterized the minor tetrachord as 'the descending ground that was associated with love in seventeenth-century opera'." Compositional form There exists a short, free musical form of the Romantic Era, called complaint or "complainte" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Tone
In music theory, a leading tone (also called subsemitone or leading note in the UK) is a musical note, note or pitch (music), pitch which resolution (music), resolves or "leads" to a note one semitone higher or lower, being a lower and upper leading tone, respectively. Typically, leading tone refers to the seventh Scale-degree, scale degree of a major scale (), a major seventh above the Tonic (music), tonic. In the Solfège#Movable do solfège, movable do solfège system, the leading tone is sung as ''si''. A leading-tone triad is a triad (music), triad built on the seventh scale degree in a major key (vii in Roman numeral analysis), while a leading-tone seventh chord is a seventh chord built on the seventh scale degree (vii7). Walter Piston considers and notates vii as V, an incomplete dominant seventh chord. (For the Roman numeral notation of these chords, see Roman numeral analysis.) Note Seventh scale degree (or lower leading tone) Typically, when people speak of ''the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |