|
Cholera Toxin
Cholera toxin (also known as choleragen, CTX, CTx and CT) is a potent enterotoxin produced by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae which causes severe watery diarrhea and dehydration that define cholera infections. The toxin is a member of the heat-labile enterotoxin family, and exists as an AB5 multimeric toxin with one enzymatically active A subunit and five receptor-binding B subunits that facilitate host cell entry. History The cholera toxin is the causative pathogenic agent of the ancient disease cholera, thought to have emerged in the Ganges Delta. For centuries the toxin remained confined to this region, but 19th-century globalisation spread it worldwide through the course of seven subsequent pandemics. When cholera arrived in London in 1832, its transmission was poorly understood, with many blaming miasma. Physician, John Snow (1813-1858) was an advocate of water contamination as the cause of its spread - famously ending an outbreak by removing a public water pump handle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterotoxin
An enterotoxin is a protein exotoxin released by a microorganism that targets the intestines. They can be chromosomally or plasmid encoded. They are heat labile (> 60 °C), of low molecular weight and water-soluble. Enterotoxins are frequently cytotoxic and kill cells by altering the apical membrane permeability of the mucosal (epithelial) cells of the intestinal wall. They are mostly pore-forming toxins (mostly chloride pores), secreted by bacteria, that assemble to form pores in cell membranes. This causes the cells to die. Clinical significance Enterotoxins have a particularly marked effect upon the gastrointestinal tract, causing traveler's diarrhea and food poisoning. The action of enterotoxins leads to increased chloride ion permeability of the apical membrane of intestinal mucosal cells. These membrane pores are activated either by increased cAMP or by increased calcium ion concentration intracellularly. The pore formation has a direct effect on the osmolarity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
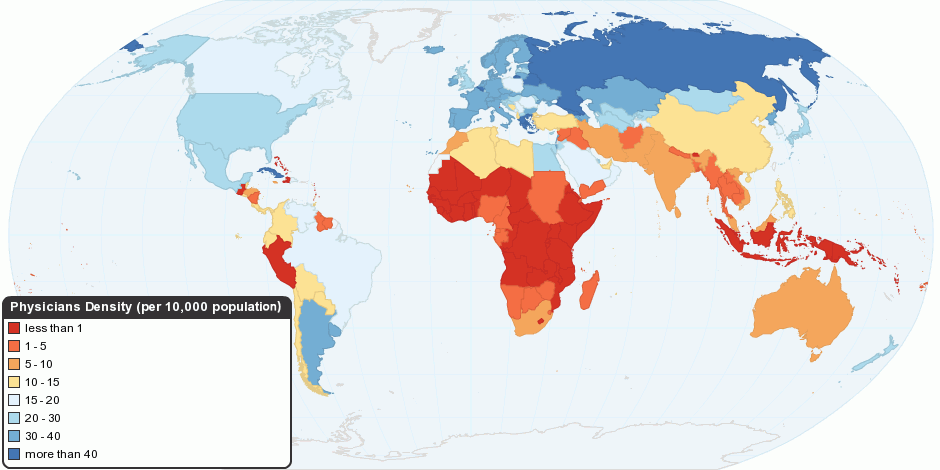
Healthcare Access
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequities, and face worse health outcomes than those who are able to access certain resources. It is not equity to simply provide every individual with the same resources; that would be equality. In order to achieve health equity, resources must be allocated based on an individual need-based principle. According to the World Health Organization, "Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". The quality of health and how health is distributed among economic and social status in a society can provide insight into the level of development within that society. Health is a basic human right and human need, and all human rights are interconnected. Thus, health must be discusse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis The synthesis of cAMP is stimulated by trophic hormones that bind to receptors on the cell surface. cAMP levels reach maximal levels within minutes and decrease gradually over an hour in cultured cells. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein protein complex, complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of ''G alpha subunit, alpha'' (Gα), ''beta'' (Gβ) and ''gamma'' (Gγ) protein subunit, subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable Protein dimer, dimeric complex re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gs Alpha Subunit
The Gs alpha subunit (Gαs, Gsα) is a subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein Gs that stimulates the cAMP-dependent pathway by activating adenylyl cyclase. Gsα is a GTPase that functions as a cellular signaling protein. Gsα is the founding member of one of the four families of heterotrimeric G proteins, defined by the alpha subunits they contain: the Gαs family, Gαi/Gαo family, Gαq family, and Gα12/Gα13 family. The Gs-family has only two members: the other member is Golf, named for its predominant expression in the olfactory system. In humans, Gsα is encoded by the GNAS complex locus, while Golfα is encoded by the GNAL gene. Function The general function of Gs is to activate intracellular signaling pathways in response to activation of cell surface G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). GPCRs function as part of a three-component system of receptor-transducer-effector. The transducer in this system is a heterotrimeric G protein, composed of three subunits: a G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADP-ribosylation
ADP-ribosylation is the addition of one or more ADP-ribose moieties to a protein. It is a reversible post-translational modification that is involved in many cellular processes, including cell signaling, DNA repair, gene regulation and apoptosis. Improper ADP-ribosylation has been implicated in some forms of cancer. It is also the basis for the toxicity of bacterial compounds such as cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, and others. History The first suggestion of ADP-ribosylation surfaced during the early 1960s. At this time, Pierre Chambon and coworkers observed the incorporation of ATP into hen liver nuclei extract. After extensive studies on the acid insoluble fraction, several different research laboratories were able to identify ADP-ribose, derived from NAD+, as the incorporated group. Several years later, the enzymes responsible for this incorporation were identified and given the name poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase. Originally, this group was thought to be a linear sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups. In inorganic chemistry, the anion appears in a few rare minerals, but the functional group has tremendous importance in biochemistry. Disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins. Compounds of the form are usually called ''persulfides'' instead. Organic disulfides Structure Disulfides have a C–S–S–C dihedral angle approaching 90°. The S–S bond length is 2.03 Å in diphenyl disulfide, similar to that in elemental sulfur. Disulfides are usually symmetric but they can also be unsymmetric. Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organosulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton (unit)
The dalton or unified atomic mass unit (symbols: Da or u, respectively) is a unit of mass defined as of the mass of an Bound state, unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state and invariant mass, at rest. It is a Non-SI units mentioned in the SI, non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. The word "unified" emphasizes that the definition was accepted by both IUPAP and IUPAC. The atomic mass constant, denoted , is defined identically. Expressed in terms of , the atomic mass of carbon-12: . Its value in International System of Units, SI units is an experimentally determined quantity. The 2022 CODATA recommended value of the atomic mass constant expressed in the SI base unit kilogram is:This value serves as a Conversion of units, conversion factor of mass from daltons to kilograms, which can easily be converted to Gram, grams and other metric units of mass. The 2019 revision of the SI redefined the kilogram by fixing the value of the Planck constant (), i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat-labile Enterotoxin Family
In molecular biology, the heat-labile enterotoxin family includes ''Escherichia coli'' heat-labile enterotoxin (Elt or LT) and cholera toxin (Ctx) secreted by ''Vibrio cholerae''. lt is so named because it is inactivated at high temperatures. Mechanism The A subunits are transported inside by the pentameric B subunits. It then acts by raising cAMP levels through ADP-ribosylation of the alpha-subunit of a Gs protein leading to the constitutive activation of adenylate cyclase. Elevated cAMP levels stimulate the activation of the CFTR channel thus stimulating secretion of chloride ions and water from the enterocyte into the gut lumen. This ionic imbalance causes watery diarrhea. In addition to its effects on chloride secretion, which involve the same steps as the effects of cholera toxin, Elt binds additional substrates: lipopolysaccharide on the surface of ''E. coli'' cells and A-type blood antigens. The importance of these binding events is not yet known. Structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
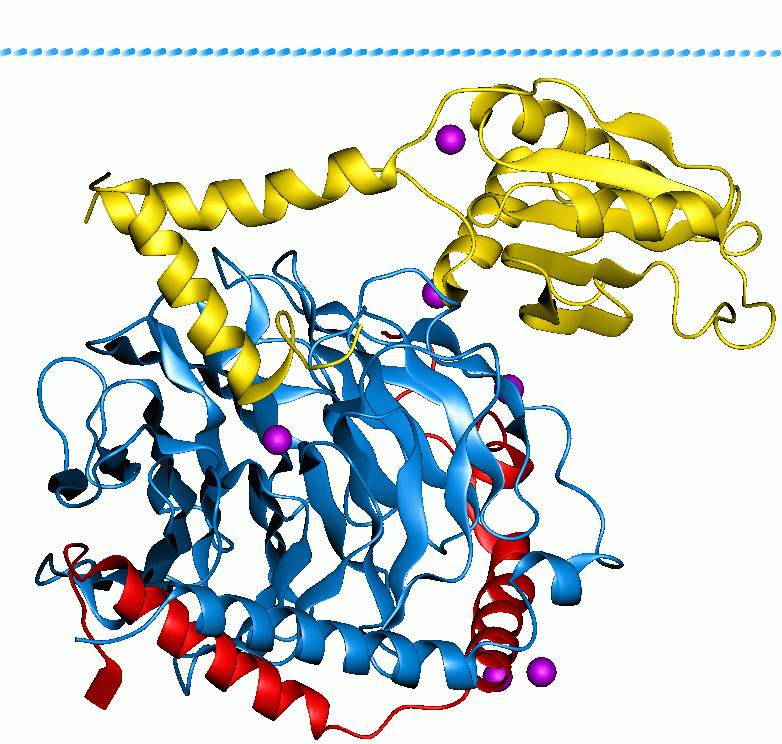
Cholera Toxin Structure
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea lasting a few days. Vomiting and muscle cramps may also occur. Diarrhea can be so severe that it leads within hours to severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. This can in turn result in Enophthalmia, sunken eyes, cold or cyanotic skin, decreased skin elasticity, wrinkling of the hands and feet, and, in severe cases, death. Symptoms start two hours to five days after exposure. Cholera is caused by a number of Serotype, types of ''Vibrio cholerae'', with some types producing more severe disease than others. It is spread mostly by Waterborne diseases, unsafe water and Foodborne illness, unsafe food that has been contaminated with human feces containing the bacteria. Undercooked shellfish is a common source. Humans are the only known host fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholera Vaccine
A cholera vaccine is a vaccine that is effective at reducing the risk of contracting cholera. The recommended cholera vaccines are administered orally to elicit local immune responses in the gut, where the intestinal cells produce antibodies against ''Vibrio cholerae'', the bacteria responsible for the illness. This immune response was poorly achieved with the injectable vaccines that were used until the 1970s. The first effective oral cholera vaccine was Dukoral, developed in Sweden in the 1980s. For the first six months after vaccination it provides about 85% protection, which decreases to approximately 60% during the first two years. When enough of the population is immunized, it may protect those who have not been immunized thereby increasing the total protective impact to more than 90 % (known as herd immunity). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of three oral cholera vaccines – Dukoral, Shanchol, and Euvichol-Plus – in combination with other mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 150 field offices worldwide. Only sovereign states are eligible to join, and it is the largest intergovernmental health organization at the international level. The WHO's purpose is to achieve the highest possible level of health for all the world's people, defining health as "a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." The main functions of the World Health Organization include promoting the control of epidemic and endemic diseases; providing and improving the teaching and training in public health, the medical treatment of disease, and related matters; and promoting the establishment of international standards for biologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |