|
Choroid Plexus Cysts
Choroid plexus cysts (CPCs) are cysts that occur within choroid plexus of the brain. They are the most common type of intraventricular cyst, occurring in 1% of all pregnancies. It is believed that many adults have one or more tiny CPCs. The fetal brain may create these cysts as a normal part of development. They are temporary and usually are gone by the 32nd week of pregnancy. CPCs are a rare cause of intermittent hydrocephalus. This is caused by a blockage of foramina within the ventricular drainage system of the central nervous system (CNS), which can lead to expansion of the ventricles, compressing the brain (the cranial cavity cannot expand to accommodate the increase in fluid volume) and possibly causing damage. Pathology The brain contains pockets or spaces called ventricles with a spongy layer of cells and blood vessels called the choroid plexus. This is in the middle of the fetal brain. The choroid plexus has the important function of producing cerebrospinal fluid. The fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the specialty (medicine), medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the Human brain, brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system, and cerebrovascular system. Neurosurgery as a medical specialty also includes non-surgical management of some neurological conditions. Education and context In different countries, there are different requirements for an individual to legally practice neurosurgery, and there are varying methods through which they must be educated. In most countries, neurosurgeon training requires a minimum period of seven years after graduating from medical school. United Kingdom In the United Kingdom, students must gain entry into medical school. The MBBS qualification (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) takes four to six years depending on the student's route. The newly qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has occurred, the affected cells divide incessantly and become cancerous, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choroid Plexus
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid. Structure Location There is a choroid plexus in each of the four ventricles. In the lateral ventricles, it is found in the body, and continued in an enlarged amount in the atrium. There is no choroid plexus in the anterior horn. In the third ventricle, there is a small amount in the roof that is continuous with that in the body, via the interventricular foramina, the channels that connect the lateral ventricles with the third ventricle. A choroid plexus is in part of the roof of the fourth ventricle. Microana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) may have poor balance, difficulty controlling urination, or mental impairment. In babies, there may be a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects (primary) or can develop later in life (secondary). Hydrocephalus can be classified via mechanism into communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Diagnosis is made by physical examination and medical imaging, such as a CT scan. Hydrocephalus is typically treated through surgery. One option is the placement of a shunt system. A procedure called an endoscopic third ventriculostomy has gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular System
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain. CSF is mostly produced by specialized Ependyma, ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. It is also produced by ependymal cells in the lining of the ventricles. In humans, there is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immune system, immunological protection to the brain inside the Human skull, skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trisomy 18
Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of a third copy of all or part of chromosome 18. Many parts of the body are affected. Babies are often born small and have heart defects. Other features include a small head, small jaw, clenched fists with overlapping fingers, and severe intellectual disability. Most cases of trisomy 18 occur due to problems during the formation of the reproductive cells or during early development. The chance of this condition occurring increases with the mother's age. Rarely, cases may be inherited. Occasionally, not all cells have the extra chromosome, known as mosaic trisomy, and symptoms in these cases may be less severe. An ultrasound during pregnancy can increase suspicion for the condition, which can be confirmed by amniocentesis. Treatment is supportive. After having one child with the condition, the risk of having a second is typically around one percent. It is the second-most common co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of investigating individuals and families affected by or at risk of genetic disorders to help them understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease. This field is considered necessary for the implementation of genomic medicine. The process integrates: * Interpretation of family and medical histories to assess the chance of disease occurrence or recurrence * Education about inheritance, testing, management, prevention, resources * Counseling to promote informed choices, adaptation to the risk or condition and support in reaching out to relatives that are also at risk History The practice of advising people about inherited traits began around the turn of the 20th century, shortly after William Bateson suggested that the new medical and biological study of heredity be called "genetics". Heredity became intertwined with social reforms when the field of modern eugenics took form. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is necessary to conclusively diagnose the majority of genetic disorders, with amniocentesis being the gold-standard procedure after 15 weeks' gestation. In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the abdomen of the pregnant woman. The needle punctures the amnion, which is the membrane that surrounds the developing fetus. The fluid within the amnion is called amniotic fluid, and because this fluid surrounds the developing fetus, it contains fetal cells. The amniotic fluid is sampled and analyzed via methods such as karyotyping and DNA analysis technology for genetic abnormalities. An amniocentesis is typically performed in the second trimester between the 15th and 20th week of gestation. Women who choose to have this test are prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
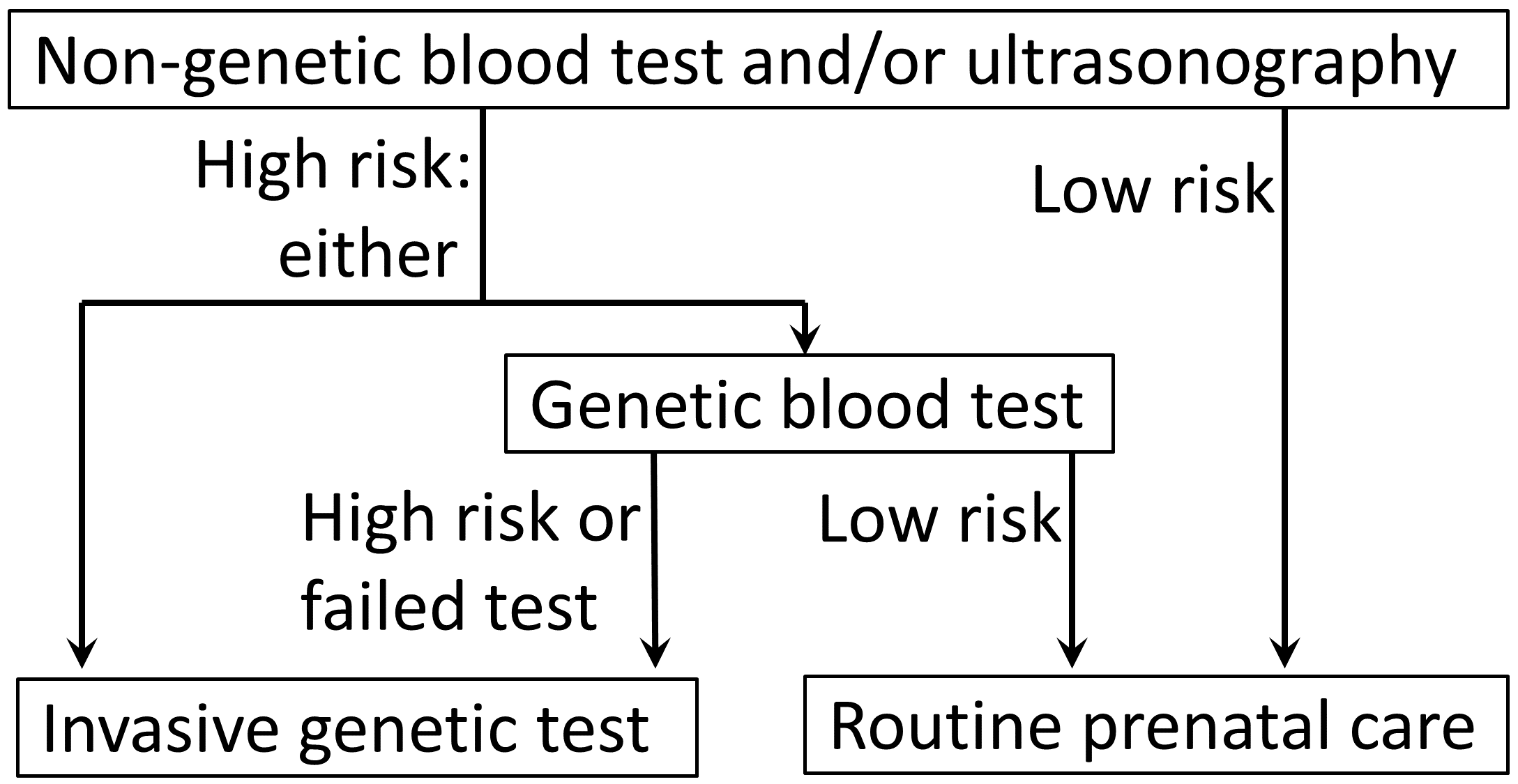
Triple Test
The triple test, also called triple screen, the Kettering test or the Bart's test, is an investigation performed during pregnancy in the second trimester to classify a patient as either high-risk or low-risk for chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defects). The term "multiple-marker screening test" is sometimes used instead. This term can encompass the "double test" and "quadruple test" (described below). The Triple screen measures serum levels of AFP, estriol, and beta-hCG, with a 70% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate. It is complemented in some regions of the United States, as the ''Quad screen'' (adding inhibin A to the panel, resulting in an 81% sensitivity and 5% false-positive rate for detecting Down syndrome when taken at 15–18 weeks of gestational age) and other prenatal diagnosis techniques, although it remains widely used in Canada and other countries. A positive screen indicates an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities (and neural tube defec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |