|
Chromate Ion
Chromate salts contain the chromate anion, . Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion, . They are oxyanions of chromium in the +6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chemical properties Potassium-chromate-sample.jpg, Potassium chromate Potassium-dichromate-sample.jpg, Potassium dichromate Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide, giving products in which peroxide, , replaces one or more oxygen atoms. In acid solution the unstable blue peroxo complex Chromium(VI) oxide peroxide, , is formed; it is an uncharged covalent molecule, which may be extracted into ether. Addition of pyridine results in the formation of the more stable complex . Acid–base properties In aqueous solution, chromate and dichromate anions exist in a chemical equilibrium. : The predominance diagram shows that the position of the equilibrium depends on both pH and the analytical concentration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball-and-stick Model
In chemistry, the ball-and-stick model is a molecular model of a chemical substance which displays both the Molecular geometry, three-dimensional position of the atoms and the chemical bond, bonds between them. The atoms are typically represented by sphere (geometry), spheres, connected by rods which represent the bonds. Double bond, Double and triple bonds are usually represented by two or three curved rods, respectively, or alternately by correctly positioned sticks for the sigma bond, sigma and pi bonds. In a good model, the angles between the rods should be the same as the Bond angle, angles between the bonds, and the distances between the centers of the spheres should be proportional to the distances between the corresponding atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. The chemical element of each atom is often indicated by the sphere's color. In a ball-and-stick model, the radius of the spheres is usually much smaller than the rod lengths, in order to provide a clearer view of the atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
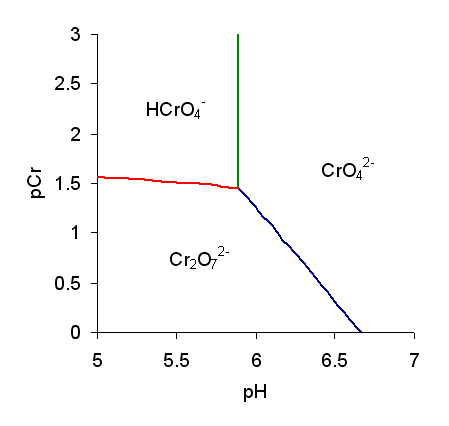
Predominance Diagram
A predominance diagram purports to show the conditions of concentration and pH where a chemical species has the highest concentration in solutions in which there are multiple acid-base equilibria. The lines on a predominance diagram indicate where adjacent species have the same concentration. Either side of such a line one species or the other predominates, that is, has higher concentration relative to the other species. To illustrate a predominance diagram, part of the one for chromate is shown at the right. pCr stands for minus the logarithm of the chromium concentration and pH stands for minus the logarithm of the hydrogen ion A hydrogen ion is created when a hydrogen atom loses or gains an electron. A positively charged hydrogen ion (or proton) can readily combine with other particles and therefore is only seen isolated when it is in a gaseous state or a nearly particl ... concentration. There are two independent equilibria, with equilibrium constants defined as follows. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laidlaw School Bus
Laidlaw (), organized as Laidlaw International, Inc. (with corporate headquarters in Naperville, Illinois) was the largest provider of intercity bus services, contract public transit and paratransit, and school bus contractor, contract school bus service in both the United States and Canada. In February 2007, FirstGroup, a bus and rail transportation operator in the United Kingdom with subsidiaries in North America, acquired Laidlaw International, Inc. FirstGroup completed the acquisition of Laidlaw International on October 1, 2007, and rebranded Laidlaw services under the FirstGroup umbrella. The deal combined North America's two largest private school bus operators—Education Services and First Student Inc.—giving them a combined 40% of the school bus contractor market. Laidlaw had grown primarily through acquisitions of other companies and independent contractor, contracting of services formerly directly provided by government entities. It was the parent company of Lai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from the Arabic word , ) is a basic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word ''alkali'' is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly of potassium carbonate, was mildly basic. After heating this substance with calcium hydroxide (''slaked lime''), a far more strongly basic substance known as ''caustic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Potential
Redox potential (also known as oxidation / reduction potential, ''ORP'', ''pe'', ''E_'', or E_) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is expressed in volts (V). Each species has its own intrinsic redox potential; for example, the more positive the reduction potential (reduction potential is more often used due to general formalism in electrochemistry), the greater the species' affinity for electrons and tendency to be reduced. Measurement and interpretation In aqueous solutions, redox potential is a measure of the tendency of the solution to either gain or lose electrons in a reaction. A solution with a higher (more positive) reduction potential than some other molecule will have a tendency to gain electrons from this molecule (i.e. to be reduced by oxidizing this other molecule) and a solution with a lower (more negative) reduction potential w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromium(III) Hydroxide
Chromium(III) hydroxide is a gelatinous green inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a polymer with an undefined structure and low solubility. It is amphoteric, dissolving in both strong alkalis and strong acids. :In alkali: :In acid: It is used as a pigment, as a mordant, and as a catalyst for organic reactions. It is manufactured by adding a solution of ammonium hydroxide Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although ... to a solution of chromium salt. Pure is as yet (2020) unknown among the mineral species. However, three natural polymorphs of the chromium(III) oxide hydroxide, CrO(OH), are known: bracewellite, grimaldiite and guyanaite. References Chromium(III) compounds Hydroxides Chromium–oxygen compounds {{Inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Solution
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in water would be represented as . The word ''aqueous'' (which comes from ''aqua'') means pertaining to, related to, similar to, or dissolved in, water. As water is an excellent solvent and is also naturally abundant, it is a ubiquitous solvent in chemistry. Since water is frequently used as the solvent in experiments, the word solution refers to an aqueous solution, unless the solvent is specified. A ''non-aqueous solution'' is a solution in which the solvent is a liquid, but is not water. Characteristics Substances that are ''hydrophobic'' ('water-fearing') do not dissolve well in water, whereas those that are '' hydrophilic'' ('water-friendly') do. An example of a hydrophilic substance is sodium chloride. In an aqueous solution the hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reduction (chemistry)
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction. There are two classes of redox reactions: * Electron transfer, Electron-transfer – Only one (usually) electron flows from the atom, ion, or molecule being oxidized to the atom, ion, or molecule that is reduced. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * Atom transfer – An atom transfers from one Substrate (chemistry), substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously, the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted ) is a quantitative property, quantitative measure of the acid strength, strength of an acid in Solution (chemistry), solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction :HA A^- + H^+ known as Dissociation (chemistry), dissociation in the context of acid–base reactions. The chemical species HA is an acid that dissociates into , called the conjugate base of the acid, and a hydron (chemistry), hydrogen ion, . The system is said to be in chemical equilibrium, equilibrium when the concentrations of its components do not change over time, because both forward and backward reactions are occurring at the same rate. The dissociation constant is defined by :K_\text = \mathrm, or by its logarithmic form :\mathrmK_\ce = - \log_ K_\text = \log_\frac where quantities in square brackets represent the molar concentrations of the species at equilibrium. For example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromic Acid
Chromic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is also a jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide. The term "chromic acid" is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (and a valence of VI or 6). It is a strong and corrosive oxidizing agent and a moderate carcinogen. Molecular chromic acid Molecular chromic acid, , in principle, resembles sulfuric acid, . It would ionize accordingly: : The p''K''a for the equilibrium is not well characterized. Reported values vary between about −0.8 to 1.6. The structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weak Acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula , to dissociate into a proton, , and an anion, . The dissociation or ionization of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions. : Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid (), perchloric acid (), nitric acid () and sulfuric acid (). A weak acid is only partially dissociated, or is partly ionized in water with both the undissociated acid and its dissociation products being present, in solution, in equilibrium with each other. : Acetic acid () is an example of a weak acid. The strength of a weak acid is quantified by its acid dissociation constant, K_a value. The strength of a weak organic acid may depend on substituent effects. The strength of an inorganic acid is dependent on the oxidation state for the atom to which the proton may be attached. Acid strength is solvent-dependent. For example, hydrogen chloride is a strong acid in aqueous solu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |