|
Cavity QED
Cavity Quantum Electrodynamics (cavity QED) is the study of the interaction between light confined in a reflective cavity and atoms or other particles, under conditions where the quantum nature of photons is significant. It could in principle be used to construct a quantum computer. The case of a single 2-level atom in the cavity is mathematically described by the Jaynes–Cummings model, and undergoes vacuum Rabi oscillations , e\rangle, n-1\rangle\leftrightarrow, g\rangle, n\rangle, that is between an excited atom and n-1 photons, and a ground state atom and n photons. If the cavity is in resonance with the atomic transition, a half-cycle of oscillation starting with no photons coherently swaps the atom qubit's state onto the cavity field's, (\alpha, g\rangle+\beta, e\rangle), 0\rangle\leftrightarrow, g\rangle(\alpha, 0\rangle+\beta, 1\rangle), and can be repeated to swap it back again; this could be used as a single photon source (starting with an excited atom), or as an interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Cavity
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times, producing Mode (electromagnetism), modes with certain resonance, resonance frequencies. Modes can be decomposed into longitudinal modes that differ only in frequency and transverse modes that have different intensity patterns across the cross section of the beam. Many types of optical cavities produce standing wave modes. Different resonator types are distinguished by the focal lengths of the two mirrors and the distance between them. Flat mirrors are not often used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nobel Laureates In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the 1895 will and testament, will of Alfred Nobel (who died in 1896), awarded for outstanding contributions in physics. As dictated by Nobel's will, the award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death. Each recipient receives a medal, a diploma and a monetary award prize that has varied throughout the years. Statistics The Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to 226 individuals as of 2024. The first prize in physics was awarded in 1901 to Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, of Germany, who received 150,782 Swedish krona, SEK. John Bardeen is the only laureate to win the prize twice—in 1956 and 1972. Lawrence Bragg, Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicke Model
The Dicke model is a fundamental model of quantum optics, which describes the interaction between light and matter. In the Dicke model, the ''light'' component is described as a single quantum mode, while the ''matter'' is described as a set of two-level systems. When the coupling between the light and matter crosses a critical value, the Dicke model shows a mean-field phase transition to a superradiant phase. This transition belongs to the Ising universality class and was realized in cavity quantum electrodynamics experiments. Although the superradiant transition bears some analogy with the lasing instability, these two transitions belong to different universality classes. Description The Dicke model is a quantum mechanical model that describes the coupling between a single-mode cavity and N two-level systems, or equivalently N spin-1/2 degrees of freedom. The model was first introduced in 1973 by K. Hepp and E. H. Lieb. Their study was inspired by the pioneering work of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting Radio Frequency
Superconducting radio frequency (SRF) science and technology involves the application of electrical Superconductivity, superconductors to radio frequency devices. The ultra-low Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical resistivity of a superconducting material allows an RF resonator to obtain an extremely high Q factor, quality factor, ''Q''. For example, it is commonplace for a 1.3 GHz niobium SRF resonant cavity at 1.8 kelvins to obtain a quality factor of ''Q''=5×1010. Such a very high ''Q'' resonator stores energy with very low loss and narrow Bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth. These properties can be exploited for a variety of applications, including the construction of high-performance particle accelerator structures. Introduction The amount of loss in an SRF resonant cavity is so minute that it is often explained with the following comparison: Galileo Galilei (1564–1642) was one of the first investigators of pendulous motion, a simple form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circuit Quantum Electrodynamics
Circuit quantum electrodynamics (circuit QED) provides a means of studying the fundamental interaction between light and matter (quantum optics). As in the field of cavity quantum electrodynamics, a single photon within a single mode cavity coherently couples to a quantum object (atom). In contrast to cavity QED, the photon is stored in a one-dimensional on-chip resonator and the quantum object is no natural atom but an artificial one. These artificial atoms usually are mesoscopic devices which exhibit an atom-like energy spectrum. The field of circuit QED is a prominent example for quantum information processing and a promising candidate for future quantum computation. In the late 2010s decade, experiments involving cQED in 3 dimensions have demonstrated deterministic gate teleportation and other operations on multiple qubits. Resonator The resonant devices in the circuit QED architecture can be implemented using a superconducting LC resonator, a high purity cavity, or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics World
''Physics World'' is the membership magazine of the Institute of Physics, one of the largest physical societies in the world. It is an international monthly magazine covering all areas of physics, pure and applied, and is aimed at physicists in research, industry, physics outreach, and education worldwide. Overview The magazine was launched in 1988 by IOP Publishing Ltd, under the founding editorship of Philip Campbell. The magazine is made available free of cost to members of the Institute of Physics, who can access a digital edition of the magazine; selected articles can be read by anyone for free online. It was redesigned in September 2005 and has an audited circulation of just under 35000. The current editor is Matin Durrani. Others on the team are Michael Banks (news editor) and Tushna Commissariat and Sarah Teah (features editors). Hamish Johnston, Margaret Harris and Tami Freeman are online editors. Alongside the print and online magazine, Physics World produces film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Wineland
David Jeffery Wineland (born February 24, 1944) is an American physicist at the Physical Measurement Laboratory of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). His most notable contributions include the laser cooling of trapped ions and the use of ions for quantum-computing operations. He received the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Serge Haroche, for "ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems." Early life and career Wineland was born in Wauwatosa, Wisconsin. He lived in Denver until he was three years old, at which time his family moved to Sacramento, California. Wineland graduated from Encina High School in Sacramento in 1961.Class of 1961 Graduation List encinahighschool.com In Sept. 1961–Dec. 1963, he studied at |
Serge Haroche
Serge Haroche (born 11 September 1944) is a French physicist who was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize for Physics jointly with David J. Wineland for "ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems", a study of the particle of light, the photon. This and his other works developed laser spectroscopy. Since 2001, Haroche is a professor at the Collège de France and holds the chair of quantum physics and in 2022 he had the Fermi Chair of Physics at University of Rome La Sapienza In 1971 he defended his doctoral thesis in physics at the University of Paris VI: his research had been conducted under the direction of Claude Cohen-Tannoudji. Early life and education Haroche was born in Casablanca, Morocco, to Albert Haroche (1920–1998), from a Moroccan Jewish family, and Valentine Haroche, born Roubleva (1921–1998), a teacher who was born in Odessa to a Jewish family of physicians who relocated to Morocco in the early 1920s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
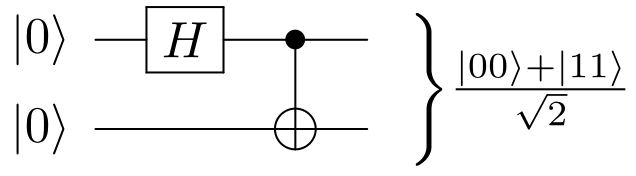
Bell State
In quantum information science, the Bell's states or EPR pairs are specific quantum states of two qubits that represent the simplest examples of quantum entanglement. The Bell's states are a form of entangled and normalized basis vectors. This normalization implies that the overall probability of the particles being in one of the mentioned states is 1: \langle \Phi, \Phi \rangle = 1. Entanglement is a basis-independent result of superposition. Due to this superposition, measurement of the qubit will " collapse" it into one of its basis states with a given probability. Because of the entanglement, measurement of one qubit will "collapse" the other qubit to a state whose measurement will yield one of two possible values, where the value depends on which Bell's state the two qubits are in initially. Bell's states can be generalized to certain quantum states of multi-qubit systems, such as the GHZ state for three or more subsystems. Understanding of Bell's states is useful in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Computer
A quantum computer is a computer that exploits quantum mechanical phenomena. On small scales, physical matter exhibits properties of both particles and waves, and quantum computing takes advantage of this behavior using specialized hardware. Classical physics cannot explain the operation of these quantum devices, and a scalable quantum computer could perform some calculations exponentially faster than any modern "classical" computer. Theoretically a large-scale quantum computer could break some widely used encryption schemes and aid physicists in performing physical simulations; however, the current state of the art is largely experimental and impractical, with several obstacles to useful applications. The basic unit of information in quantum computing, the qubit (or "quantum bit"), serves the same function as the bit in classical computing. However, unlike a classical bit, which can be in one of two states (a binary), a qubit can exist in a superposition of its two " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximally Entangled State
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon where the quantum state of each Subatomic particle, particle in a group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical physics and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics. Measurement#Quantum mechanics, Measurements of physical properties such as position (vector), position, momentum, Spin (physics), spin, and polarization (waves), polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be anticlockwise. However, this behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |