|
Chins
The chin is the forward pointed part of the anterior mandible ( mental region) below the lower lip. A fully developed human skull has a chin of between 0.7 cm and 1.1 cm. Evolution The presence of a well-developed chin is considered to be one of the morphological characteristics of ''Homo sapiens'' that differentiates them from other human ancestors such as the closely related Neanderthals. Early human ancestors have varied symphysial morphology, but none of them have a well-developed chin. The origin of the chin is traditionally associated with the anterior–posterior breadth shortening of the dental arch or tooth row; however, its general mechanical or functional advantage during feeding, developmental origin, and link with human speech, physiology, and social influence are highly debated. Functional perspectives Robinson (1913) suggests that the demand to resist masticatory stresses triggered bone thickening in the mental region of the mandible and ultimately formed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th-century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by changes in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
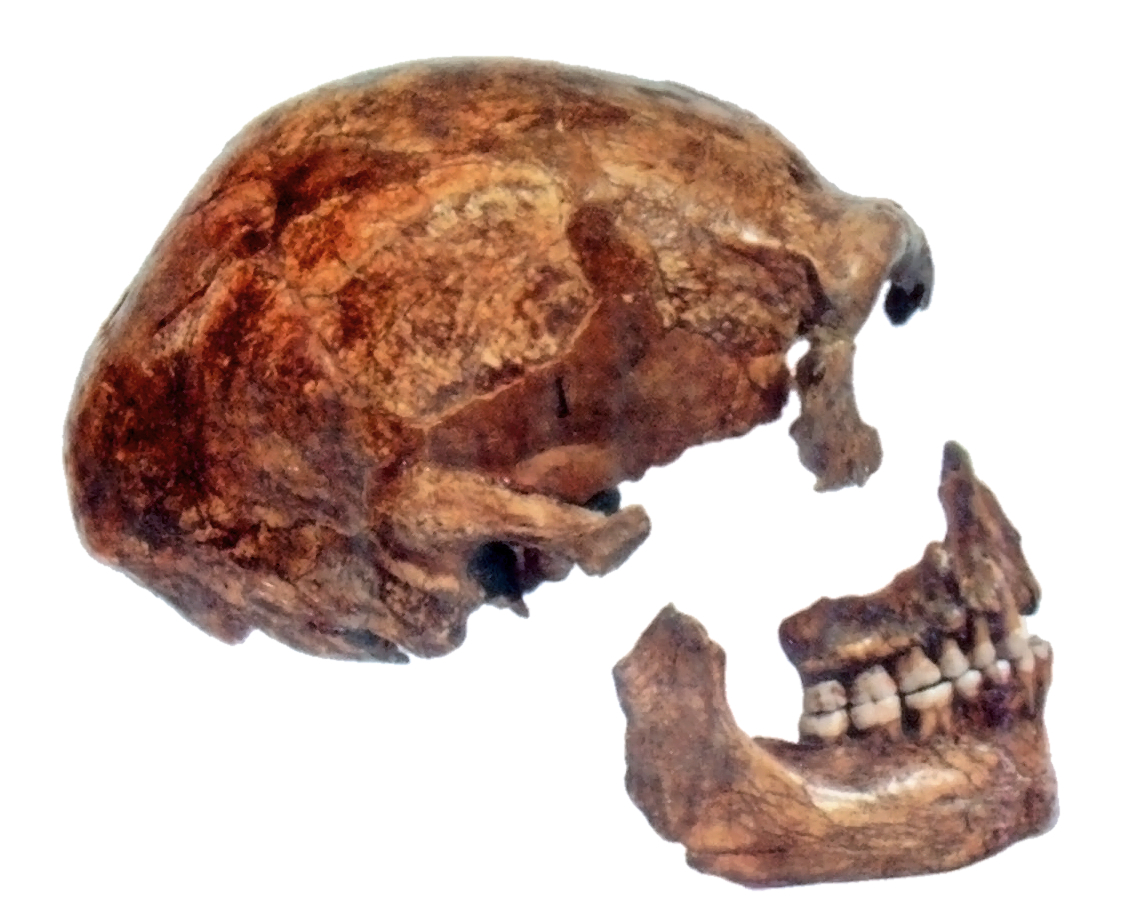
Neanderthal Anatomy
Neanderthal anatomy is characterised by a long, flat skull and a stocky body plan. When first discovered, Neanderthals were thought to be anatomically comparable to Aboriginal Australians, in accord with historical race concepts. As more fossils were discovered in the early 20th century, French palaeontologist Marcellin Boule defined them as a slouching, apelike species; a popular image until the middle of the century. Neanderthal features gradually accreted in European populations over the Chibanian, Middle Pleistocene, driven by natural selection in a cold climate, as well as genetic drift when populations crashed during glacial periods. This culminated in the "classical Neanderthal" anatomy by the Last Interglacial. The Neanderthal skull is distinctive by namely a rounded supraorbital torus (brow ridge), large orbit (anatomy), orbits (eye sockets) and nose, and an occipital bun at the back of the skull. The jaws and teeth are strong, which may have been a response to habitual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers and simians (monkeys and apes). Primates arose 74–63 million years ago first from small terrestrial animal, terrestrial mammals, which adapted for life in tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to the challenging environment among Canopy (biology), tree tops, including large brain sizes, binocular vision, color vision, Animal communication, vocalizations, shoulder girdles allowing a large degree of movement in the upper limbs, and opposable thumbs (in most but not all) that enable better grasping and dexterity. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Tubercle
The mandibular symphysis In human anatomy, the facial skeleton of the skull the external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the mandibular symphysis (Latin: ''symphysis menti'') or line of junction where the two lateral ha ... divides below and encloses a triangular eminence, the mental protuberance, the base of which is depressed in the center but raised on either side to form the mental tubercle. The two mental tubercles along with the medial mental protuberance are collectively called the mental trigone. References External links Diagram at face-and-emotion.com(Item #1) Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and Visual impairment, problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms Features that may result from a high level of GH or expanding tumor include: * Headaches * Enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, lips, and ears, and a general thickening of the skin * Soft tissue swelling of internal organs, notably the heart with the attendant weakening of its muscularity, and the kidneys, also the vocal cords resulting in a characteristic thick, deep voice and slowing of speech * Generalized expansion of the skull at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Symphysis
In human anatomy, the facial skeleton of the skull the external surface of the mandible is marked in the median line by a faint ridge, indicating the mandibular symphysis (Latin: ''symphysis menti'') or line of junction where the two lateral halves of the mandible typically fuse in the first year of life (6–9 months after birth). It is not a true symphysis as there is no cartilage between the two sides of the mandible. This ridge divides below and encloses a triangular eminence, the mental protuberance, the base of which is depressed in the center but raised on either side to form the mental tubercle. The lowest (most inferior) end of the mandibular symphysis — the point of the chin — is called the "menton". It serves as the origin for the geniohyoid and the genioglossus muscles. Other animals Solitary mammalian carnivores that rely on a powerful canine bite to subdue their prey have a strong mandibular symphysis, while pack hunters delivering shallow bites have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y-shape
Many shapes have metaphorical names, i.e., their names are metaphors: these shapes are named after a most common object that has it. For example, "U-shape" is a shape that resembles the letter U, a bell-shaped curve has the shape of the vertical cross section of a bell, etc. These terms may variously refer to objects, their cross sections or projections. Types of shapes Some of these names are "classical terms", i.e., words of Latin or Ancient Greek etymology. Others are English language constructs (although the base words may have non-English etymology). In some disciplines, where shapes of subjects in question are a very important consideration, the shape naming may be quite elaborate, see, e.g., the taxonomy of shapes of plant leaves in botany. * Astroid * Aquiline, shaped like an eagle's beak (as in a Roman nose) * Bell-shaped curve * Biconic shape, a shape in a way opposite to the hourglass: it is based on two oppositely oriented cones or truncated cones with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimple
A dimple, also called a gelasin (, ), and a fovea buccalis, is a small natural indentation in the flesh on a part of the human body, most notably in the cheek. Numerous cultures believe that cheek dimples are a good luck charm that entices people who perceive them as physically attractive, but they are also associated with heroism and innocence, which has been included in literature for many centuries. Medical research debates whether cheek dimples can be inherited or which type of allele they are, but it is certain that humans with cheek dimples are more likely to have them in both cheeks. Depth and length appearances are affected by the shape of the skull and dimples can appear and disappear due to age. There are four types of facial dimples, including cheek, and the cleft chin (sometimes nicknamed a "chin dimple"). Overview Cheek dimples when present, show up when a person makes a facial expression, such as smiling, whereas a chin dimple is a small line on the chin that stay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Jawbone Front
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |