|
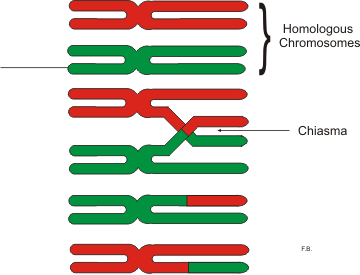
Chiasma (genetics)
In genetics, a chiasma (: chiasmata) is the point of contact, the physical link, between two (non-sister) chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes. At a given chiasma, an exchange of genetic material can occur between both chromatids, what is called a chromosomal crossover, but this is much more frequent during meiosis than mitosis. In meiosis, absence of a chiasma generally results in improper chromosomal segregation and aneuploidy. Points of crossing over become visible as chiasma after the synaptonemal complex dissembles and the homologous chromosomes slightly apart from each other. The phenomenon of genetic chiasmata (''chiasmatypie'') was discovered and described in 1909 by Frans Alfons Janssens, a Professor at the Catholic University of Leuven (1834–1968), University of Leuven in Belgium. Following synapsis, each homologous pair of synapsed chromosomes consists of four chromatids called a Tetrad (chromosomal formation), tetrad, this is referred to interchangeably a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis Crossover
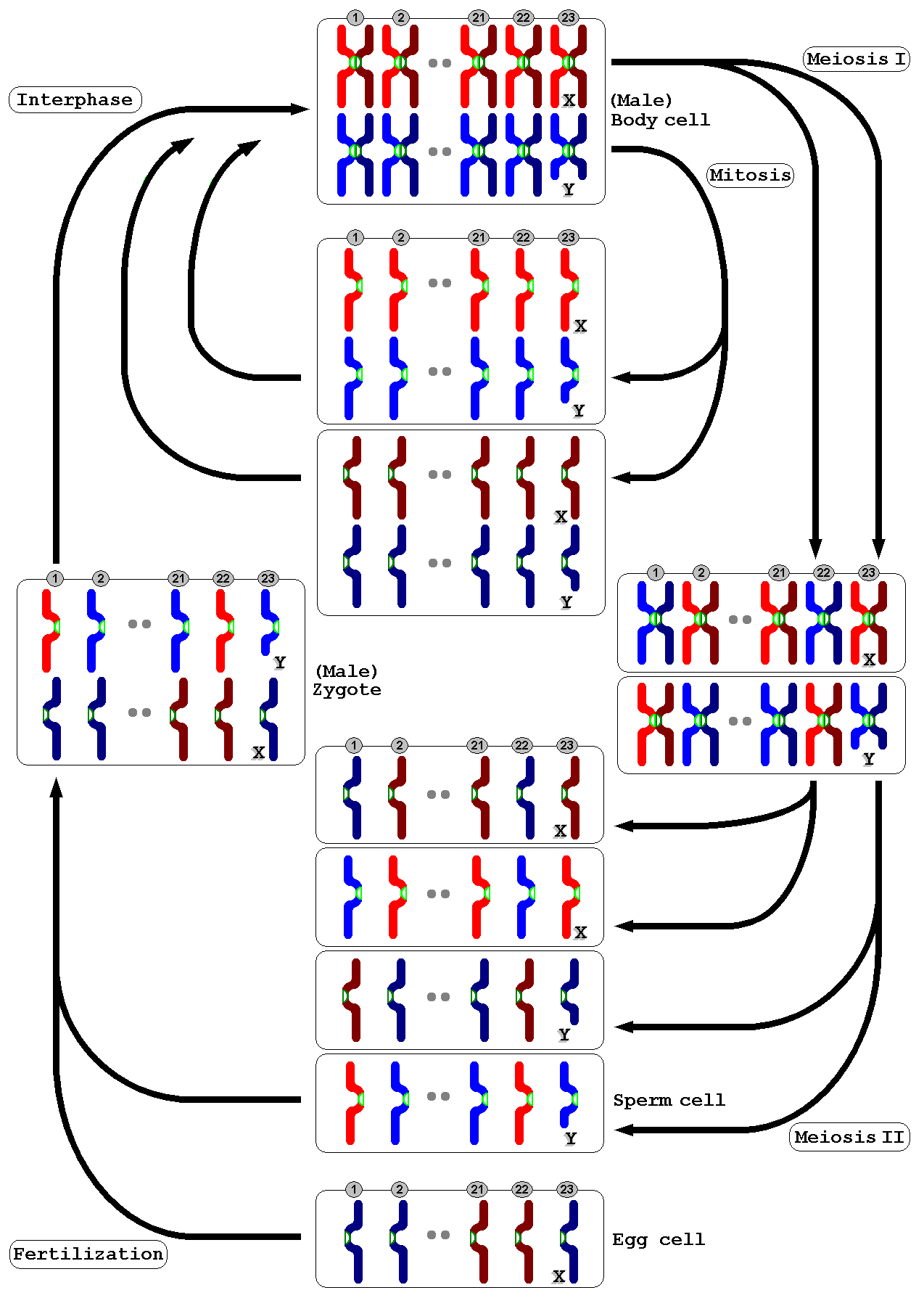
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in Sexual reproduction, sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is Chromosomal crossover, crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrad (chromosomal Formation)
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
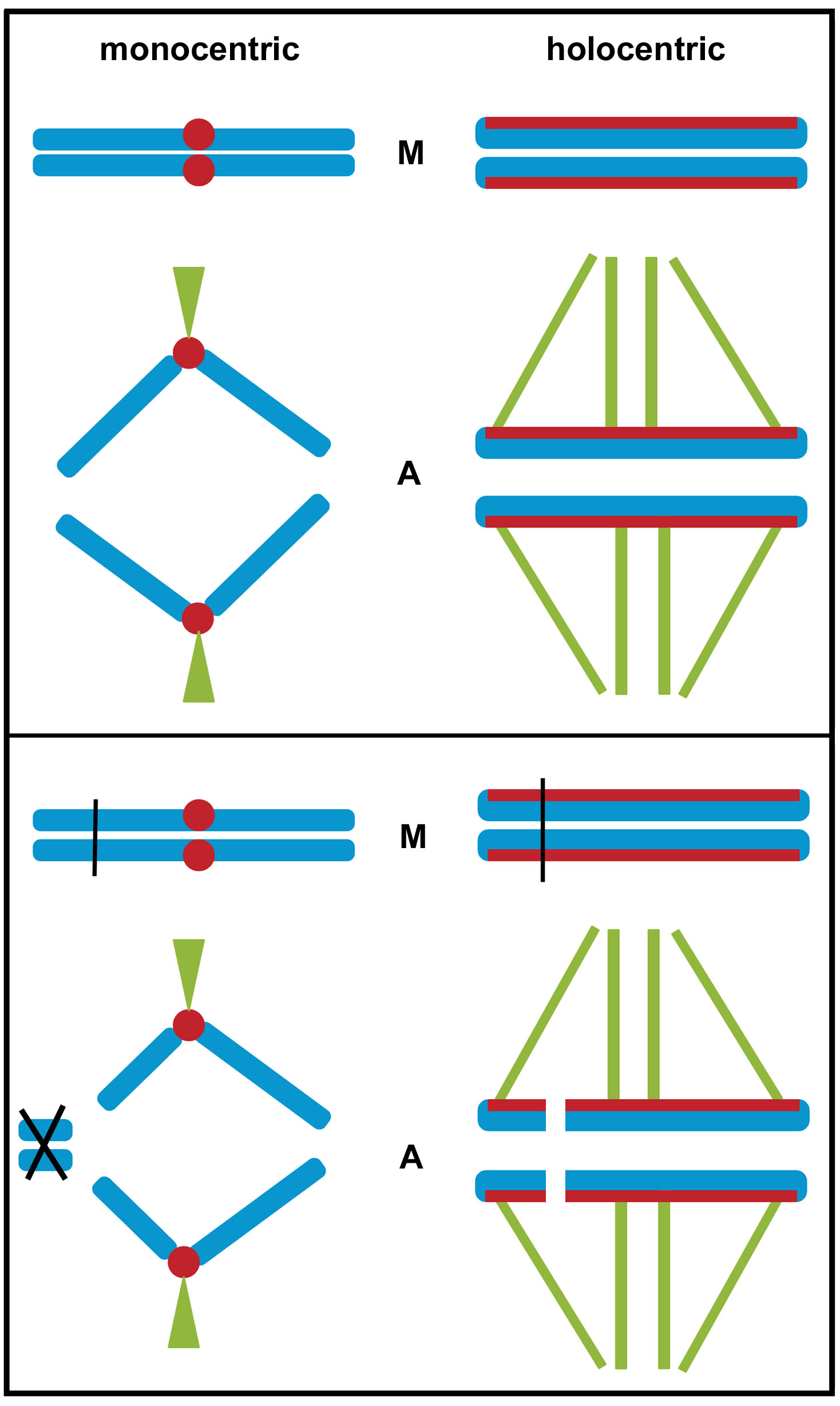
Holocentric Chromosome
Holocentric chromosomes are chromosomes that possess multiple kinetochores along their length rather than the single centromere typical of other chromosomes. They were first described in cytogenetic experiments in 1935. Since this first observation, the term holocentric chromosome has referred to chromosomes that: i) lack the primary constriction corresponding to the centromere observed in monocentric chromosomes; and ii) possess multiple kinetochores dispersed along the entire chromosomal axis, such that microtubules bind to the chromosome along its entire length and move broadside to the pole from the metaphase plate. Holocentric chromosomes are also termed ''holokinetic'', because, during cell division, the sister chromatids move apart in parallel and do not form the classical V-shaped figures typical of monocentric chromosomes. Holocentric chromosomes have evolved several times during both animal and plant evolution, and are currently reported in about eight hundred diverse spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Crossover
Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes' sister chromatids, non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs in the ''pachytene'' stage of prophase I of meiosis during a process called synapsis. Synapsis is usually initiated before the synaptonemal complex develops and is not completed until near the end of prophase I. Crossover usually occurs when matching regions on matching chromosomes break and then reconnect to the other chromosome, resulting in Chiasma (genetics), chiasma which are the visible evidence of crossing over. History of discovery Crossing over was described, in theory, by Thomas Hunt Morgan; the term crossover was coined by Morgan and Eleth Cattell. Hunt relied on the discovery of Frans Alfons Janssens who described the phenomenon in 1909 and had called it "chiasmatypie". Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryotes, genetic recombination during meiosis can lead to a novel set of genetic information that can be further passed on from parents to offspring. Most recombination occurs naturally and can be classified into two types: (1) ''interchromosomal'' recombination, occurring through independent assortment of alleles whose loci are on different but homologous chromosomes (random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I); & (2) ''intrachromosomal'' recombination, occurring through crossing over. During meiosis in eukaryotes, genetic recombination involves the pairing of homologous chromosomes. This may be followed by information transfer between the chromosomes. The information transfer may occur without physical exchange (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy vacuum ultraviolet, ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation; whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. Nearly all types of laser light are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area cannot be sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at Ionization energies of the elements (data page), different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanoplus Femurrubrum
''Melanoplus femurrubrum'', the red-legged grasshopper, is a species of grasshopper belonging to the genus ''Melanoplus''. It is one of the most common grasshoppers found in Mexico, the United States, and Canada. This grasshopper is frequently used as a model organism in scientific studies, due to their abundance throughout North America and behavioral response to changes in climate. Identification ''Melanoplus femurrubrum'' is a medium-sized grasshopper, in which males can range in length from – , whereas females can range from – long. This grasshopper has a reddish-brown back, a greenish-yellow belly, and red hind tibiae, hence its specific name ''femurrubrum'' (''femur'' = thigh, ''rubrum'' = red). Wings of ''M. femurrubrum'' typically extend beyond the tip of the abdomen. Males have an enlarged abdomen, with a U-shaped sub-genital plate. Habitat ''Melanoplus femurrubrum'' can be found in a variety of habitats found throughout most of North America, but prefer grassl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
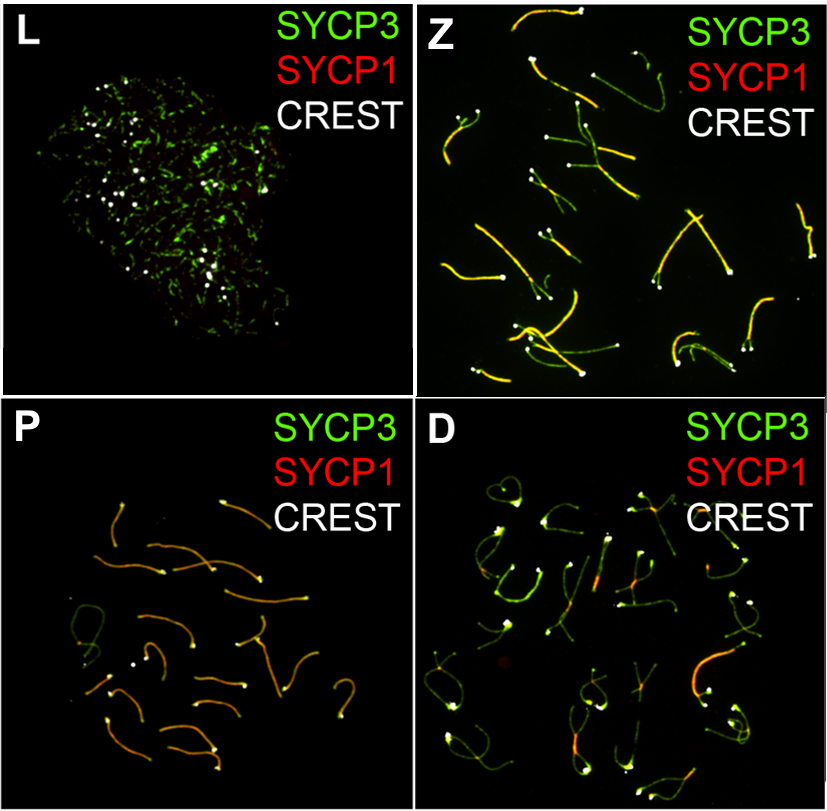
Pachytene
The ''pachytene'' stage ( /ˈpækɪtiːn/ ''PAK-i-teen''; from Greek words meaning "thick threads".), also known as ''pachynema'', is the third stage of prophase I during meiosis, the specialized cell division that reduces chromosome number by half to produce haploid gametes. It follows the zygotene stage and is followed by the stage Diplotene Synapsed chromosomes During pachytene, the homologous chromosomes are fully synapsed along their lengths by the completed synaptonemal complex protein structure formed in the previous stages. This holds the homologous closely paired, allowing intimate DNA interactions. Chromosome condensation The chromosomes reach their highest level of condensation during pachytene. Each chromosome consists of two closely associated sister chromatids along their entire length. The chromosomes appear as distinct, well-defined threadlike structures under the microscope. Sex chromosomes, however, are not wholly identical, and only exchange information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplotene
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
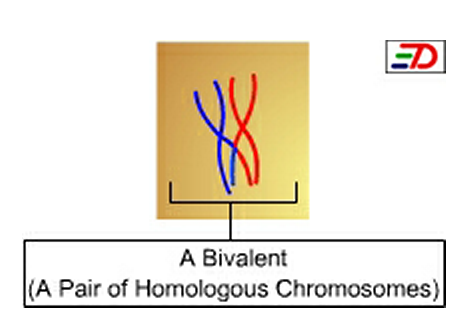
Bivalent (genetics)
In cellular biology, a bivalent is one pair of chromosomes (homologous chromosomes) in a tetrad. A tetrad is the association of a pair of homologous chromosomes (4 sister chromatids) physically held together by at least one DNA crossover. This physical attachment allows for alignment and segregation of the homologous chromosomes in the first meiotic division. In most organisms, each replicated chromosome (composed of two identical sisters chromatid) elicits formation of DNA double-strand breaks during the leptotene phase. These breaks are repaired by homologous recombination, that uses the homologous chromosome as a template for repair. The search for the homologous target, helped by numerous proteins collectively referred as the synaptonemal complex, cause the two homologs to pair, between the leptotene and the pachytene phases of meiosis I. Formation The formation of a bivalent occurs during the first division of meiosis (in the zygotene stage of meiotic prophase 1). In mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapsis
Synapsis or Syzygy is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I of meiosis. When homologous chromosomes synapse, their ends are first attached to the nuclear envelope. These end-membrane complexes then migrate, assisted by the extranuclear cytoskeleton, until matching ends have been paired. Then the intervening regions of the chromosome are brought together, and may be connected by a protein-DNA complex called the synaptonemal complex (SC). The SC protein scaffold stabilizes the physical pairing of homologous chromosomes by polymerizing between them during meiotic prophase. During synapsis, autosomes are held together by the synaptonemal complex along their whole length, whereas for sex chromosomes, this only takes place at one end of each chromosome. This is not to be confused with mitosis. Mitosis also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |