|
Carbonyl Cyanide M-chlorophenyl Hydrazone
Carbonyl cyanide ''m''-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP; also known as ) is a chemical inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation. It is a nitrile, hydrazone and protonophore. In general, CCCP causes the gradual destruction of living cells and death of the organism, although mild doses inducing partial decoupling have been shown to increase median and maximum lifespan in '' C. elegans'' models, suggesting a degree of hormesis. CCCP causes an uncoupling of the proton gradient that is established during the normal activity of electron carriers in the electron transport chain. The chemical acts essentially as an ionophore and reduces the ability of ATP synthase to function optimally. It is routinely used as an experimental uncoupling agent in cell and molecular biology, particularly in the study of mitophagy, where it was integral in discovering the role of the Parkinson's disease-associated ubiquitin ligase Parkin. Outside of its effects on mitochondria, CCCP may also disrupt lysosomal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose is released by the cell in the citric acid cycle, producing carbon dioxide and the energetic reducing agent, electron donors NADH and FADH. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules and O2 to ATP synthase, produce ATP, which is used throughout the cell whenever energy is needed. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from the electron donors to a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrile
In organic chemistry, a nitrile is any organic compound that has a functional group. The name of the compound is composed of a base, which includes the carbon of the , suffixed with "nitrile", so for example is called " propionitrile" (or propanenitrile). The prefix '' cyano-'' is used interchangeably with the term ''nitrile'' in industrial literature. Nitriles are found in many useful compounds, including methyl cyanoacrylate, used in super glue, and nitrile rubber, a nitrile-containing polymer used in latex-free laboratory and medical gloves. Nitrile rubber is also widely used as automotive and other seals since it is resistant to fuels and oils. Organic compounds containing multiple nitrile groups are known as cyanocarbons. Inorganic compounds containing the group are not called nitriles, but cyanides instead. Though both nitriles and cyanides can be derived from cyanide salts, most nitriles are not nearly as toxic. Structure and basic properties The N−C−C geom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazone
Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure . They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen =O with the = functional group. They are formed usually by the action of hydrazine on ketones or aldehydes. Synthesis Hydrazine, organohydrazines, and 1,1-diorganohydrazines react with aldehydes and ketones to give hydrazones. : Phenylhydrazine reacts with reducing sugars to form hydrazones known as osazones, which was developed by German chemist Emil Fischer as a test to differentiate monosaccharides. Uses image:Pigment Yellow 97.svg, left, Pigment Yellow 97, a popular yellow colorant, is a hydrazone., 160px Hydrazones are the basis for various analyses of ketones and aldehydes. For example, dinitrophenylhydrazine coated onto a silica sorbent is the basis of an adsorption cartridge. The hydrazones are then eluted and analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a ultraviolet, UV detector. The compound carbonyl cyanide-p-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protonophore
A protonophore, also known as a proton translocator, is an ionophore that moves protons across lipid bilayers or other type of membranes. This would otherwise not occur as protons cations (H+) have positive charge and hydrophilic properties, making them unable to cross without a channel or transporter in the form of a protonophore. Protonophores are generally aromatic compounds with a negative charge, that are both hydrophobic and capable of distributing the negative charge over a number of atoms by π- orbitals which delocalize a proton's charge when it attaches to the molecule. Both the neutral and the charged protonophore can diffuse across the lipid bilayer by passive diffusion and simultaneously facilitate proton transport. Protonophores uncouple oxidative phosphorylation via a decrease in the membrane potential of the inner membrane of mitochondria. They stimulate mitochondria respiration and heat production. Protonophores (uncouplers) are often used in biochemistry research t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormesis
Hormesis is a two-phased dose-response relationship to an environmental agent whereby low-dose amounts have a beneficial effect and high-dose amounts are either inhibitory to function or toxic. Within the hormetic zone, the biological response to low-dose amounts of some stressors is generally favorable. An example is the breathing of oxygen, which is required in low amounts (in air) via respiration in living animals, but can be toxic in high amounts, even in a managed clinical setting. In toxicology, hormesis is a dose-response phenomenon to xenobiotics or other stressors. In physiology and nutrition, hormesis has regions extending from low-dose deficiencies to homeostasis, and potential toxicity at high levels. Physiological concentrations of an agent above or below homeostasis may adversely affect an organism, where the hormetic zone is a region of homeostasis of balanced nutrition. In pharmacology, the hormetic zone is similar to the therapeutic window. In the context of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncoupler
An uncoupler or uncoupling agent is a molecule that disrupts oxidative phosphorylation in prokaryotes and mitochondria or photophosphorylation in chloroplasts and cyanobacteria by dissociating the reactions of ATP synthesis from the electron transport chain. The result is that the cell or mitochondrion expends energy to generate a proton-motive force, but the proton-motive force is dissipated before the ATP synthase can recapture this energy and use it to make ATP. Because the intracellular supply of protons is replenished, uncouplers actually stimulate cellular metabolism and oxygen consumption (despite their inhibitory effects on oxidative phosphorylation) and increase the energy cost of generating ATP. Uncouplers are capable of transporting protons through mitochondrial and lipid membranes. Description Classical uncouplers have five properties: # the complete release of respiratory control # the substitution of all coupled processes ( ATP synthesis, transhydrogenation, reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATP Synthase
ATP synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi). ATP synthase is a molecular machine. The overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is: * ADP + Pi + 2H+out ATP + H2O + 2H+in ATP synthase lies across a cellular membrane and forms an aperture that hydron (chemistry), protons can cross from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, imparting energy for the synthesis of ATP. This electrochemical gradient is generated by the electron transport chain and allows cells to store energy in ATP for later use. In prokaryote, prokaryotic cells ATP synthase lies across the plasma membrane, while in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells it lies across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Organisms capable of photosynthesis also have ATP synthase across the thylakoid membrane, which in plants is located in the chloroplast and in cyanobacteria is located in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitophagy
Mitophagy is the selective degradation of mitochondria by autophagy. It often occurs to defective mitochondria following damage or stress. The process of mitophagy was first described in 1915 by Margaret Reed Lewis and Warren Harmon Lewis. Ashford and Porter used electron microscopy to observe mitochondrial fragments in liver lysosomes by 1962, and a 1977 report suggested that "mitochondria develop functional alterations which would activate autophagy." The term "mitophagy" was coined by J.J. Lemasters et al. in 2005, though earlier uses dating back to at least 1998 can be found. Mitophagy is key in keeping the cell healthy. It promotes turnover of mitochondria and prevents accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria which can lead to cellular degeneration. It is mediated by Atg32 (in yeast) and NIX and its regulator BNIP3 in mammals. Mitophagy is regulated by PINK1 and parkin proteins. In addition to the selective removal of damaged mitochondria, mitophagy is also required to ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become more prevalent as the disease progresses. The motor symptoms are collectively called parkinsonism and include tremors, bradykinesia, spasticity, rigidity as well as postural instability (i.e., difficulty maintaining balance). Non-motor symptoms develop later in the disease and include behavior change (individual), behavioral changes or mental disorder, neuropsychiatric problems such as sleep abnormalities, psychosis, anosmia, and mood swings. Most Parkinson's disease cases are idiopathic disease, idiopathic, though contributing factors have been identified. Pathophysiology involves progressive nerve cell death, degeneration of nerve cells in the substantia nigra, a midbrain region that provides dopamine to the basal ganglia, a system invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ubiquitin Ligase
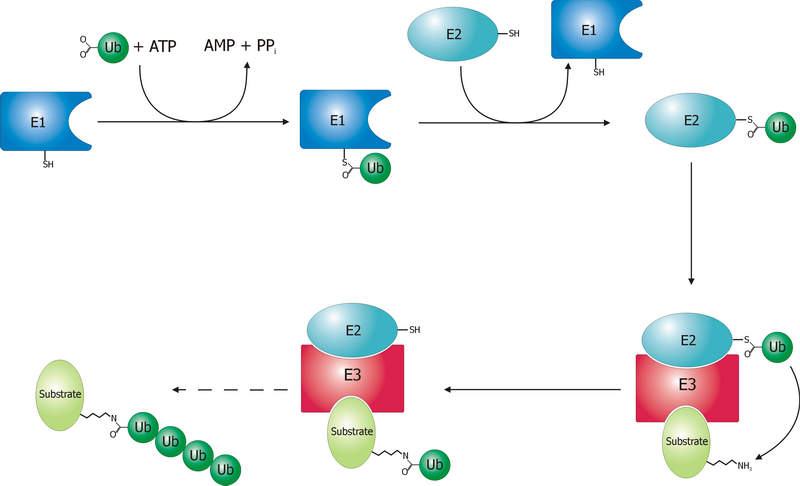
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another protein (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
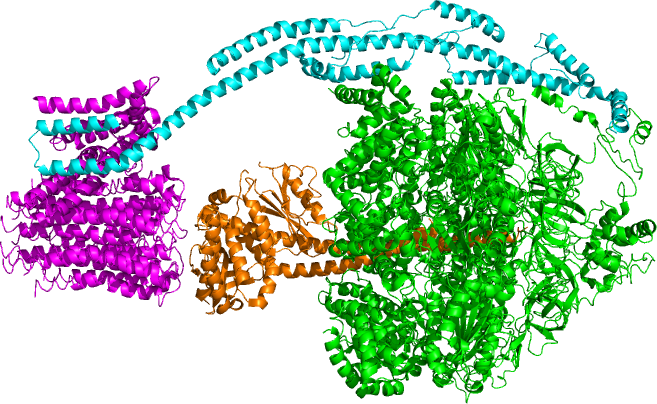
Parkin (ligase)
Parkin is a 465-amino acid residue E3 ubiquitin ligase, a protein that in humans and mice is encoded by the ''PARK2'' gene. Parkin plays a critical role in ubiquitination – the process whereby molecules are covalently labelled with ubiquitin (Ub) and directed towards degradation in proteasomes or lysosomes. Ubiquitination involves the sequential action of three enzymes. First, an E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme binds to inactive Ub in eukaryotic cells via a thioester bond and mobilises it in an ATP-dependent process. Ub is then transferred to an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme before being conjugated to the target protein via an E3 ubiquitin ligase. There exists a multitude of E3 ligases, which differ in structure and substrate specificity to allow selective targeting of proteins to intracellular degradation. In particular, parkin recognises proteins on the outer membrane of mitochondria upon cellular insult and mediates the clearance of damaged mitochondria via autophagy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone
Carbonyl cyanide-''p''-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone (FCCP) is an ionophore that is a mobile ion carrier. It is referred to as an Uncoupler, uncoupling agent because it disrupts Adenosine triphosphate, ATP ATP synthase, synthesis by transporting hydrogen ions through the mitochondrial membrane before they can be used to provide the energy for oxidative phosphorylation. It is a nitrile and hydrazone. FCCP was first described in 1962 by Heytler. See also * Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone, Carbonyl cyanide ''m''-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP) References {{reflist Ionophores Nitriles Trifluoromethyl ethers Uncouplers Hydrazones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |