|
Cervical Ripening
Cervical effacement or cervical ripening refers to the thinning and shortening of the cervix. This process occurs during Childbirth, labor to prepare the cervix for dilation to allow the fetus to pass through the vagina. While this is a normal, physiological process that occurs at the later end of pregnancy, it can also be Labor induction, induced through medications and procedures. During gestation, the cervix maintains pregnancy by increasing synthesis of various Protein, proteins. These proteins have defined interactions that allow the formation of matrix proteins to help fortify the uterine cervix. Toward the end of pregnancy, a series of hormone-mediated biochemical process takes place to degrade the collagen and fiber network to cause the cervix to ripen during labor. Failure to ripen the cervix during labor may delay its onset and cause complications. Current efforts to induce labor include Cervical effacement#Pharmacologic, pharmacologic, Cervical effacement#Non-pharmacolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
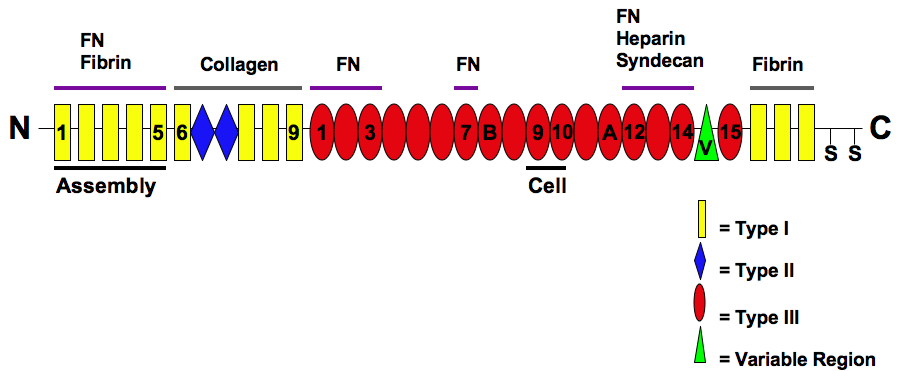
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Umbilical Cord Prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse is when the umbilical cord comes out of the uterus with or before the presenting part of the baby. The concern with cord prolapse is that pressure on the cord from the baby will compromise blood flow to the baby. It usually occurs during childbirth, labor but can occur anytime after the rupture of membranes. The greatest risk factors are an abnormal position of the baby within the uterus and a Premature birth, premature or small baby. Other risk factors include a Multiple birth, multiple pregnancy, more than one previous delivery, and too much amniotic fluid. Whether amniotomy, medical rupture of the amniotic sac is a risk is controversial. The diagnosis should be suspected if there is a sudden decrease in the baby's heart rate during labor. Seeing or feeling the cord confirms the diagnosis. Management focuses on quick delivery, usually by cesarean section. Filling the bladder or pushing up the baby by hand is recommended until this can take place. Somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Breech Birth
A breech birth is when a baby is born bottom first instead of Cephalic presentation, head first, as is normal. Around 3–5% of pregnant women at term (37–40 weeks pregnant) have a breech baby. Due to their higher than average rate of possible complications for the baby, breech births are generally considered higher risk. Breech births also occur in many other mammals such as dogs and horses, see veterinary obstetrics. Most babies in the breech position are delivered via caesarean section because it is seen as safer than being Vaginal birth, born vaginally. Doctors and Midwife, midwives in the developing world often lack many of the skills required to safely assist women giving birth to a breech baby vaginally. Also, delivering all breech babies by caesarean section in developing countries is difficult to implement as there are not always resources available to provide this service. Cause With regard to the fetal presentation during pregnancy, three periods have been distingu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vaginal Delivery
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucous membrane, mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for Copulation (zoology), copulation and birth. It also channels Menstruation (mammal), menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. To accommodate smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual intercourse or other sexual activity, vaginal moisture increases during sexual arousal in human females and other female mammals. This increase in moisture provides vaginal lubrication, which reduces friction. The texture of the vaginal walls creates friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulates it toward ejaculation, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because vaginal delivery would put the mother or child at risk (of paralysis or even death). Reasons for the operation include, but are not limited to, obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, pre-eclampsia, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, shoulder presentation, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of Vaginal birth after previous C-section, vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Preterm Birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the Childbirth, birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks Gestational age (obstetrics), gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 34 weeks, Late preterm infant, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies (American English) or premmies (Australian English). Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their Visual impairment, vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be. The cause of spontaneous preterm birth is often not known. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elastography
Elastography is any of a class of medical imaging diagnostic methods that map the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue. The main idea is that whether the tissue is hard or soft will give diagnostic information about the presence or status of disease. For example, cancerous tumours will often be harder than the surrounding tissue, and diseased livers are stiffer than healthy ones. The most prominent techniques use ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to make both the stiffness map and an anatomical image for comparison. Historical background Palpation is the practice of feeling the stiffness of a person's or animal's tissues with the health practitioner's hands. Manual palpation dates back at least to 1500 BC, with the Egyptian Ebers Papyrus and Edwin Smith Papyrus both giving instructions on diagnosis with palpation. In ancient Greece, Hippocrates gave instructions on many forms of diagnosis using palpation, including palpation of the breasts, wounds, bowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vaginal Delivery
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucous membrane, mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for Copulation (zoology), copulation and birth. It also channels Menstruation (mammal), menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. To accommodate smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual intercourse or other sexual activity, vaginal moisture increases during sexual arousal in human females and other female mammals. This increase in moisture provides vaginal lubrication, which reduces friction. The texture of the vaginal walls creates friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulates it toward ejaculation, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cervical Exam
A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma (e.g. sexual assault). It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the vulva 2) the internal exam with palpation (commonly called the ''bimanual exam'') to examine the uterus, ovaries, and structures adjacent to the uterus (adnexae) and 3) the internal exam using a speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer (the Pap test). Some clinician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bishop's Score
Bishop score, also Bishop's score or cervix score, is a pre-labor scoring system to assist in predicting whether induction of labor will be required. It has also been used to assess the likelihood of spontaneous preterm delivery. The Bishop score was developed by Professor Emeritus of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Edward Bishop, and was first published in August 1964. Components The total score is calculated by assessing the following five components on manual vaginal examination by a trained professional: * Cervical dilation in centimeters *Cervical effacement as a percentage *Cervical consistency by provider assessment/judgement *Cervical position *Fetal station, the position of the top of the fetal head in relation to the pelvic bones, specifically the ischial spines. The Bishop score grades patients who would be most likely to achieve a successful induction. The duration of labor is inversely correlated with the Bishop score; “A Bishop score of 9 conveys a high likelihood f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pelvic Exam Nci-vol-1786-300
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |