|
Chemical Safety
Chemical safety includes all safety policies, procedures and practices designed to minimize the risk of exposure to potentially hazardous chemicals. This includes the risks of exposure to persons handling the chemicals, to the surrounding environment, and to the communities and ecosystems within that environment. Manufactured chemicals, either pure or in mixtures, solutions and emulsions, are ubiquitous in modern society, at industrial, occupational and private scale. However, there are chemicals that should not mix or get in contact with others, as they can produce byproducts that may be toxic, carcinogenic, explosive etc., or can be dangerous in themselves. To avoid disasters and mishaps, maintaining safety is paramount. Chemical safety refers to safety issues surrounding the use, production, transport and handling of chemicals at large or small manufacturing facilities, laboratories, non-chemical sites that use manufactured chemicals for their business, or homes during everyday a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety
Safety is the state of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk. Meanings The word 'safety' entered the English language in the 14th century. It is derived from Latin , meaning uninjured, in good health, safe. There are two slightly different meanings of "safety". For example, " home safety" may indicate a building's ability to protect against external harm events (such as weather, home invasion, etc.), or may indicate that its internal installations (such as appliances, stairs, etc.) are safe (not dangerous or harmful) for its inhabitants. Discussions of safety often include mention of related terms. Security is such a term. With time the definitions between these two have often become interchanged, equated, and frequently appear juxtaposed in the same sentence. Readers are left to conclude whether they comprise a redundancy. This confuses the uniqueness that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health And Safety At Work Etc
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, pain (including mental pain), or injury. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive stress. Some factors affecting health are due to individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are beyond both individual and group choices, such as genetic disorders. History The meaning of health has evolved over time. In keeping with the biomedical perspective, early definit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WorkSafe New Zealand
WorkSafe is New Zealand's primary workplace health and safety regulator. WorkSafe has over 550 staff based across New Zealand who work to lift New Zealand's health and safety performance and support workers to return home healthy and safe. WorkSafe's role As the regulator of the workplace health and safety system, WorkSafe has three key roles: Regulatory confidence * Undertaking regulatory activity to provide confidence that New Zealand workplaces are appropriately managing health and safety * Enabling New Zealand to have confidence in WorkSafe as the primary health and safety regulator * Supporting confidence in the effectiveness of the health and safety regulatory regime. Harm prevention * Targeting critical risks at all levels (sector and system-wide) using intelligence * Delivering targeted interventions to address harm drivers (including workforce capability, worker engagement and effective governance) * Influencing attitudes and behaviour to improve health and safety r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health And Safety At Work (Hazardous Substances) Regulations 2017
The Health and Safety at Work (Hazardous Substances) Regulations 2017 is a New Zealand statutory instrument made under the provisions of the Health and Safety at Work Act 2015. The regulations set out controls on the use and management of a wide range of general and specific substances, how they may be used and stored and the penalties for failing to comply general requirements imposed on employers to protect employees and other persons from the hazards of substances used at work by risk assessment, control of exposure, health surveillance and incident planning. There are also duties on employees to take care of their own exposure to hazardous substances. It define ''hazardous'' as ''Hazardous substance means, unless expressly provided otherwise by regulations or an EPA notice, any substance'' ''(a) with 1 or more of the following intrinsic properties, (i) explosiveness , (ii) flammability, (iv) corrosiveness, (v) toxicity (including chronic toxicity), (vi) ecotoxicity, with or w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
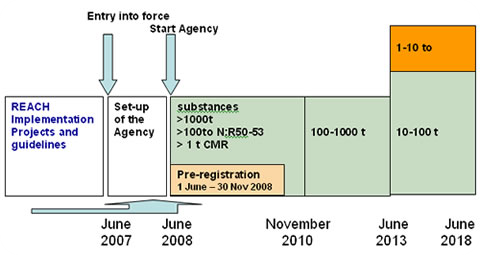
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation And Restriction Of Chemicals
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH. Overview When REACH is fully in force, it will require all companies manufacturing or importing chemical substances into the European Union in quantities of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Chemicals Agency
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA; ) is an agency of the European Union working for the safe use of chemicals. It manages the technical and administrative aspects of the implementation of the European Union regulation called Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). ECHA is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's chemicals legislation. ECHA has to ascertain that companies comply with the legislation, advances the safe use of chemicals, provides information on chemicals and addresses chemicals of concern. It is located in Helsinki, Finland and is operational since 2007. ECHA is an independent and mature regulatory agency established by REACH. It is not a subsidiary entity of the European Commission. The agency is headed by Executive Director Sharon McGuinness. Establishment The ECHA was created by European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006 to manage the then-new legislation to regulate the manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directive 89/391/EEC
Directive 89/391/EEC is a European Union directive with the objective to introducing measures to encourage improvements in the safety and health of workers at work. It is described as a "Framework Directive" for occupational safety and health (OSH) by the European Agency for Safety and Health at Work. History and effect The proposal for the directive was adopted by the European Commission on 24 February 1988 and transmitted to the European Parliament and the Council of the European Union, which consulted the European Economic and Social Committee. The proposal was approved with amendments in the first and second readings by the European Parliament, after which the Commission adopted amended proposals. The Council approved the re-examined proposal on 12 June 1989. Directive 89/391/EEC entered into force on 19 June 1989 and member states were obligated to bring into force laws, regulations and administrative provisions to comply with it by 31 December 1992. The directive was amend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as earthworms and woodlice), or decomposer (such as fungi or bacteria). It is not the same as a food web. A food chain depicts relations between species based on what they consume for energy in trophic levels, and they are most commonly quantified in length: the number of links between a trophic consumer and the base of the chain. Food chain studies play an important role in many biological studies. Food chain stability is very important for the survival of most species. When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction or immense decreases of survival of a species. Many food chains and food webs contain a keystone species, a species that has a large impact on the surrounding environment and that can directly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Organic Pollutant
Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are organic compounds that are resistant to degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes. They are toxic and adversely affect human health and the environment around the world. Because they can be transported by wind and water, most POPs generated in one country can and do affect people and wildlife far from where they are used and released. The effect of POPs on human and environmental health was discussed, with intention to eliminate or severely restrict their production, by the international community at the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001. Most POPs are pesticides or insecticides, and some are also solvents, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals. Although some POPs arise naturally (e.g. from volcanoes), most are man-made. The "dirty dozen" POPs identified by the Stockholm Convention include aldrin, chlordane, dieldrin, endrin, heptachlor, HCB, mirex, toxaphene, PCBs, DDT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. The most common example of a CFC is dichlorodifluoromethane (R-12). R-12, also commonly called Freon, is used as a refrigerant. Many CFCs have been widely used as refrigerants, propellants (in aerosol applications), gaseous fire suppression systems, and solvents. As a result of CFCs contributing to ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere, the manufacture of such compounds has been phased out under the Montreal Protocol, and they are being replaced with other products such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) including R-410A, R-134a and 2,3,3,3-Tetrafluoropropene, R-1234yf. Structure, properties and production As in simpler alkanes, carbons in CFCs bond with tetrahe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lower atmosphere to (dioxygen). Ozone is formed from dioxygen by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges within the Earth's atmosphere. It is present in very low concentrations throughout the atmosphere, with its highest concentration high in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, which absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Ozone's odor is reminiscent of chlorine, and detectable by many people at concentrations of as little as in air. Ozone's O3 chemical structure, structure was determined in 1865. The molecule was later proven to have a bent structure and to be weakly diamagnetism, diamagnetic. At standard temperature and pressure, ozone is a pale blue gas that condenses at cryogenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |