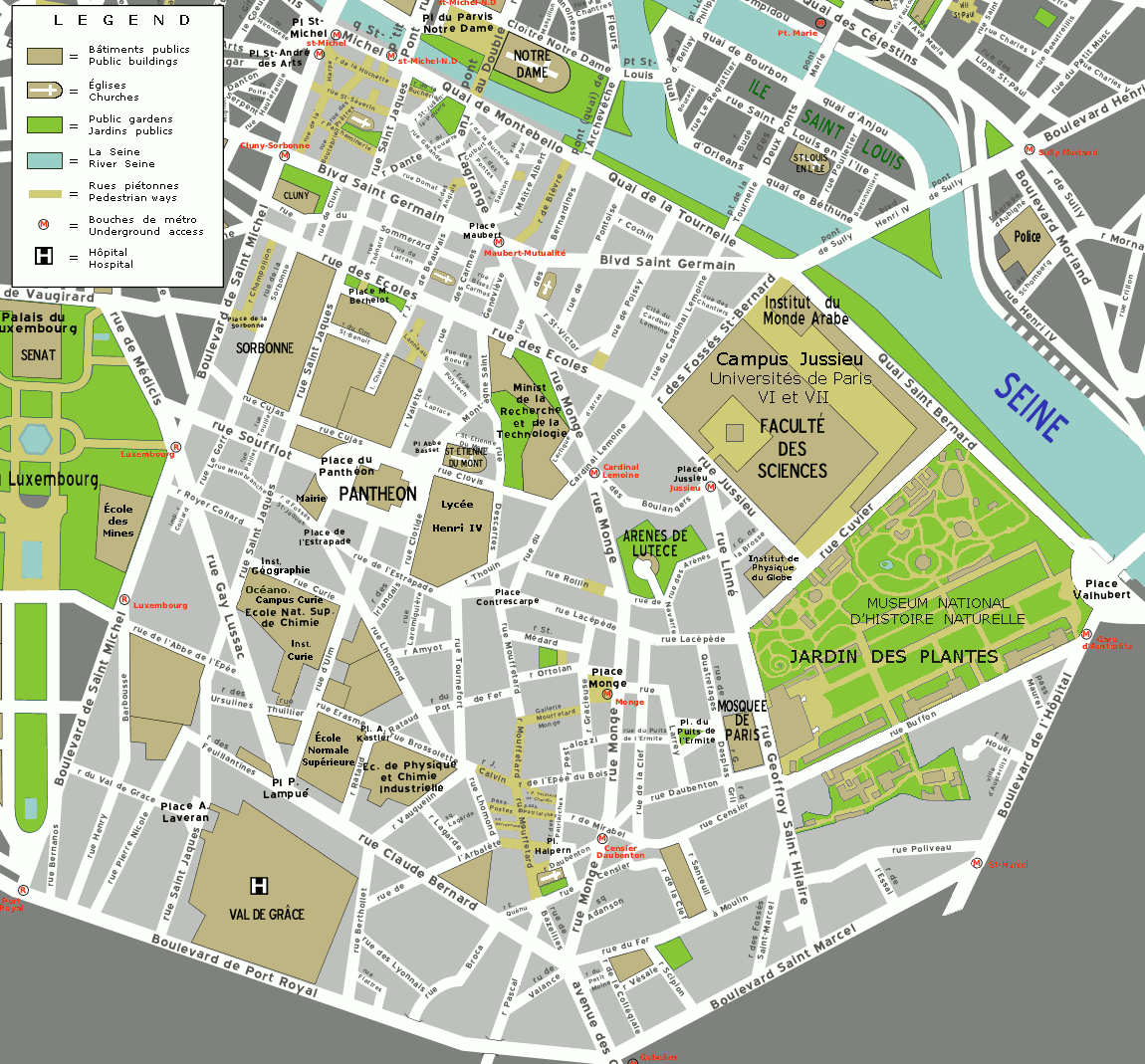
|
Catacombs Of Paris
The Catacombs of Paris (, ) are underground ossuaries in Paris, France, which hold the remains of more than six million people. Built to consolidate Paris's ancient stone quarries, they extend south from the ("Gate of Hell") former city gate. The ossuary was created as part of the effort to eliminate the effects of the city's overflowing cemeteries. Preparation work began shortly after a 1774 series of basement wall collapses around the Holy Innocents' Cemetery added a sense of urgency to the cemetery-eliminating measure, and from 1788, nightly processions of covered wagons transferred remains from most of Paris's cemeteries to a mine shaft opened near the . The ossuary remained largely forgotten until it became a novelty-place for concerts and other private events in the early 19th century; after further renovations and the construction of accesses around , it was opened to public visitation from 1874. Since 2013, the Catacombs have numbered among the fourteen City of Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Historic Site
A historic site or heritage site is an official location where pieces of political, military, cultural, or social history have been preserved due to their cultural heritage value. Historic sites are usually protected by law, and many have been recognized with official historic status. A historic site may be any building, landscape, site or structure that is of local, regional, national, or global significance. Usually this also means the site must be at least 50 years or older. Classification, records and conservation The conservation of historical heritage depends on the legislation of local governing bodies. In some, a national authority is responsible for the management of all classified sites, while in others regional entities are in charge. According to civil law expert Estefanía Hernández Torres, whose doctoral thesis deals with historical heritage and property registration, "the protection of historical heritage is one of the main concerns of civilized societies. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
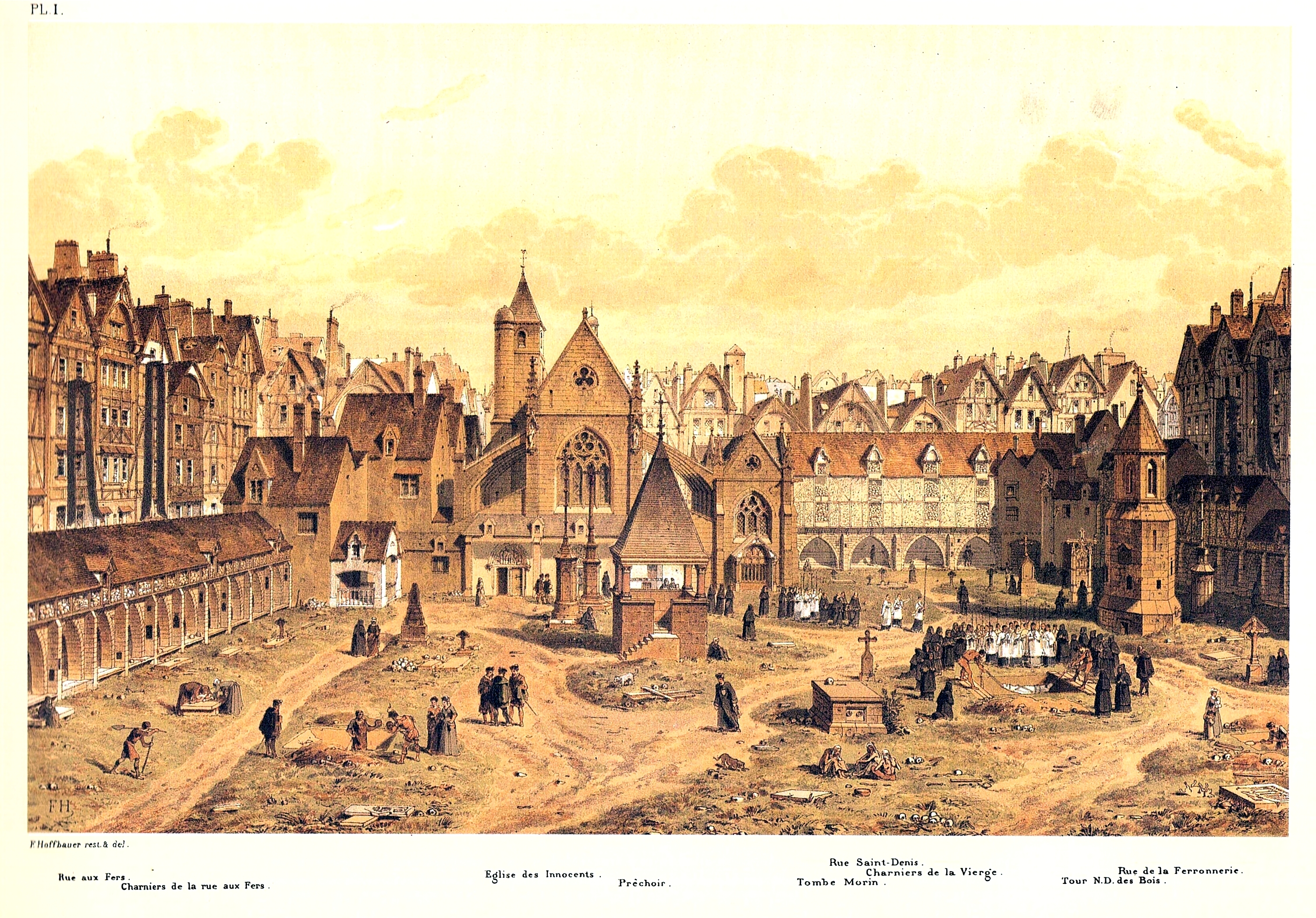
Rue De La Lingerie
''Ruta graveolens'', commonly known as rue, common rue or herb-of-grace, is a species of the genus ''Ruta'' grown as an ornamental plant and herb. It is native to the Mediterranean. It is grown throughout the world in gardens, especially for its bluish leaves, and sometimes for its tolerance of hot and dry soil conditions. It is also cultivated as a culinary herb, and to a lesser extent as an insect repellent and incense. Etymology The specific epithet ''graveolens'' refers to the strong-smelling leaves.J. D. Douglas and Merrill C. Tenney Description Rue is a woody, perennial shrub. Its leaves are oblong, blue green and arranged bipinnately with rounded leaflets; they release a strong aroma when they are bruised. The flowers are small with 4 to 5 dull yellow petals in cymes. The first flower in each cyme is pentamerous (five sepals, five petals, five stamens and five carpels. All the others are tetramerous (four of each part). They bear brown seed capsules when pollinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Errancis Cemetery
Errancis Cemetery or ''Cimetière des Errancis'' is a former cemetery in the 8th arrondissement of Paris and was one of the cemeteries (the others being Madeleine Cemetery, Picpus Cemetery, Chapelle expiatoire and the Cemetery of Saint Margaret) used to dispose of the corpses of guillotine victims during the French Revolution. History and location Errancis Cemetery opened on March 5, 1793, and was closed on April 23, 1797. On the site there are now apartments. The cemetery was located between the current Boulevard de Courcelles, Rue de Rocher, Rue de Monceau and Rue de Miromesnil, at that time a plot running along '' le mur des Fermiers-Généraux''. During the French Revolution The cemetery was used for the bodies of victims of the guillotine after the Madeleine Cemetery was closed. It was used for this purpose between March 25, 1793, until the end of May 1795. The memorial plaque, located on Rue de Monceau between number 97 and the corner with Rue de Rocher, states that 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Madeleine Cemetery
Madeleine Cemetery (in French known as ''Cimetière de la Madeleine'') is a former cemetery in the 8th arrondissement of Paris and was one of the four cemeteries (the others being Errancis Cemetery, Picpus Cemetery and the Cemetery of Saint Margaret) used to dispose of the corpses of guillotine victims during the French Revolution. The cemetery was named after Mary Magdalene, known in French as Sainte-Madeleine. History In 1720, the parish of Sainte-Madeleine de la Ville-l’Évêque bought a piece of land of approximately 45x19m destined to become the third cemetery of the parish. It became known as the Madeleine Cemetery. The cemetery was closed on 25 March 1794, reputedly because it was full, but maybe for sanitary reasons, as it was located in an affluent part of Paris. Major interments were the 133 victims of the firework celebration of the marriage of the Dauphin (the future Louis XVI) to Marie Antoinette of Habsburg-Lorraine on 30 May 1770 and those of the Swiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saint-Étienne-des-Grès, Paris
Saint-Étienne-des-Grès was a church and parish in Paris, France, formerly located in the Latin Quarter on the Rue Saint-Jacques. History Saint-Étienne-des-Grès was located on the Rue Saint-Jacques, on the site of the present Faculty of Law. It was one of the early centers of Christianity in Paris; it stood on a site said to be that of an oratory which was erected by St. Denis to St. Stephen. Its foundation dates to around the sixth century. Saint-Étienne was one of five Merovingian churches marking the road from Paris to Orleans. The original church was destroyed by the Vikings, but rebuilt in the 11th century. Canons were installed in 1045 to serve the church and pray for the king. It became a parish sometime before 1080, but the parish was absorbed by St. Benedict's between 1195 and 1205. The Chapter existed until 1790. The collegiate church was demolished in 1792. Notre Dame de Bonne Délivrance The church notably contained a Black Madonna, the ''Notre Dame de Bonne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
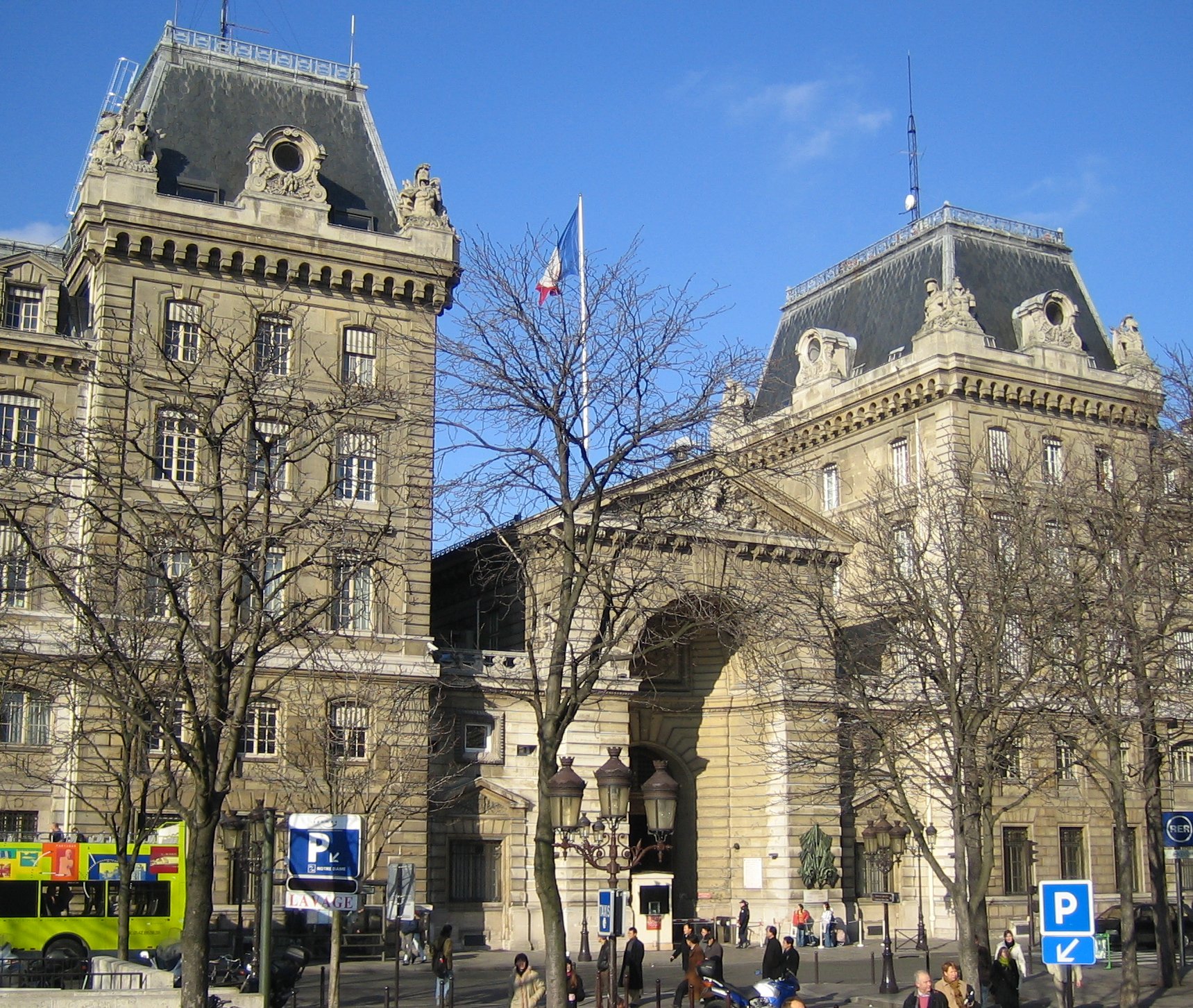
Paris Police Prefecture
The Paris Police Prefecture ( ), officially the Police Prefecture (), is the unit of the French Minister of the Interior (France), Ministry of the Interior that provides police, emergency services, and various administrative services to the population of the city of Paris and the surrounding three suburban of Hauts-de-Seine, Seine-Saint-Denis, and Val-de-Marne. It is headed by the Paris Prefect of Police (), officially called the Prefect of Police (). The Paris Police Prefecture supervises the Paris Police force, the Paris Fire Brigade, and various administrative departments in charge of issuing ID cards and driver licenses or monitoring alien residents. The Prefecture of Police also has security duties in the wider Île-de-France as the is also (Prefect for the Defense zone). Since 2017, it has acquired direct responsibility for the three main airports of the Paris area (Charles de Gaulle Airport, Charles de Gaulle, Orly Airport, Orly and Paris–Le Bourget Airport, Le Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir-apparent of Louis XV, King Louis XV), and Maria Josepha of Saxony, Dauphine of France, Maria Josepha of Saxony, Louis became the new Dauphin of France, Dauphin when his father died in 1765. In 1770, he married Marie Antoinette. He became King of France and Navarre on his grandfather's death on 10 May 1774, and reigned until the proclamation of the abolition of the monarchy, abolition of the monarchy on 21 September 1792. From 1791 onwards, he used the style of king of the French. The first part of Louis XVI's reign was marked by attempts to reform the French government in accordance with Enlightened absolutism, Enlightenment ideas. These included efforts to increase Edict of Versailles, tolerance toward non-Catholics as well as abolishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boulevard Saint-Michel
The Boulevard Saint-Michel () is one of the two major streets in the Latin Quarter of Paris, France, the other being the Boulevard Saint-Germain. It is a tree-lined boulevard which runs south from the Pont Saint-Michel on the Seine and Place Saint-Michel, crosses the Boulevard Saint-Germain and continues alongside the Sorbonne and the Jardin du Luxembourg, ending at the Place Camille Jullian just before the Port-Royal RER station and the Avenue de l'Observatoire. It was created by Baron Haussmann to run parallel to the Rue Saint-Jacques which marks the historical north-south axis of Paris. It is known colloquially as ''Boul'Mich'' in French. The boulevard serves as a boundary between the 5th and 6th arrondissements of Paris; odd-numbered buildings on the eastern side are in the 5th arrondissement and even numbers on the western side are in the 6th. It has a length of 1,380 m (4,530 ft), an average width of 30 m (98 ft) and takes its name from the Pont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Val-de-Grâce
The Val-de-Grâce (; Hôpital d'instruction des armées du Val-de-Grâce or HIA Val-de-Grâce) was a military hospital located at 74 boulevard de Port-Royal in the 5th arrondissement of Paris, France. It was closed as a hospital in 2016. History The church of the Val-de-Grâce was built by order of Queen Anne of Austria, wife of Louis XIII. After the birth of her son Louis XIV after 23 years of childless marriage, Anne showed her gratitude to the Virgin Mary by building a church on the land of a Benedictine convent. Louis XIV is said to have laid the cornerstone for the Val-de-Grâce in a ceremony that took place 1 April 1645, when he was seven years old. The church of the Val-de-Grâce, designed by François Mansart and Jacques Lemercier, is considered by some as Paris's best example of baroque architecture (curving lines, elaborate ornamentation, and harmony of different elements). Construction began in 1645 and was completed in 1667. The Benedictine nuns provided medical ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lutetian Limestone
Lutetian limestone (in French language, French, ''calcaire lutécien'', and formerly ''calcaire grossier'') — also known as “Paris stone” — is a variety of limestone particular to the Eocene-aged deposits in the Paris Basin of France, most notably underlying the city of Paris, France, Paris. It has been a source of wealth as an economic and versatile building material since ancient Roman times (see Mines of Paris) and has contributed markedly to the unique visual appeal of the “City of Light”. It has been hailed as “the warm, elusive, cream-grey stone of the French capital”. In addition to Paris, the Lutetian limestone also extends north and eastwards through France, and has also been mined in areas such as Reims, Rheims, Laon and Soissons. Its formation dates to the Eocene epoch's Lutetian age, between . The name "Lutetian" derives from Lutetia (French, ''Lutèce'') which was the name of Paris in ancient times. The Lutetian age was named after the limestone of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plan Paris Gerards1908 Jms
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with details of timing and resources, used to achieve an objective to do something. It is commonly understood as a temporal set of intended actions through which one expects to achieve a goal. For spatial or planar topologic or topographic sets see map. Plans can be formal or informal: * Structured and formal plans, used by multiple people, are more likely to occur in projects, diplomacy, careers, economic development, military campaigns, combat, sports, games, or in the conduct of other business. In most cases, the absence of a well-laid plan can have adverse effects: for example, a non-robust project plan can cost the organization time and money. * Informal or ad hoc plans are created by individuals in all of their pursuits. The most popular ways to describe plans are by their breadth, time frame, and specificity; however, these planning classifications are not independent of one another. For instance, there is a close rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |