|
Carcinisation
Carcinisation (or carcinization) is an example of convergent evolution in which a crustacean evolves into a crab-like form from a non-crab-like form. The term was introduced into evolutionary biology by L. A. Borradaile, who described it as "one of the many attempts of Nature to evolve a crab". Most carcinised crustaceans belong to the infraorder Anomura. Definition of carcinised morphology It was stated by Lancelot Alexander Borradaile in 1916 that: Keiler et al., 2017 defines a carcinised morphology as follows: * "The carapace is flatter than it is broad and possesses lateral margins" * "The sternites are fused into a wide sternal plastron which possesses a distinct emargination on its posterior margin." * "The pleon is flattened and strongly bent, in dorsal view completely hiding the tergites of the fourth pleonal segment, and partially or completely covers the plastron" Examples Carcinisation is believed to have occurred independently in at least five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting " tail" ( abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the world's oceans, in freshwater, and on land, are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, and have a single pair of pincers. They first appeared during the Jurassic Period. Description Crabs are generally covered with a thick exoskeleton, composed primarily of highly mineralized chitin, and armed with a pair of chelae (claws). Crabs vary in size from the pea crab, a few millimeters wide, to the Japanese spider crab, with a leg span up to . Several other groups of crustaceans with similar appearances – such as king crabs and porcelain crabs – are not true crabs, but have evolved features similar to true crabs through a process known as carcinisation. Environment Crabs are found in all of the world's oceans, as well as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomura
Anomura (sometimes Anomala) is a group of decapod crustaceans, including hermit crabs and others. Although the names of many anomurans include the word ''crab'', all true crabs are in the sister group to the Anomura, the Brachyura (the two groups together form the clade Meiura). Description The name Anomura derives from an old classification in which reptant decapods were divided into Macrura (long-tailed), Brachyura (short-tailed) and Anomura (differently-tailed). The alternative name Anomala reflects the unusual variety of forms in this group; whereas all crabs share some obvious similarities, the various groups of anomurans are quite dissimilar. The group has been moulded by several instances of carcinisation – the development of a crab-like body form. Thus, the king crabs (Lithodidae), porcelain crabs (Porcellanidae) and hairy stone crab (Lomisidae) are all separate instances of carcinisation. As decapods (meaning ''ten-legged''), anomurans have ten pereiopods, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
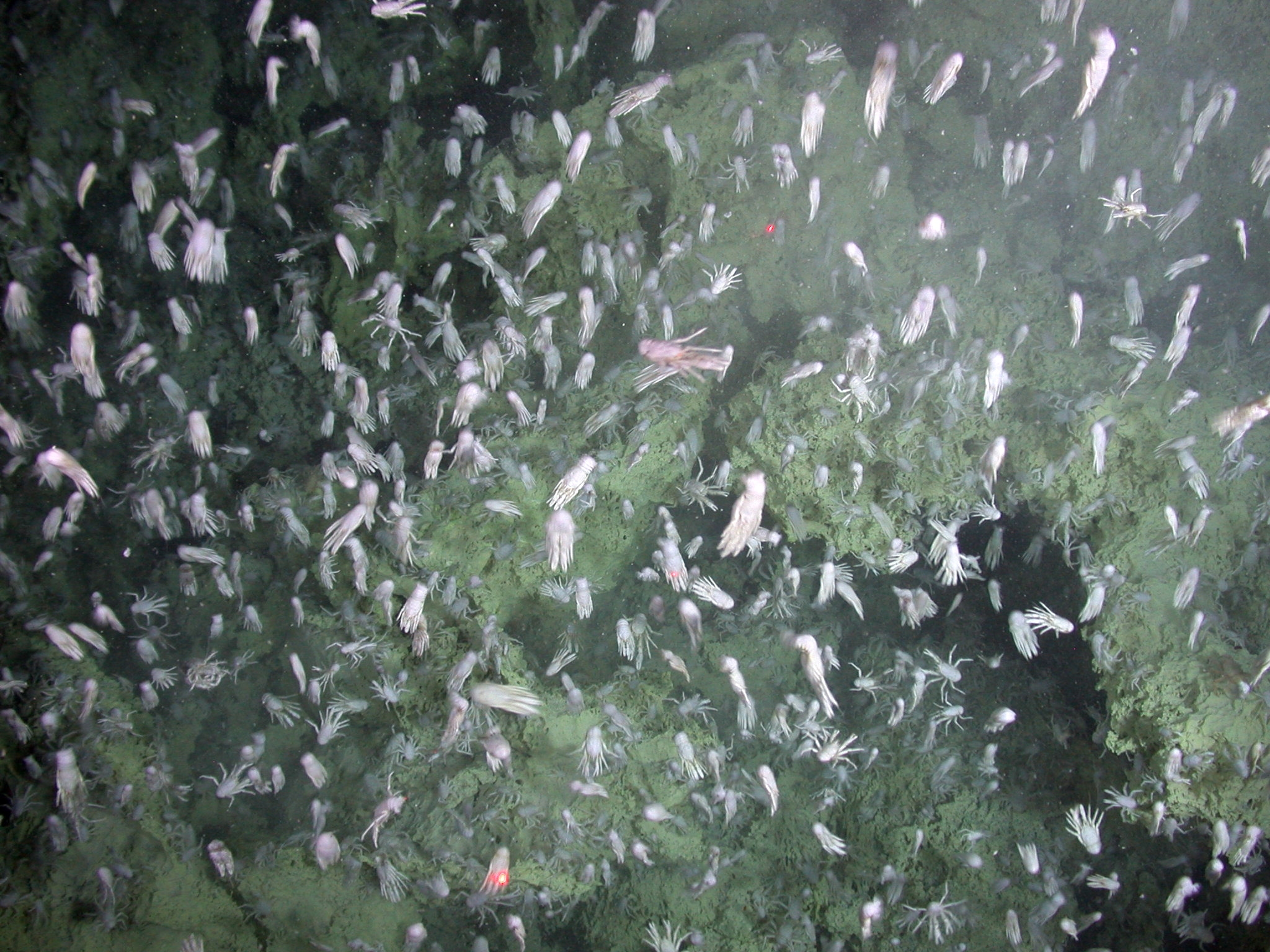
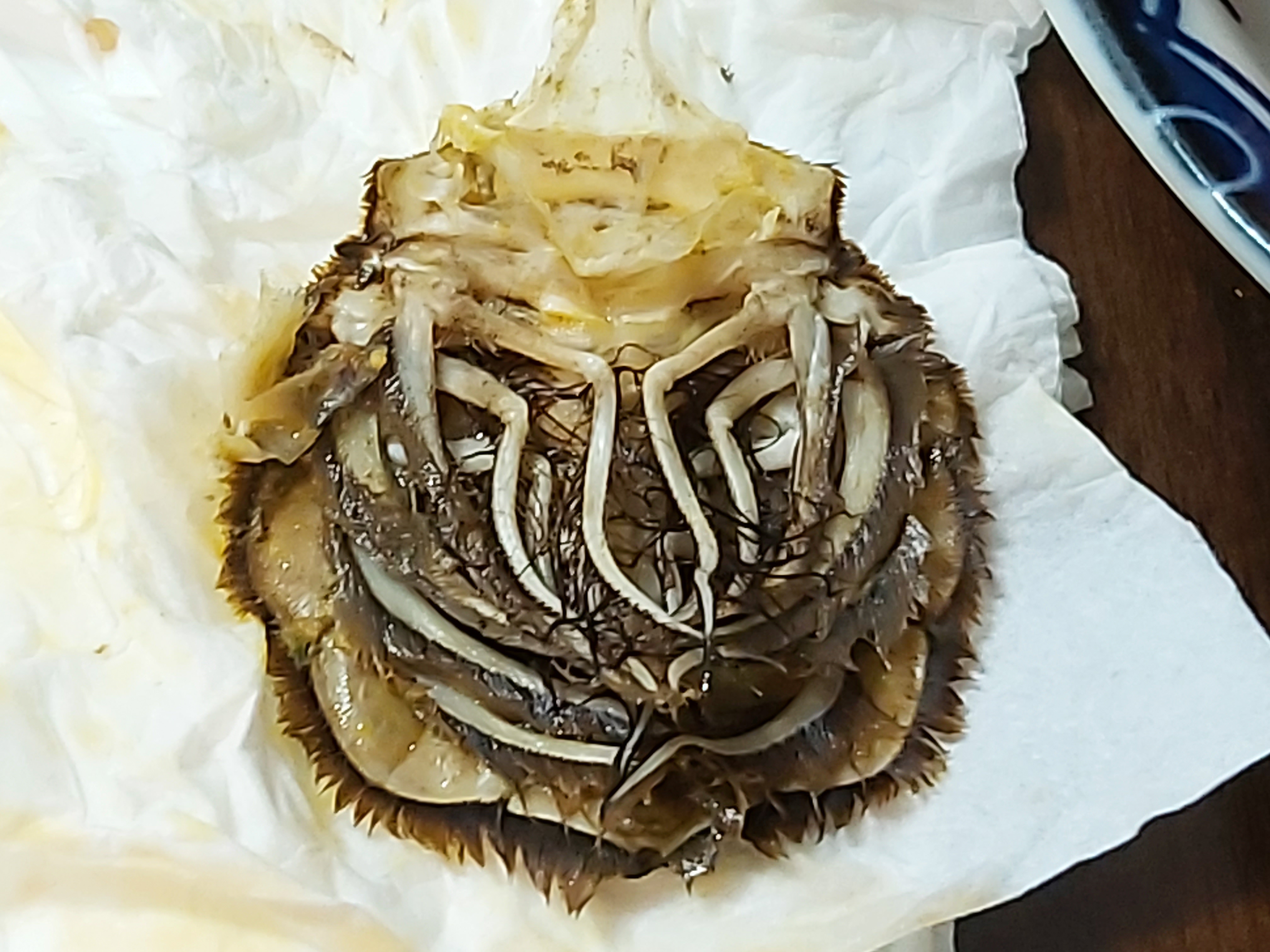
King Crab
King crabs are a taxon of decapod crustaceans chiefly found in cold seas. Because of their large size and the taste of their meat, many species are widely caught and sold as food, the most common being the red king crab (''Paralithodes camtschaticus''). King crabs are generally thought to be derived from hermit crab-like ancestors within the Paguridae, which may explain the asymmetry still found in the adult forms. This ancestry is supported by several anatomical peculiarities which are present only in king crabs and hermit crabs. Although some doubt still exists about this hypothesis, king crabs are the most widely quoted example of carcinisation among the Decapoda. The evidence for this explanation comes from the asymmetry of the king crab's abdomen, which is thought to reflect the asymmetry of hermit crabs, which must fit into a spiral shell. Controversial taxon Although formerly classified among the hermit crabs in the superfamily Paguroidea, king crabs are now place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairy Stone Crab
The hairy stone crab (''Lomis hirta'') is a crab-like crustacean that lives in the littoral zone of southern Australia from Bunbury, Western Australia, to the Bass Strait. It is the only species in its family. It is wide, slow-moving, and covered in brown hair which camouflages it against the rocks upon which it lives. Some controversy exists about the relationship between ''L. hirta'' and the other anomuran families. Candidates for its closest relatives have included hermit crabs, specifically king crabs, and '' Aegla''. It is clear, however, that ''Lomis'' represents a separate case of carcinisation Carcinisation (or carcinization) is an example of convergent evolution in which a crustacean evolves into a crab-like form from a non-crab-like form. The term was introduced into evolutionary biology by L. A. Borradaile, who describ .... Notes References {{Taxonbar, from=Q3781116 Anomura Crustaceans of Australia Crustaceans described in 1818 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcelain Crab
Porcelain crabs are decapod crustaceans in the widespread family Porcellanidae, which superficially resemble true crabs. They have flattened bodies as an adaptation for living in rock crevices. They are delicate, readily losing limbs when attacked, and use their large claws for maintaining territories. They first appeared in the Tithonian age of the Late Jurassic epoch, 145–152 million years ago. Description Porcelain crabs are small, usually with body widths less than . They share the general body plan of a squat lobster, but their bodies are more compact and flattened, an adaptation for living and hiding under rocks. Porcelain crabs are quite fragile animals, and often shed their limbs to escape predators, hence their name. The lost appendage can grow back over several moults. Porcelain crabs have large chelae (claws), which are used for territorial struggles, but not for catching food. The fifth pair of pereiopods is reduced and used for cleaning. Evolution Porcelain cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancelot Alexander Borradaile
Lancelot Alexander Borradaile (1872 – 20 October 1945) was an English zoologist, noted for his work on crustaceans and his books ''The Invertebrata'' and ''Manual of Elementary Zoology''. Legacy Borradaile may be best known for his undergraduate textbook titled ''Manual of Elementary Zoology'', and for ''The Invertebrata: a manual for the use of students'', co-written with F. A. Potts. As well as these generalist works, Borradaile also worked as a carcinologist. He published an important monograph ''On the Pontoniinae'' in 1917, based on material collected by the 1905 Percy Sladen Trust Expedition to the Indian Ocean, led by John Stanley Gardiner. He worked extensively on crabs and similar animals, and coined the term "carcinisation" to describe "one of the many attempts of Nature to evolve a crab". He is commemorated in the scientific names ''Metapenaeopsis borradaili'', ''Athanas borradailei'', '' Corallianassa borradailei'', '' Accalathura borradailei'' and ''Petrolisthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleon
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic Period
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined. By the beginning of the Jurassic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configuration of continents. It is the latest of three geological eras since complex life evolved, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. It started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians (placentals) in the northern hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia) in the southern hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squat Lobster
Squat lobsters are dorsoventrally flattened crustaceans with long tails held curled beneath the cephalothorax. They are found in the two superfamilies Galatheoidea and Chirostyloidea, which form part of the decapod infraorder Anomura, alongside groups including the hermit crabs and mole crabs. They are distributed worldwide in the oceans, and occur from near the surface to deep sea hydrothermal vents, with one species occupying caves above sea level. More than 900 species have been described, in around 60 genera. Some species form dense aggregations, either on the sea floor or in the water column, and a small number are commercially fished. Description The two main groups of squat lobsters share most features of their morphology. They resemble true lobsters in some ways, but are somewhat flattened dorsoventrally, and are typically smaller. Squat lobsters vary in carapace length (measured from the eye socket to the rear edge), from in the case of '' Munidopsis aries'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Pacific Species Of Petrolisthes, Allopetrolisthes, And Liopetrolisthes (Porcellanidae)
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)