|
Chemoprophylaxis For Tuberculosis
Chemoprevention or chemoprophylaxis refers to the administration of a medication for the purpose of preventing disease or infection. Antibiotics, for example, may be administered to patients with disorders of immune system function to prevent bacterial infections (particularly opportunistic infection). Antibiotics may also be administered to healthy individuals to limit the spread of an epidemic, or to patients who have repeated infections (such as urinary tract infections) to prevent recurrence. It may also refer to the administration of heparin to prevent deep venous thrombosis in hospitalized patients. In some cases, chemoprophylaxis is initiated to prevent the spread of an existing infection in an individual to a new organ system, as when intrathecal chemotherapy is administered in patients with malignancy to prevent further infection. The use of chemoprophylaxis is limited primarily by two factors: risk and financial costs. * All medications have the potential to cause side e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medicine, medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are Drug class, classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of controlled substance, control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
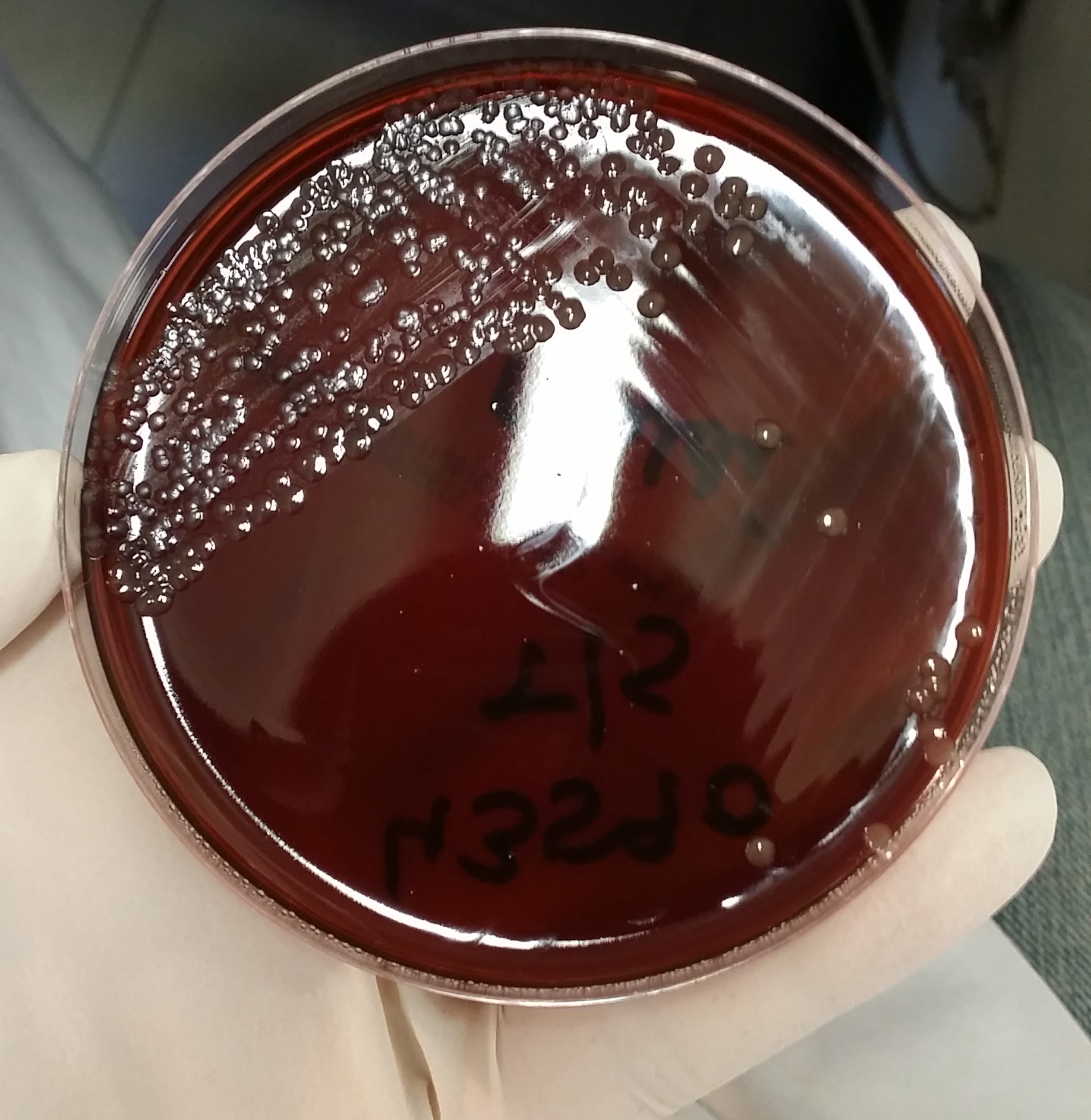
Neisseria Meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carriers of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen, it causes developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly in Africa and Asia. It occurs worldwide in both epidemic and endemic form. ''N. meningitidis'' is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, chewing on toys and through sharing a source of fresh water. It has also been reported to be Sexually transmitted infection, transmitted through oral sex and cause urethritis in men. It infects its hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statin
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. As lipid-lowering medications, statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol; they are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes, and abnormal blood levels of certain liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage, and very rarely rhabdomyolysis. They act by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspirin
Aspirin () is the genericized trademark for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk. For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes. Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. One common adverse effect is an upset stomach. More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma. Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on other blood thinners. Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy. It is not generally recommended in children with infections ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Prevention
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health and efficiency. Leavell, H. R., & Clark, E. G. (1979). Preventive Medicine for the Doctor in his Community (3rd ed.). Huntington, NY: Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company. Disease and disability are affected by environmental factors, genetic predisposition, disease agents, and lifestyle choices, and are dynamic processes that begin before individuals realize they are affected. Disease prevention relies on anticipatory actions that can be categorized as primal, primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Each year, millions of people die of preventable causes. A 2004 study showed that about half of all deaths in the United States in 2000 were due to preventable behaviors and exposures. Leading causes included cardiovascular disease, chron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors. The primary cause of skin cancer is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning devices. Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed form of cancer in humans. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC), squamous-cell skin cancer (SCC) and melanoma. The first two, along with a number of less common skin cancers, are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it but is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin that may be shiny with telangiectasia, small blood vessels running over it or may present as a raised area wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metformin
Metformin, sold under the brand name Glucophage, among others, is the main first-line medication for the treatment of type2 diabetes, particularly in people who are overweight. It is also used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome, and is sometimes used as an off-label adjunct to lessen the risk of metabolic syndrome in people who take antipsychotic medication. It has been shown to inhibit inflammation, and is not associated with weight gain. Metformin is taken by mouth. Metformin is generally well tolerated. Common adverse effects include diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. It has a small risk of causing low blood sugar. High blood lactic acid level (acidosis) is a concern if the medication is used in overly large doses or prescribed in people with severe kidney problems. Metformin is a biguanide anti- hyperglycemic agent. It works by decreasing glucose production in the liver, increasing the insulin sensitivity of body tissues, and increasing GDF15 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anand Reddi
Anand Reddi is a global health policy expert, public health advocate and biopharma executive. Reddi works on health system strengthening initiatives with a focus on global health, implementation science, health financing and public health advocacy. A major focus of scholarship is global HIV scale-up including the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR). Since 2014, his focus has shifted to public-private global health partnerships to support access to essential medicines between by the biopharma private sector. He served on the board of directors of the AIDS Healthcare Foundation from 2009 to 2011 and was a founding member of the board of directors of the Bay Area Global Health Alliance. Early life and education Reddi pursued his undergraduate studies at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor and a medical degree at the University of Colorado School of Medicine. He was a Fulbright Scholar to KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, focusing on pediatric antiretroviral scale-up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael B
Michael may refer to: People * Michael (given name), a given name * he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect)">Michael (surname)">he He ..., a given name * Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael Given name * Michael (bishop elect), English 13th-century Bishop of Hereford elect * Michael (Khoroshy) (1885–1977), cleric of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church of Canada * Michael Donnellan (fashion designer), Michael Donnellan (1915–1985), Irish-born London fashion designer, often referred to simply as "Michael" * Michael (footballer, born 1982), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1993), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born February 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born March 1996), Brazilian footballer * Michael (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian football ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GiveWell
GiveWell is an American non-profit charity assessment and effective altruism-focused organization. GiveWell focuses primarily on the cost-effectiveness of the organizations that it evaluates, rather than traditional metrics such as the percentage of the organization's budget that is spent on overhead. History In 2006, Holden Karnofsky and Elie Hassenfeld, who worked at a hedge fund in Connecticut, formed an informal group with colleagues to evaluate charities based on data and performance metrics similar to those they used at the fund, and were surprised to find the data often didn't exist. The next year, Karnofsky and Hassenfeld formed GiveWell as a nonprofit to provide financial analyst services to donors. They eventually decided to rate charities based on the metric of how much money it cost to save a life. In the first year, funding to run the nonprofit was provided by a fund called the Clear Fund into which the former members of informal club, now directors of GiveWell, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |