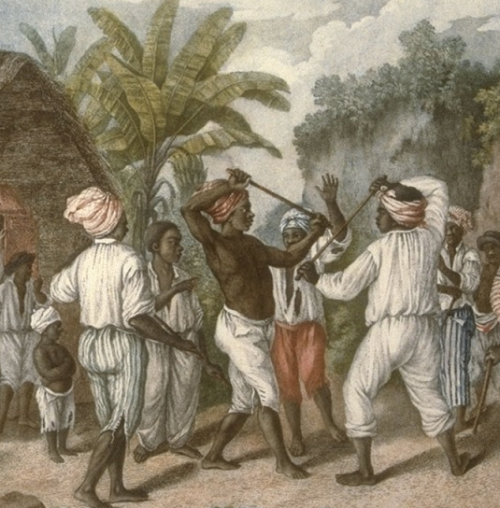|
Chantwell
As early as the 1780s, the word kaiso was used to describe a French creole song and, in Trinidad, kaiso seems to have been perfected by the chantwells (singers, mostly female) during the first half of the 19th centurThe chantwells, assisted by alternating in call-and-response style with a chorus, were a central component of the practice called Calinda (stick-fighting). Calinda was a central component of early carnival celebrations in Trinidad, and after emancipation (1834), Afro- Creoles essentially took over the streets during carnival. Elite French Creole revellers, for their part, moved their carnival celebrations indoors and to private parties. Kaiso used satirical and insulting lyrics, and is related to the picong tradition. Kaiso singers, called chantwells, sang primarily in French creole. Chantwells The "chantwell" is another incarnation of the African "griot" tradition. On the Caribbean plantations African griots became chantwells, preserving the tribe’s history and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calypsonian
A calypsonian, originally known as a ''chantwell'', is a musician from the anglophone Caribbean who sings songs of the Calypso music, calypso genre. Calypsos are musical renditions having their origins in the West African griot tradition. Originally called "Kaiso" in Trinidad, these songs, based on West African Yoruba music, Yoruba, Ewe music, Ewe-Fon and Akan people, Akan musical beats, were sung by slaves and later ex-slaves in Trinidad and Tobago during recreation time and about a host of topics – their land of origin, social relationships on the plantations and the lives of community members, including plantation managers, overseers and owners. Traditionalists see calypso as Women in Trinidad and Tobago#Role of Music in Gender Performance, social commentary because in earlier years it served the purpose of telling stories, relaying news events and giving criticisms of persons and policy. Calypso was therefore divided into two classes: the social commentaries, which had son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rapso
Rapso is a form of Trinidadian music that grew out of the social unrest of the 1970s. Black Power and unions grew in the 1970s, and rapso grew along with them. The first recording was "Blow 'Way" by Lancelot Layne in 1970. Six years later, Cheryl Byron (founder of the New York City based Something Positive Dance Company) was scorned when she sang rapso at a calypso tent. She is now called the "Mother of Rapso". It has been described as "". Though often described as a fusion of native soca and calypso with American hip hop, rapso is uniquely Trinidadian. History Rapso music is itself an evolution of the chantwell or griot tradition of African music in the diaspora. It is called "the poetry of Calypso" and "". Rapso is the poetic "rap" form of Trinbagonian music—the next evolutionary step of Calypso and Soca music. It also has origins in the oral tradition elements of the performances of traditional masquerade characters in Trinidad Carnival. Traditional masquerade ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calypso Music
Calypso is a style of Caribbean music that originated in Trinidad and Tobago from Afro-Trinidadians during the early- to mid-19th century and spread to the rest of the Caribbean Antilles by the mid-20th century. Its rhythms can be traced back to West African Kaiso and the arrival of French planters and their slaves from the French Antilles in the 18th century. It is characterized by highly rhythmic and harmonic vocals, and was historically most often sung in a French creole and led by a griot. As calypso developed, the role of the griot became known as a '' chantuelle'' and eventually, ''calypsonian''. As English replaced "patois" ( Antillean) as the dominant language, calypso migrated into English, and in so doing it attracted more attention from the government. It allowed the masses to challenge the actions of the unelected Governor and Legislative Council, and the elected town councils of Port of Spain and San Fernando. Calypso continued to play an important role in po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calinda
Calinda (also spelled kalinda or kalenda) is a martial art, as well as a kind of folk music and war dance in the Caribbean which arose in the 1720s. It was brought to the Caribbean by Africans In the transatlantic slave trade and is based on native African combat dances. History Calinda is a kind of stick-fighting commonly seen practiced during Trinidad and Tobago Carnival.Shane K. Bernard and Julia Girouard, "'Colinda': Mysterious Origins of a Cajun Folksong," '' Journal of Folklore Research'' 29 (January–April 1992: 37–52. It is the national martial art of Trinidad and Tobago. French planters with their slaves, free coloureds and mulattos from neighboring islands of Grenada, Guadeloupe, Martinique and Dominica migrated to Trinidad during the Cedula of Population in 1783. Carnival had arrived with the French, and slaves who could not participate formed a parallel celebration (which eventually became known as Canboulay between 1858 and 1884). After the Emancipation of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiso
Kaiso is a type of music popular in Trinidad and Tobago, and other countries, especially of the Caribbean, such as Grenada, Belize, Barbados, St. Lucia, and Dominica, which originated in West Africa particularly among the Efik and Ibibio people of Nigeria, and later evolved into calypso music. Kaiso music has its origins in West Africa (particularly in present-day Nigeria) and in the Kingdom of Kongo and was brought over by the enslaved Africans, who (in the early history of the art form) used it to sing about their masters. The people would also gather in "kaiso" tents where a griot or lead singer would lead them in song. Many early kaisos were sung in French Creole by an individual called a chantwell. Kaiso songs are generally narrative in form and often have a cleverly concealed political subtext. Kaiso performers are known as kaisonians. In Barbados, ''kaiso'' refers to a form of stage-presented calypso, such as at the crop over festival. Terminology The term ''kaiso' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancelot Layne
Lancelot Layne (died 28 July 1990) was a rapso artist from Trinidad and Tobago. Biography Lancelot Layne was born to a Ms. Ethel Strawn (''née'' Serrano) and raised in Gonzales, Trinidad, a village near Port of Spain. He had a start in many local singing shows and showcase forums in and about Trinidad. During his career, he travelled around the world giving lectures and shows at many music institutions and universities, and was one of the first artists to bring the music of Trinidad and Tobago to the rest of the world. Layne took many trips to Africa, after studying African history. A 1998 United Nations Radio programme described the links between calypso and highlife music, focusing on an exchange of visits between Layne and high life musician Koo Nimo of Ghana. In later years, Layne joined the Orisa faith. He had a son, Brian Llenwyn Layne, and twin daughters, Niasha and Anuska, who are accomplished pannists. He is often described as being the founder of rapso; his 1970 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinidad And Tobago Styles Of Music
Trinidad is the larger, more populous island of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the country. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is the southernmost island in the Caribbean. With an area of , it is also the fifth-largest in the Caribbean. Name The original name for the island in the Arawakan languages was which meant "Land of the Hummingbird". Christopher Columbus renamed it ('The Island of the Trinity'), fulfilling a vow he had made before setting out on his third voyage. This has since been shortened to ''Trinidad''. Indo-Trinidadians called the island चीनीदत्त , 𑂒𑂲𑂢𑂲𑂠𑂞𑂹𑂞 , , ''Chinidat'' or ''Chinidad'' in Trinidadian Hindustani which translated to the land of sugar. The usage of the term goes back to the 19th century when recruiters from India would call the island ''Chinidat'' as a way of luring workers into indentureship. On Tuesday, 31 Jul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Music Genres
The 18th century lasted from 1 January 1701 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCCI) to 31 December 1800 (MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the Atlantic Revolutions. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures. The Industrial Revolution began mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. The European colonization of the Americas and other parts of the world intensified and associated mass migrations of people grew in size as part of the Age of Sail. During the century, slave trading expanded across the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, while declining in Russia and China. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dancehall
Dancehall is a genre of Jamaican popular music that originated in the late 1970s. Initially, dancehall was a more sparse version of reggae than the roots reggae, roots style, which had dominated much of the 1970s.Barrow, Steve & Dalton, Peter (2004) "The Rough Guide to Reggae, 3rd edn.", Rough Guides, This music genre wasn't officially named until the 1980s, when the two words ''Dance'' and ''Hall'' (referring to the common venue) were joined to form ''Dancehall'', which was then promoted internationally for the first time. At that time digital instrumentation became more prevalent, changing the sound considerably, with digital dancehall (or "ragga") becoming increasingly characterized by faster rhythms. Key elements of dancehall music include its extensive use of Jamaican Patois rather than Jamaican English, Jamaican standard English and a focus on the track instrumentals (or "riddims"). Dancehall saw initial mainstream success in Jamaica in the 1980s; by the 1990s, it became i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiphop Music
Hip-hop or hip hop (originally disco rap) is a popular music Music genre, genre that emerged in the early 1970s from the African Americans, African-American community of New York City. The style is characterized by its synthesis of a wide range of musical techniques. Hip-hop includes rapping often enough that the terms can be used synonymously. However, "hip-hop" more properly denotes an entire hip-hop culture, subculture. Other key markers of the genre are the disc jockey, turntablism, scratching, beatboxing, and hip hop production, instrumental tracks. Cultural interchange has always been central to the hip-hop genre. It simultaneously borrows from its social environment while commenting on it. The hip-hop genre and culture emerged from block parties in ethnic minority neighborhoods of New York City, particularly The Bronx, Bronx. DJs began expanding the instrumental Break (music), breaks of popular records when they noticed how excited it would make the crowds. The extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brother Resistance
Lutalo Masimba (24 October 1954 – 13 July 2021), born Roy Lewis and known professionally as Brother Resistance, was a rhythm poet and musician from Trinidad and Tobago. He died on 13 July 2021, after being diagnosed with cancer. Background and career Born in 1954 as Roy Lewis in East Dry River, Laventille, Trinidad and Tobago, he began writing poetry in primary school, and went on to study at Queen's Royal College. He was influenced by Trinidad's 1970 Black Power movement to become conscious of his African identity, and he would eventually change his name to Lutalo Masimba in 1982, in order to better reflect his heritage. He assumed the soubriquet "Brother Resistance" when he began performing and chanting his poetry at school. He went on to further studies at the University of the West Indies, St. Augustine, graduating with a B.Sc. degree in Social Sciences with History in 1980. Brother Resistance became, together with Brother Shortman, the lead singer of the Network Riddi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |