|
Carry-lookahead Adder
A carry-lookahead adder (CLA) or fast adder is a type of Adder (electronics), electronics adder used in digital logic. A carry-lookahead adder improves speed by reducing the amount of time required to determine carry bits. It can be contrasted with the simpler, but usually slower, ripple-carry adder (RCA), for which the carry bit is calculated alongside the sum bit, and each stage must wait until the previous carry bit has been calculated to begin calculating its own sum bit and carry bit. The carry-lookahead adder calculates one or more carry bits before the sum, which reduces the wait time to calculate the result of the larger-value bits of the adder. Already in the mid-1800s, Charles Babbage recognized the performance penalty imposed by the ripple-carry used in his Difference engine, Difference Engine, and subsequently designed mechanisms for ''anticipating carriage'' for his never-built Analytical Engine. Konrad Zuse is thought to have implemented the first carry-lookahead ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adder (electronics)
An adder, or summer, is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of microprocessor, processors, adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALUs). They are also used in other parts of the processor, where they are used to calculate address space, addresses, database index, table indices, increment and decrement operators and similar operations. Although adders can be constructed for many number representations, such as binary-coded decimal or excess-3, the most common adders operate on binary numbers. In cases where two's complement or ones' complement is being used to represent negative numbers, it is trivial to modify an adder into an adder–subtractor. Other signed number representations require more logic around the basic adder. History George Stibitz invented the 2-bit binary adder (the Model K (calculator), Model K) in 1937. Binary adders Half adder The half adder adds two single binary digits A and B. It has two outputs, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Adder
An adder, or summer, is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of processors, adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALUs). They are also used in other parts of the processor, where they are used to calculate addresses, table indices, increment and decrement operators and similar operations. Although adders can be constructed for many number representations, such as binary-coded decimal or excess-3, the most common adders operate on binary numbers. In cases where two's complement or ones' complement is being used to represent negative numbers, it is trivial to modify an adder into an adder–subtractor. Other signed number representations require more logic around the basic adder. History George Stibitz invented the 2-bit binary adder (the Model K) in 1937. Binary adders Half adder The half adder adds two single binary digits A and B. It has two outputs, sum (S) and carry (C). The carry signal represents an overf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculative Execution
Speculative execution is an optimization (computer science), optimization technique where a computer system performs some task that may not be needed. Work is done before it is known whether it is actually needed, so as to prevent a delay that would have to be incurred by doing the work after it is known that it is needed. If it turns out the work was not needed after all, most changes made by the work are reverted and the results are ignored. The objective is to provide more Concurrency (computer science), concurrency if extra Resource (computer science), resources are available. This approach is employed in a variety of areas, including branch predictor, branch prediction in instruction pipeline, pipelined CPU, processors, value prediction for exploiting value locality, prefetching Instruction prefetch, memory and File system, files, and optimistic concurrency control in Relational database management system, database systems. Speculative multithreading is a special case of specu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carry Operator
The carry operator, symbolized by the ¢ sign, is an abstraction of the operation of determining whether a portion of an adder network generates or propagates a carry Carry or carrying may refer to: People *Carry (name) Finance * Carried interest (or carry), the share of profits in an investment fund paid to the fund manager * Carry (investment), a financial term: the carry of an asset is the gain or cost of .... It is defined as follows: :(G_1, P_1) \ ¢ (G_2, P_2) = (G_1 \lor G_2 P_1, P_2 P_1) External links * http://www.aoki.ecei.tohoku.ac.jp/arith/mg/algorithm.html Computer arithmetic {{comp-sci-theory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carry-skip Adder
A carry-skip adder (also known as a carry-bypass adder) is an adder implementation that improves on the delay of a ripple-carry adder with little effort compared to other adders. The improvement of the worst-case delay is achieved by using several carry-skip adders to form a block-carry-skip adder. Unlike other fast adders, carry-skip adder performance is increased with only some of the combinations of input bits. This means, speed improvement is only probabilistic. Single carry-skip adder The worst case for a simple one level ripple-carry adder occurs, when the propagate-condition is true for each digit pair (a_i, b_i). Then the carry-in ripples through the n-bit adder and appears as the carry-out after \tau_(n) \approx n \cdot \tau_. For each operand input bit pair (a_i,b_i) the propagate-conditions p_i = a_i \oplus b_i are determined using an XOR-gate. When all propagate-conditions are ''true'', then the carry-in bit c_0 determines the carry-out bit. The ''n''-bit-carry-sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Gate
A transmission gate (TG) is an analog gate similar to a relay that can conduct in both directions or block by a control signal with almost any voltage potential. It is a CMOS-based switch, in which PMOS passes a strong 1 but poor 0, and NMOS passes strong 0 but poor 1. Both PMOS and NMOS work simultaneously. Structure In principle, a transmission gate is made up of two field-effect transistors (FET), in which – in contrast to traditional discrete field-effect transistors – the substrate terminal (bulk) is not connected internally to the source terminal. The two transistors, an n-channel MOSFET and a p-channel MOSFET, are connected in parallel with the drain and source terminals of the two transistors connected together. Their gate terminals are connected to each other by a NOT gate (inverter), to form the control terminal. Unlike with discrete FETs, the substrate terminal is not connected to the source connection. Instead, the substrate terminals are connected to the resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Logic (digital Electronics)
In integrated circuit design, dynamic logic (or sometimes clocked logic) is a design methodology in combinational logic circuits, particularly those implemented in metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology. It is distinguished from the so-called static logic by exploiting temporary storage of information in stray and gate capacitances. It was popular in the 1970s and has seen a recent resurgence in the design of high-speed digital electronics, particularly central processing units (CPUs). Dynamic logic circuits are usually faster than static counterparts and require less surface area, but are more difficult to design. Dynamic logic has a higher average rate of voltage transitions than static logic, but the capacitive loads being transitioned are smaller so the overall power consumption of dynamic logic may be higher or lower depending on various tradeoffs. When referring to a particular logic family, the dynamic adjective usually suffices to distinguish the design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss ", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type semiconductor, p-type and n-type semiconductor, n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including Nonvolatile BIOS memory, CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data conversion, data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1948, Bardeen and Brattain patented an insulated-gate transistor (IGFET) with an inversion layer. Bardeen's concept forms the basis of CMOS technology today. The CMOS process was presented by Fairchild Semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Families
In computer engineering, a logic family is one of two related concepts: * A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compatible logic levels and power supply characteristics within a family. Many logic families were produced as individual components, each containing one or a few related basic logical functions, which could be used as "building-blocks" to create systems or as so-called "glue" to interconnect more complex integrated circuits. * A logic family may also be a set of techniques used to implement logic within VLSI integrated circuits such as CPU, central processors, memories, or other complex functions. Some such logic families use dynamic logic (digital logic)#Static versus dynamic logic, static techniques to minimize design complexity. Other such logic families, such as domino logic, use dynamic logic (digital logic), clocked dynamic techniques to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination, for example in the electromagnetic field, a wire, gas, fluid or solid body. Physics * An electromagnetic wave travelling through a medium has a propagation delay determined by the speed of light in that particular medium, or ca. 1 nanosecond per in a vacuum. * An electric signal travelling through a wire has an propagation delay of ca. 1 nanosecond per . See also radio propagation, velocity factor, signal velocity and mechanical wave. Electronics Logic gates can have a gate delay ranging from picoseconds to more than 10 nanoseconds, depending on the technology being used. It is the time between the gate input becoming stable and the gate output becoming stable. Manufacturers often refer to the time from the input changing to 50% of its final input level, to the output reaching 50% of its final output level; this may depend on the direction of the level change, in which case separate fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
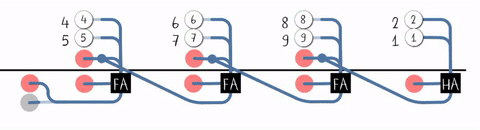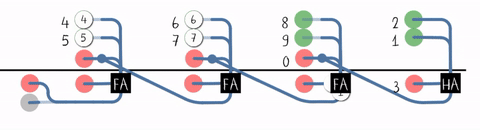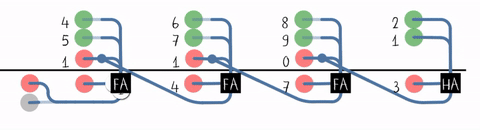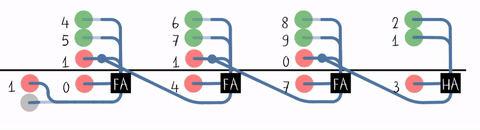
Lookahead-carry Unit
A lookahead carry unit (LCU) is a logical unit in digital circuit design used to decrease calculation time in adder units and used in conjunction with carry look-ahead adder A carry-lookahead adder (CLA) or fast adder is a type of electronics adder used in digital logic. A carry-lookahead adder improves speed by reducing the amount of time required to determine carry bits. It can be contrasted with the simpler, but ...s (CLAs). 4-bit adder A single 4-bit CLA is shown below: 16-bit adder By combining four 4-bit CLAs, a 16-bit adder can be created but additional logic is needed in the form of an LCU. The LCU accepts the group propagate (P_G) and group generate (G_G) from each of the four CLAs. P_G and G_G have the following expressions for each CLA adder: :P_G = P_0 \cdot P_1 \cdot P_2 \cdot P_3 :G_G = G_3 + G_2 \cdot P_3 + G_1 \cdot P_2 \cdot P_3 + G_0 \cdot P_1 \cdot P_2 \cdot P_3 The LCU then generates the carry input for each CLA. Assume that P_i is P_G and G_i is G_G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |