|
Capsular Polishing
Phacoemulsification is a cataract surgery method in which the internal lens of the eye which has developed a cataract is emulsified with the tip of an ultrasonic handpiece and aspirated from the eye. Aspirated fluids are replaced with irrigation of balanced salt solution to maintain the volume of the anterior chamber during the procedure. This procedure minimises the incision size and reduces the recovery time and risk of surgery-induced astigmatism. It is best suited to relatively soft cataracts, where the ultrasonic energy required is moderate, and insertion of foldable intraocular prosthetic lenses, which take advantage of the small incision possible. It is the most common procedure for cataract removal in the developed world, with an excellent prognosis in uncomplicated cases. Etymology The term originated from phaco- (Greek ''phako-'', comb. form of ''phakós'', lentil; see lens) + emulsification. Contraindications The same general contraindications for cataract surgery ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peristaltic Pump
A peristaltic pump, also commonly known as a roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained in a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. Most peristaltic pumps work through rotary motion, though linear peristaltic pumps have also been made. The rotor has a number of "wipers" or "rollers" attached to its external circumference, which compress the flexible tube as they rotate by. The part of the tube under compression is closed, forcing the fluid to move through the tube. Additionally, as the tube opens to its natural state after the rollers pass, more fluid is drawn into the tube. This process is called peristalsis and is used in many biological systems such as the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, there will be two or more rollers compressing the tube, trapping a body of fluid between them. The body of fluid is transported through the tube, toward the pump outlet. Peristaltic pumps may run continuousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyelid Speculum
A speculum (Latin for 'mirror'; : specula or speculums) is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision. History Vaginal and anal specula were used by the ancient Greeks and Romans, and speculum artifacts have been found in Pompeii. The modern vaginal speculum, developed by J. Marion Sims, consists of a hollow cylinder with a rounded end that is divided into two hinged parts, somewhat like the beak of a duck. This speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate it for examination of the vagina and cervix. A more modern vaginal speculum was developed by Marie Boivin (1773–1841), a French midwife, inventor, and obstetrics writer who has been called one of the most important women in medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disinfection
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface. Disinfectants can also be used to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculum (medical)
A speculum (Latin for 'mirror'; : specula or speculums) is a medical tool for investigating body orifices, with a form dependent on the orifice for which it is designed. In old texts, the speculum may also be referred to as a diopter or dioptra. Like an endoscope, a speculum allows a view inside the body; endoscopes, however, tend to have optics while a speculum is intended for direct vision. History Vaginal and anal specula were used by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and Ancient Rome, Romans, and speculum Artifact (archaeology), artifacts have been found in Pompeii. The modern vaginal speculum, developed by J. Marion Sims, consists of a hollow cylinder with a rounded end that is divided into two hinged parts, somewhat like the beak of a duck. This speculum is inserted into the vagina to dilate it for examination of the vagina and cervix. A more modern vaginal speculum was developed by Marie Boivin (1773–1841), a French midwife, inventor, and obstetrics writer who has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Povidone-iodine
Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may also be used for minor wounds. It may be applied to the skin as a liquid, an ointment or a powder. Side effects include skin irritation and sometimes swelling. If used on large wounds, kidney problems, high blood sodium, and metabolic acidosis may occur. It is not recommended in women who are less than 32 weeks pregnant. Frequent use is not recommended in people with thyroid problems or who are taking lithium. Povidone-iodine is a chemical complex of povidone, hydrogen iodide, and elemental iodine. The recommended strength solution contains 10% Povidone, with total iodine species equaling 10,000 ppm or 1% total titratable iodine. It works by releasing iodine which results in the death of a range of microorganisms. Povidone-iodine c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly Angiogenesis, vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
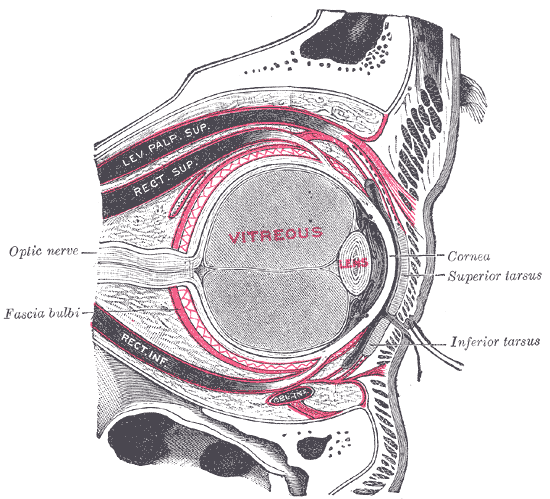
Globe Of The Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ in the visual system that reacts to visible light allowing eyesight. Other functions include maintaining the circadian rhythm, and keeping balance. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accounts for most of the optical power of the eye and accomplishes most of the focusing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focusing of light into images; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anaesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It allows patients to undergo surgical and dental procedures with reduced pain and distress. In many situations, such as cesarean section, it is safer and therefore superior to general anesthesia. The following terms are often used interchangeably: * ''Local anesthesia'', in a strict sense, is anesthesia of a small part of the body such as a tooth or an area of skin. * ''Regional anesthesia'' is aimed at anesthetizing a larger part of the body such as a leg or arm. * ''Conduction anesthesia'' encompasses a great variety of local and regional anesthetic techniques. Medical A local anesthetic is a drug that causes reversible local anesthesia and a loss of nociception. When it is used on specific nerve pathways (nerve block), effects such as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrobulbar Block
A retrobulbar block is a regional anesthetic nerve block in the retrobulbar space, which is the area located behind the globe of the eye. Injection of local anesthetic into this space constitutes the retrobulbar block. This injection provides akinesia of the extraocular muscles by blocking cranial nerves II, III, and VI, thereby preventing movement of the globe. Cranial nerve IV lies outside the muscle cone, and therefore is not affected by the local anesthesia. As a result, intorsion of the eye is still possible. It also provides sensory anesthesia of the conjunctiva, cornea and uvea by blocking the ciliary nerves. This block is most commonly employed for cataract surgery, but also provides anesthesia for other intraocular surgeries. Side effects and complications Complications associated with this block are either ocular or systemic. Local ocular complications include hematoma formation, optic nerve damage and perforation of the globe with possible blindness. Systemic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Tenon Injection
Sub-Tenon injection is an ocular route of drug administration. It involves administration of a medication to the area between the sclera and the Tenon's capsule. Posterior sub-Tenons steroid injections (PSTSI) is used in the treatment of posterior ocular inflammation, such as chronic uveitis. This route is also reported to be used to administer triamcinolone acetonide (a corticosteroid Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...) in the treatment of macular telangiectasia type 1. Also, it is used in the ocular anesthesia. Eye Wiki. References {{Reflist[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |