|
Chancellor Of The Tang Dynasty
The Grand chancellor (China), chancellor () was a semi-formally designated office position for a number of high-level officials at one time during the Tang dynasty of China. This list also includes List of chancellors of Wu Zetian, chancellors of the short-lived Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty, which is typically treated as an interregnum of the Tang dynasty by historians. Origins Ouyang Xiu, the author of the ''New Book of Tang'', asserts that the Tang dynasty inherited its bureaucracy from its dynastic predecessor, the Sui dynasty, under which the founder Emperor Wen of Sui divided his government into five main bureaus: * ''Shàng shū shěng'' () – The Department of State Affairs * ''Mén xià shěng'' () – The Menxia Sheng, Chancellery * ''Nèi shǐ shěng'' () – The Legislative Bureau (note different tone than the eunuch bureau below) * ''Mì shū shěng'' () – The Palace Library * ''Nèi shì shěng'' () – The Eunuch (court official), Eunuch bureau ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Chancellor (China)
The grand chancellor (, among other titles), also translated as counselor-in-chief, chancellor, chief councillor, chief minister, imperial chancellor, lieutenant chancellor and prime minister, was the highest-ranking executive official in the Imperial China, imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history, and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly, even during a particular Dynasties of China, dynasty. Professor Zhu Zongbin of Peking University outlined the role of "grand chancellor" as one with the power to oversee all jurisdictional matters, the right to decide and to draft edicts with other ministers, and the position of chief advisor to the Emperor of China, emperor. This extended even to the ability to criticize the emperor's edicts and decisions. Thus, the grand chancellor served as the emperor's chief of staff and main political advisor, often exercising power second only to the empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Taizong Of Tang
Emperor Taizong of Tang (28January 59810July 649), previously Prince of Qin, personal name Li Shimin, was the second emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649. He is traditionally regarded as a co-founder of the dynasty for his role in encouraging his father Li Yuan (Emperor Gaozu) to rebel against the Sui dynasty at Jinyang in 617. Taizong subsequently played a pivotal role in defeating several of the dynasty's most dangerous opponents and solidifying its rule over China proper. Taizong is considered to be one of the greatest emperors in China's history, and henceforth his reign became regarded as the exemplary model against which all future emperors were measured. His era, the "Reign of Zhenguan" () is considered a golden age in ancient Chinese history and was treated as required studying material for future crown princes. Taizong continued to develop imperial examination systems. He asked his officials to be loyal to policies, not people, in order to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Entendre
A double entendre (plural double entendres) is a figure of speech or a particular way of wording that is devised to have a double meaning, one of which is typically obvious, and the other often conveys a message that would be too socially unacceptable, or offensive to state directly. A double entendre may exploit puns or word play to convey the second meaning. Double entendres generally rely on multiple meanings of words, or different interpretations of the same primary meaning. They often exploit ambiguity and may be used to introduce it deliberately in a text. Sometimes a homophone can be used as a pun. When three or more meanings have been constructed, this is known as a "triple entendre", etc. Etymology According to the Merriam-Webster Unabridged Dictionary and the Oxford English Dictionary, the expression comes from the rare and obsolete French (language), French expression, which literally meant "double meaning" and was used in the senses of "double understanding" or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Yue (Tang Dynasty)
Zhang Yue () (667 – 9 February 731), courtesy name Daoji (道濟) or Yuezhi (說之), formally Duke Wenzhen of Yan (燕文貞公), was a Chinese historian, military general, poet, and politician. He served as an official under Wu Zetian's Zhou dynasty, a chancellor of the Tang dynasty, chancellor with three separate stints during the reigns of Emperor Ruizong of Tang, Emperor Ruizong and under Emperor Xuanzong of Tang, Emperor Xuanzong. He was known for having suggested the transition of Tang central government armed forces from being conscription-based to recruitment-based, and for turning the office of the chancellor into a specialized post with strong executive powers. Zhang Yue was a well-respected literary figure of his time, and was ranked alongside Su Ting (Duke Wenxian of Xu, another of Emperor Xuanzong's chancellors) as the two great writers of the Kaiyuan era. They were known in unison as 燕许大手笔 ("Immense pen-brushes from Yan and Xu"). Background Zhang Yue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei Yan
Pei Yan (裴炎) (died November 30, 684), courtesy name Zilong (子隆), was a Chinese politician during the Tang dynasty, serving as a chancellor during the reign of Emperor Gaozong, as well as the regency of his wife Empress Wu (later known as Wu Zetian) over their sons Emperor Zhongzong and Emperor Ruizong. He was well trusted by Emperor Gaozong and Empress Wu late in Emperor Gaozong's reign, but drew Empress Wu's ire after he advised her, then empress dowager, to end her regency and return power to Emperor Ruizong. In 684, she accused him of treason and executed him. Background Pei Yan was from Jiang Prefecture (絳州, part of modern Yuncheng, Shanxi), and it is not known when he was born. When he was young, he became a student at the imperial university, and it was said that during vacations, the other students would often go out to travel, but Pei kept studying. After he studied at the university for more than a year, he was due to be recommended for an official pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Ruizong Of Tang
Emperor Ruizong of Tang (22 June 662 – 13 July 716), personal name Li Dan, also known at times during his life as Li Xulun, Li Lun, Wu Lun, and Wu Dan, was the fifth and ninth emperor of the Chinese Tang dynasty. He was the eighth son of Emperor Gaozong and the fourth son of Emperor Gaozong's second wife Empress Wu. He was wholly a figurehead during his first reign when he was controlled by his mother, and he was the titular and puppet ruler of the Tang Empire from 684 to 690. During his second reign after his mother's death, significant power and influence was exercised by his sister Princess Taiping. In February 684, Li Dan's mother Empress Wu demoted his older brother Emperor Zhongzong (Li Xian) who had attempted to rule free of his mother and named him emperor (as Emperor Ruizong). Emperor Ruizong, however, was a hollow figurehead under control of his mother and had no real power, even nominally, his name was not included in the issued documents or orders. He was not ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü Yin
Lü Yin (呂諲) (712–762), formally Count Su of Xuchang (須昌肅伯), was a Chinese military general and politician during the Tang dynasty, serving as a chancellor during the reign of Emperor Suzong. Historians often regarded him as being more capable as a regional governor, later in his career, than as a chancellor. Before serving as chancellor Lü Yin was born in 712, around the time when Emperor Xuanzong became emperor. His family was from Pu Prefecture (蒲州, roughly modern Yuncheng, Shanxi) and traced its ancestry to the ruling Jiang clan of Qi during the Spring and Autumn period. Lü himself was said to be ambitious and studious in his youth, but was poor and could not support himself. A wealthy man from his locale, Cheng Chubin () was impressed with Lü's talent and believed that he would one day be successful, and Cheng decided to give his daughter to Lü in marriage. After the marriage, both Cheng Chubin and his son Cheng Zhen () supported Lü financially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Lin (Tang Chancellor)
Li Lin (李麟) (694–759), formally Duke De of Bao (褒德公), was a Chinese politician during the Tang dynasty, serving as a chancellor during the reign of Emperor Suzong — although he was commissioned by Emperor Suzong's father Emperor Xuanzong, not Emperor Suzong. Background Li Lin was born in 694, during the reign of Wu Zetian. He was a member of the imperial Li clan of the Tang dynasty — although he was distant in lineage from the imperial lineage itself. His great-great-great-grandfather Li Qidou (李乞豆) was a younger brother of Li Hu (李虎), the grandfather of Tang's founding emperor Emperor Gaozu, who was the grandfather of Wu Zetian's husband Emperor Gaozong. Li Lin's father Li Jun (李濬) served successively as the prefect of three different prefecture and was known for his honesty. Li Jun died during the ''Kaiyuan'' era (713–741) of Emperor Gaozong's and Wu Zetian's grandson Emperor Xuanzong while serving as the military governor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
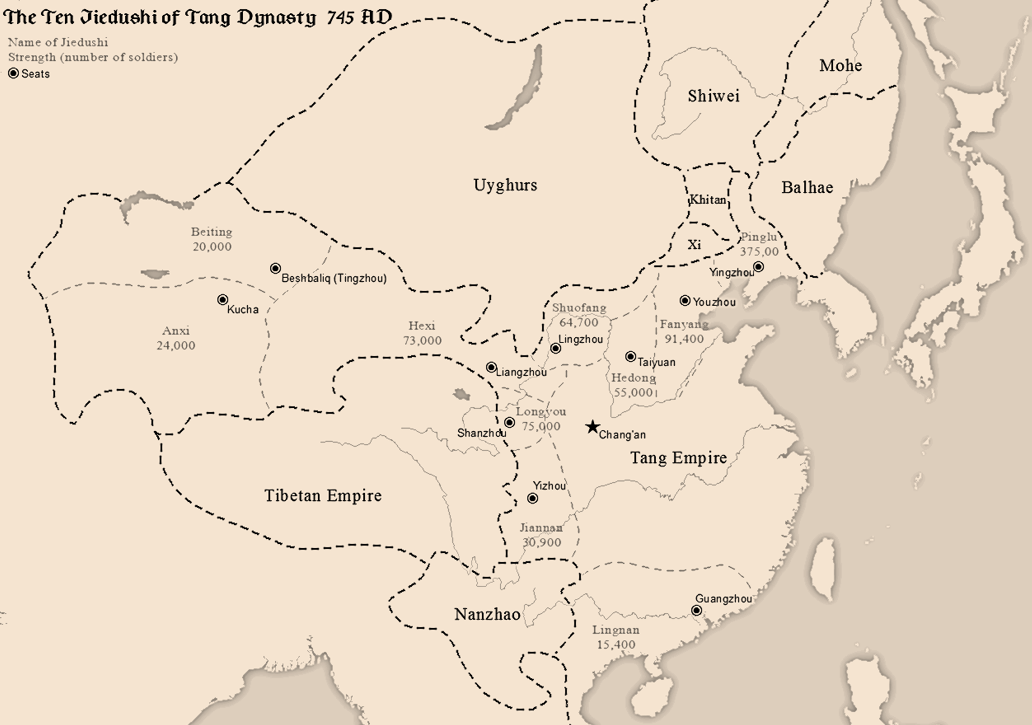
Anshi Rebellion
The An Lushan rebellion was a civil war in China that lasted from 755 to 763, at the approximate midpoint of the Tang dynasty (618–907). It began as a commandery rebellion attempting to overthrow and replace the Tang government with the rogue Yan dynasty. The rebels succeeded in capturing the imperial capital Chang'an after the emperor had fled to Sichuan, but eventually succumbed to internal divisions and counterattacks by the Tang and their allies. The rebellion spanned the reigns of three Tang emperors: Xuanzong, Suzong, and Daizong. On 16 December 755, An Lushan, the ''jiedushi'' of the Taiyuan Commandery, mobilized his army and marched to Fanyang. An Lushan led the rebellion for two years before he was assassinated by his son An Qingxu. Two years after An Qingxu's ascension, Shi Siming, the governor of Pinglu Commandery and a close ally of An Lushan, killed An Qingxu and usurped the leadership. Shi Siming ruled for two years, but was in turn killed by his own son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Gaozong Of Tang
Emperor Gaozong of Tang (21 July 628 – 27 December 683), personal name Li Zhi, was the third Emperor of China, emperor of the Chinese Tang dynasty, ruling from 649 to 683; after January 665, he handed power over the empire to his second wife Empress Wu (the future Wu Zetian), and her decrees were carried out with greater force than the decrees of Emperor Gaozong's. Emperor Gaozong was the youngest son of Emperor Taizong of Tang, Emperor Taizong and Empress Zhangsun; his elder brothers were Li Chengqian and Li Tai. Emperor Gaozong's reign saw the primacy of Empress Wu, who became the effective power behind the Tang rule. Emperor Gaozong was aided in his rule by Empress Wu during the later years of his reign after a series of strokes left him incapacitated. Emperor Gaozong effectively after January 665 delegated all matters of state to his strong wife; after that Empress Wu acted as the power behind the emperor, "hanging the curtain and listening to politics" (''Chuílián tīn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xuanzong Of Tang
Emperor Xuanzong of Tang (; 8 September 685 – 3 May 762), personal name Li Longji, was an Emperor of China, emperor of the Tang dynasty of China, reigning from 712 to 756. His reign of 44 years was the longest during the Tang dynasty. Through two palace coups, he seized the throne and inherited an empire still in its golden age. He was initially assisted by capable chancellors like Yao Chong, Song Jing and Zhang Yue (Tang dynasty), Zhang Yue who were already serving as government officials before Xuanzong ascended the throne. However, under Emperor Xuanzong, the empire reached its turning point and went into sharp decline and near collapse, due to numerous political missteps throughout his long reign, such as over-trusting chancellors Li Linfu, Yang Guozhong and general An Lushan, with Tang's golden age (metaphor), golden age ending in the An Lushan rebellion. Background Li Longji was born at the Tang dynasty eastern capital Luoyang in 685, during the first reign of his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |