|
Chatbots
A chatbot (originally chatterbot) is a software application or web interface designed to have textual or spoken conversations. Modern chatbots are typically online and use generative artificial intelligence systems that are capable of maintaining a conversation with a user in natural language and simulating the way a human would behave as a conversational partner. Such chatbots often use deep learning and natural language processing, but simpler chatbots have existed for decades. Although chatbots have existed since the late 1960s, the field gained widespread attention in the early 2020s due to the popularity of OpenAI's ChatGPT, followed by alternatives such as Microsoft's Copilot, DeepSeek and Google's Gemini. Such examples reflect the recent practice of basing such products upon broad foundational large language models, such as GPT-4 or the Gemini language model, that get fine-tuned so as to target specific tasks or applications (i.e., simulating human conversation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini (chatbot)
Gemini, formerly known as Bard, is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by Google. Based on the large language model (LLM) Gemini (language model), of the same name, it was launched in 2023 in response to the rise of OpenAI's ChatGPT. It was previously based on the LaMDA and PaLM LLMs. Google's LaMDA, which was announced and developed in 2021, was kept under wraps for fear. OpenAI's unexpected triumph with ChatGPT in November 2022, though, spurred Google to quickly get its employees mobilized and react. This resulted in the partial roll-out of Bard in March 2023, and then to other nations in May. Bard became popular at the 2023 Google I/O keynote and subsequently upgraded to the Gemini LLM in December. In February 2024, Google brought Bard and Duet AI under the same Gemini brand, introducing an Android app. Background In November 2022, OpenAI launched ChatGPT, a chatbot based on the GPT-3 family of large language models (LLMs). ChatGPT gained worldwide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by OpenAI and released on November 30, 2022. It uses large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4o as well as other Multimodal learning, multimodal models to create human-like responses in text, speech, and images. It has access to features such as searching the web, using apps, and running programs. It is credited with accelerating the AI boom, an ongoing period of rapid investment in and public attention to the field of artificial intelligence (AI). Some observers have raised concern about the potential of ChatGPT and similar programs to displace human intelligence, enable plagiarism, or fuel misinformation. ChatGPT is built on OpenAI's proprietary series of generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) models and is Fine-tuning (machine learning), fine-tuned for conversational applications using a combination of supervised learning and reinforcement learning from human feedback. Successive user AI prompt, prompts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
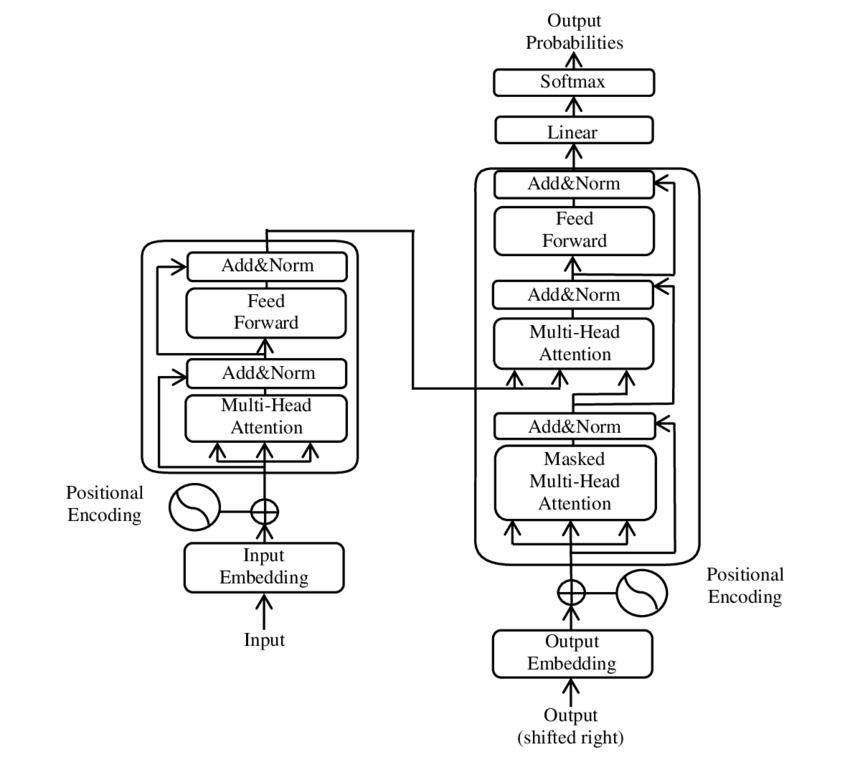
Large Language Models
A large language model (LLM) is a language model trained with Self-supervised learning, self-supervised machine learning on a vast amount of text, designed for natural language processing tasks, especially Natural language generation, language generation. The largest and most capable LLMs are Generative pre-trained transformer, generative pretrained transformers (GPTs), which are largely used in Generative artificial intelligence, generative Chatbot, chatbots such as ChatGPT or Gemini (chatbot), Gemini. LLMs can be Fine-tuning (deep learning), fine-tuned for specific tasks or guided by prompt engineering. These models acquire Predictive learning, predictive power regarding syntax, semantics, and Ontology (information science), ontologies inherent in human Text corpus, language corpora, but they also inherit inaccuracies and Algorithmic bias, biases present in the Training, validation, and test data sets, data they are trained in. History Before the emergence of transformer-bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Copilot
Microsoft Copilot (or simply Copilot) is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot developed by Microsoft. Based on the GPT-4 series of large language models, it was launched in 2023 as Microsoft's primary replacement for the discontinued Cortana (virtual assistant), Cortana. The service was introduced in February 2023 under the name ''Bing Chat'', as a built-in feature for Microsoft Bing and Microsoft Edge. Over the course of 2023, Microsoft began to unify the ''Copilot'' branding across its various chatbot products, cementing the "copilot" analogy. At its Microsoft Build#2023, Build 2023 conference, Microsoft announced its plans to integrate Copilot into Windows 11, allowing users to access it directly through the taskbar. In January 2024, a dedicated Copilot key was announced for Windows keyboards. Copilot utilizes the Microsoft Prometheus model, built upon OpenAI's GPT-4 foundational large language model, which in turn has been Fine-tuning (deep learning), fine-tuned us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Customer Service
Customer service is the assistance and advice provided by a company to those who buy or use its products or services, either in person or remotely. Customer service is often practiced in a way that reflects the strategies and values of a firm, and levels vary according to the industry. Good quality customer service is usually measured through customer retention. Successful customer service interactions are dependent on employees "who can adjust themselves to the personality of the customer". Customer service for some firms is part of the firm's intangible assets and can differentiate it from others in the industry. One good customer service experience can change the entire perception a customer holds towards the organization. It is expected that AI-based chatbots will significantly impact customer service and call centre roles and will increase productivity substantially. Many organisations have already adopted AI chatbots to improve their customer service experience.Krishnan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Artificial Intelligence
Generative artificial intelligence (Generative AI, GenAI, or GAI) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that uses generative models to produce text, images, videos, or other forms of data. These models Machine learning, learn the underlying patterns and structures of their training data and use them to produce new data based on the input, which often comes in the form of natural language Prompt (natural language), prompts. Generative AI tools have become more common since an "AI boom" in the 2020s. This boom was made possible by improvements in transformer (machine learning model), transformer-based deep learning, deep neural networks, particularly large language models (LLMs). Major tools include chatbots such as ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, Copilot, Gemini (chatbot), Gemini, Grok (chatbot), Grok, and DeepSeek (chatbot), DeepSeek; text-to-image models such as Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL-E; and text-to-video models such as Sora (text-to-video model), Sora and Veo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Assistant
A virtual assistant (VA) is a software agent that can perform a range of tasks or services for a user based on user input such as commands or questions, including verbal ones. Such technologies often incorporate chatbot capabilities to streamline task execution. The interaction may be via text, graphical interface, or voice - as some virtual assistants are able to interpret human speech and respond via synthesized voices. In many cases, users can ask their virtual assistants questions, control home automation devices and media playback, and manage other basic tasks such as email, to-do lists, and calendars - all with verbal commands. In recent years, prominent virtual assistants for direct consumer use have included Apple's Siri, Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Samsung's Bixby. Also, companies in various industries often incorporate some kind of virtual assistant technology into their customer service or support. Into the 2020s, the emergence of artificial intelligence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeepSeek (chatbot)
DeepSeek is a generative artificial intelligence chatbot by the Chinese company DeepSeek. Released on 10 January 2025, DeepSeek-R1 surpassed ChatGPT as the most downloaded freeware app on the iOS App Store in the United States by 27 January. DeepSeek's success against larger and more established rivals has been described as "upending AI" and initiating "a global AI space race". DeepSeek's compliance with Chinese government censorship policies and its data collection practices have also raised concerns over privacy and information control in the model, prompting regulatory scrutiny in multiple countries. However, it has also been praised for its open weights and infrastructure code, energy efficiency and contributions to open-source artificial intelligence. History On 10 January 2025, DeepSeek released the chatbot, based on the DeepSeek-R1 model, for iOS and Android. By 27 January, DeepSeek-R1 surpassed ChatGPT as the most-downloaded freeware app on the iOS App Store in the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELIZA
ELIZA is an early natural language processing computer program developed from 1964 to 1967 at MIT by Joseph Weizenbaum. Created to explore communication between humans and machines, ELIZA simulated conversation by using a pattern matching and substitution methodology that gave users an illusion of understanding on the part of the program, but had no representation that could be considered really understanding what was being said by either party. Whereas the ELIZA program itself was written (originally) in MAD-SLIP, the pattern matching directives that contained most of its language capability were provided in separate "scripts", represented in a lisp-like representation. The most famous script, DOCTOR, simulated a psychotherapist of the Rogerian school (in which the therapist often reflects back the patient's words to the patient), and used rules, dictated in the script, to respond with non-directional questions to user inputs. As such, ELIZA was one of the first chatterbots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1949,. Turing wrote about the ‘imitation game’ centrally and extensively throughout his 1950 text, but apparently retired the term thereafter. He referred to ‘ istest’ four times—three times in pp. 446–447 and once on p. 454. He also referred to it as an ‘experiment’—once on p. 436, twice on p. 455, and twice again on p. 457—and used the term ‘viva voce’ (p. 446). See also #Versions, below. Turing gives a more precise version of the question later in the paper: " ese questions reequivalent to this, 'Let us fix our attention on one particular digital computer C. Is it true that by modifying this computer to have an adequate storage, suitably increasing its speed of action, and providing it with an appropriate programme, C can be made to play satisfactorily the part of A in the imitation game, the part of B being taken by a man? is a test of a machine's ability to exhibit intellige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AI Boom
The AI boom is an ongoing period of rapid Progress in artificial intelligence, progress in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) that started in the late 2010s before gaining international prominence in the early 2020s. Examples include large language models and generative AI applications developed by OpenAI as well as Protein structure prediction, protein folding prediction led by Google DeepMind. This period is sometimes referred to as an AI spring, to contrast it with previous AI winters. History In 2012, a University of Toronto research team used artificial neural networks and deep learning techniques to lower the error rate below 25% for the AlexNet, first time during the ImageNet challenge for object recognition in computer vision. The event catalyzed the AI boom later that decade, when many alumni of the ImageNet challenge became leaders in the tech industry. In March 2016, AlphaGo beat Lee Sedol in AlphaGo versus Lee Sedol, a five-game match, marking the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |