|
Calotype
Calotype or talbotype is an early photographic process introduced in 1841 by William Henry Fox Talbot, using paper coated with silver iodide. Paper texture effects in calotype photography limit the ability of this early process to record low contrast details and textures. The term ''calotype'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), "beautiful", and (), "impression". The process Talbot made his first successful camera photographs in 1835 using paper sensitised with silver chloride, which darkened in proportion to its exposure to light. This early "photogenic drawing" process was a ''printing-out'' process, i.e., the paper had to be exposed in the camera until the image was fully visible. A very long exposure—typically an hour or more—was required to produce an acceptable negative. In late 1840, Talbot worked out a very different ''developing-out'' process (a concept pioneered by the daguerreotype process introduced in 1839), in which only an extremely faint or completely i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
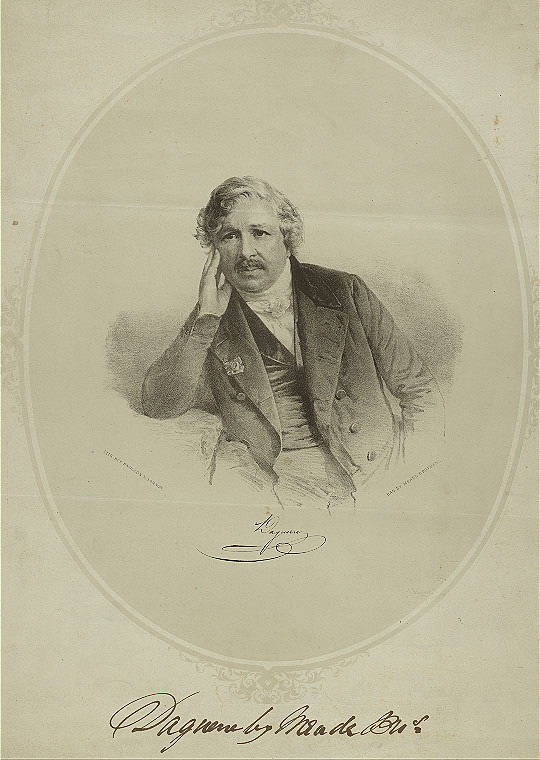
William Fox Talbot
William Henry Fox Talbot FRS FRSE FRAS (; 11 February 180017 September 1877) was an English scientist, inventor, and photography pioneer who invented the salted paper and calotype processes, precursors to photographic processes of the later 19th and 20th centuries. His work in the 1840s on photomechanical reproduction led to the creation of the photoglyphic engraving process, the precursor to photogravure. He was the holder of a controversial patent that affected the early development of commercial photography in Britain. He was also a noted photographer who contributed to the development of photography as an artistic medium. He published ''The Pencil of Nature'' (1844–46), which was illustrated with original salted paper prints from his calotype negatives and made some important early photographs of Oxford, Paris, Reading, and York. A polymath, Talbot was elected to the Royal Society in 1831 for his work on the integral calculus, and researched in optics, chemistry, elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper Texture Effects In Calotype Photography
Paper texture effects in calotype photography limit the ability of this early process to record low contrast details and textures. A calotype is a photographic negative produced on uncoated paper. (See Paper negative.) An important feature is that a relatively short exposure in a camera produces a latent image that is subsequently made visible by development. Then positive images for viewing are obtained by contact printing. This technique was in use principally from 1840 into the 1850s, when it was displaced by photography on glass. Skilled photographers were able to achieve dramatic results with the calotype process, and the reason for its eclipse may not be evident from viewing reproductions of early work. Background Practical photography plausibly dates from the announcement of the Daguerreotype in 1839. This stimulated work by others: in 1840, the Englishman Talbot discovered what he called the calotype process for making photographic negatives on writing paper with the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Calotype Club
The Edinburgh Calotype Club (1843 – c.1850s) of Scotland was the first photographic club in the world. Its members consisted of pioneering photographers primarily from Edinburgh and St Andrews. The efforts of the Club's members resulted in the production of two of the world's earliest assembled photographic albums, consisting of more than 300 images. Foundation The group was formed after the introduction of calotype photography to Edinburgh gentlemen by David Brewster, then Principal of St Andrews University, and also a close friend of the inventor of the calotype process, Henry Fox Talbot. Talbot sent Brewster examples of his work well before publishing on his findings, and it was Brewster who suggested that Talbot should only patent his invention in England, and not Scotland, which eventually allowed for the club's formation. Talbot sent Brewster examples of his calotype photography, but Brewster had to turn to a colleague at St Andrews, the Professor of Chemistry Dr J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Print
The salt print was the dominant paper-based photographic process for producing positive prints (from negatives) from 1839 until approximately 1860. The salted paper technique was created in the mid-1830s by English scientist and inventor Henry Fox Talbot. He made what he called "sensitive paper" for "photogenic drawing" by wetting a sheet of writing paper with a weak solution of ordinary table salt (sodium chloride), blotting and drying it, then brushing one side with a strong solution of silver nitrate. This produced a tenacious coating of silver chloride an especially light-sensitive chemical condition. The paper darkened where it was exposed to light. When the darkening was judged to be sufficient, the exposure was ended and the result was stabilized by applying a ''strong'' solution of salt, which altered the chemical balance and made the paper only slightly sensitive to additional exposure. In 1839, washing with a solution of sodium thiosulfate ("hypo") was found to be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Daguerre
Louis-Jacques-Mandé Daguerre ( , ; 18 November 1787 – 10 July 1851) was a French artist and photographer, recognized for his invention of the eponymous daguerreotype process of photography. He became known as one of the fathers of photography. Though he is most famous for his contributions to photography, he was also an accomplished painter, scenic designer, and a developer of the diorama theatre. Biography Louis Daguerre was born in Cormeilles-en-Parisis, Val-d'Oise, France. He was apprenticed in architecture, theatre design, and panoramic painting to Pierre Prévost, the first French panorama painter. Exceedingly adept at his skill of theatrical illusion, he became a celebrated designer for the theatre, and later came to invent the diorama, which opened in Paris in July 1822. In 1829, Daguerre partnered with Nicéphore Niépce, an inventor who had produced the world's first heliograph in 1822 and the oldest surviving camera photograph in 1826 or 1827. Niépce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
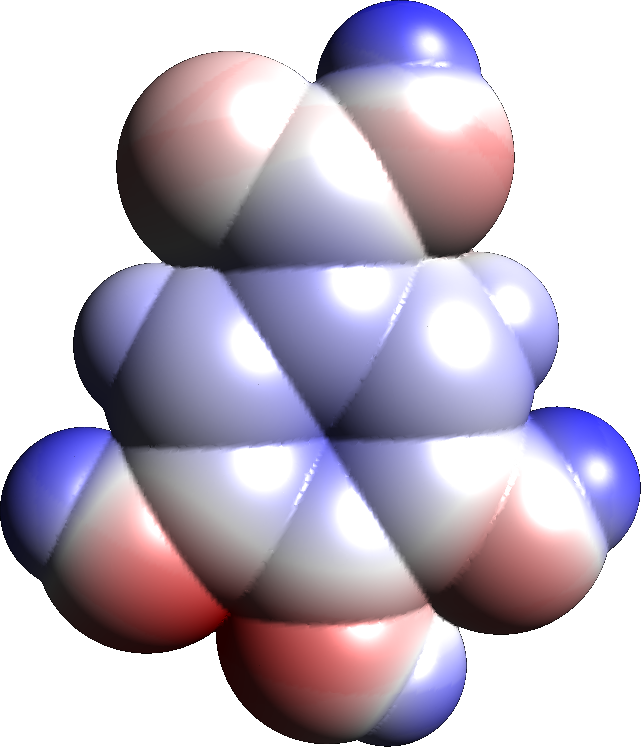
Gallic Acid
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6 H2( OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates". Isolation and derivatives Gallic acid is easily freed from gallotannins by acidic or alkaline hydrolysis. When heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, gallic acid converts to rufigallol. Hydrolyzable tannins break down on hydrolysis to give gallic acid and glucose or ellagic acid and glucose, known as gallotannins and ellagitannins, respectively. Biosynthesis Gallic acid is formed from 3-dehydroshikimate by the action of the enzyme shikimate dehydrogenase to produce 3,5-didehydroshikimate. This latter compound aromatizes. Reactions Oxidation and oxidative coupling Alkaline solutions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative (photography)
In photography, a negative is an image, usually on a strip or sheet of transparent plastic film, in which the lightest areas of the photographed subject appear darkest and the darkest areas appear lightest. This reversed order occurs because the extremely light-sensitive chemicals a camera film must use to capture an image quickly enough for ordinary picture-taking are darkened, rather than bleached, by exposure to light and subsequent photographic processing. In the case of color negatives, the colors are also reversed into their respective complementary colors. Typical color negatives have an overall dull orange tint due to an automatic color-masking feature that ultimately results in improved color reproduction. Negatives are normally used to make positive prints on photographic paper by projecting the negative onto the paper with a photographic enlarger or making a contact print. The paper is also darkened in proportion to its exposure to light, so a second reversal resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translucent
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Bromide
Silver bromide (AgBr) is a soft, pale-yellow, water-insoluble salt well known (along with other silver halides) for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgBr is widely used in photographic films and is believed by some to have been used for making the Shroud of Turin. The salt can be found naturally as the mineral bromargyrite. Preparation Although the compound can be found in mineral form, AgBr is typically prepared by the reaction of silver nitrate with an alkali bromide, typically potassium bromide: :AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) → AgBr(s)+ KNO3(aq) Although less convenient, the compound can also be prepared directly from its elements. Modern preparation of a simple, light-sensitive surface involves forming an emulsion of silver halide crystals in a gelatine, which is then coated onto a film or other support. The crystals are formed by precipitation in a controlled environment to produce small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Fixer
Photographic fixer is a mix of chemicals used in the final step in the photographic processing of film or paper. The fixer stabilises the image, removing the unexposed silver halide remaining on the photographic film or photographic paper, leaving behind the reduced metallic silver that forms the image. By fixation, the film or paper is insensitive to further action by light. Without fixing, the remaining silver halide would darken and cause fogging of the image. Fixation is commonly achieved by treating the film or paper with a solution of thiosulfate salt. Popular salts are sodium thiosulfate—commonly called hypo—and ammonium thiosulfate—commonly used in modern rapid fixer formulae. Fixation involves these chemical reactions (X = halide, typically Br−):Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. :AgX + 2 S2O32− → g(S2O3)2sup>3− + X− :AgX + 3 S2O32− → g(S2O3)3sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Thiosulphate
Sodium thiosulfate (sodium thiosulphate) is an inorganic compound with the formula . Typically it is available as the white or colorless pentahydrate, . The solid is an efflorescent (loses water readily) crystalline substance that dissolves well in water. Sodium thiosulfate is used in gold mining, water treatment, analytical chemistry, the development of silver-based photographic film and prints, and medicine. The medical uses of sodium thiosulfate include treatment of cyanide poisoning and pityriasis. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Uses Sodium thiosulfate is used predominantly in industry. For example, it is used to convert dyes to their soluble colorless forms, which are called leuco. It is also used to bleach "wool, cotton, silk, ...soaps, glues, clay, sand, bauxite, and... edible oils, edible fats, and gelatin." Medical uses Sodium thiosulfate is used in the treatment of cyanide poisoning. Other uses include topical treatment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
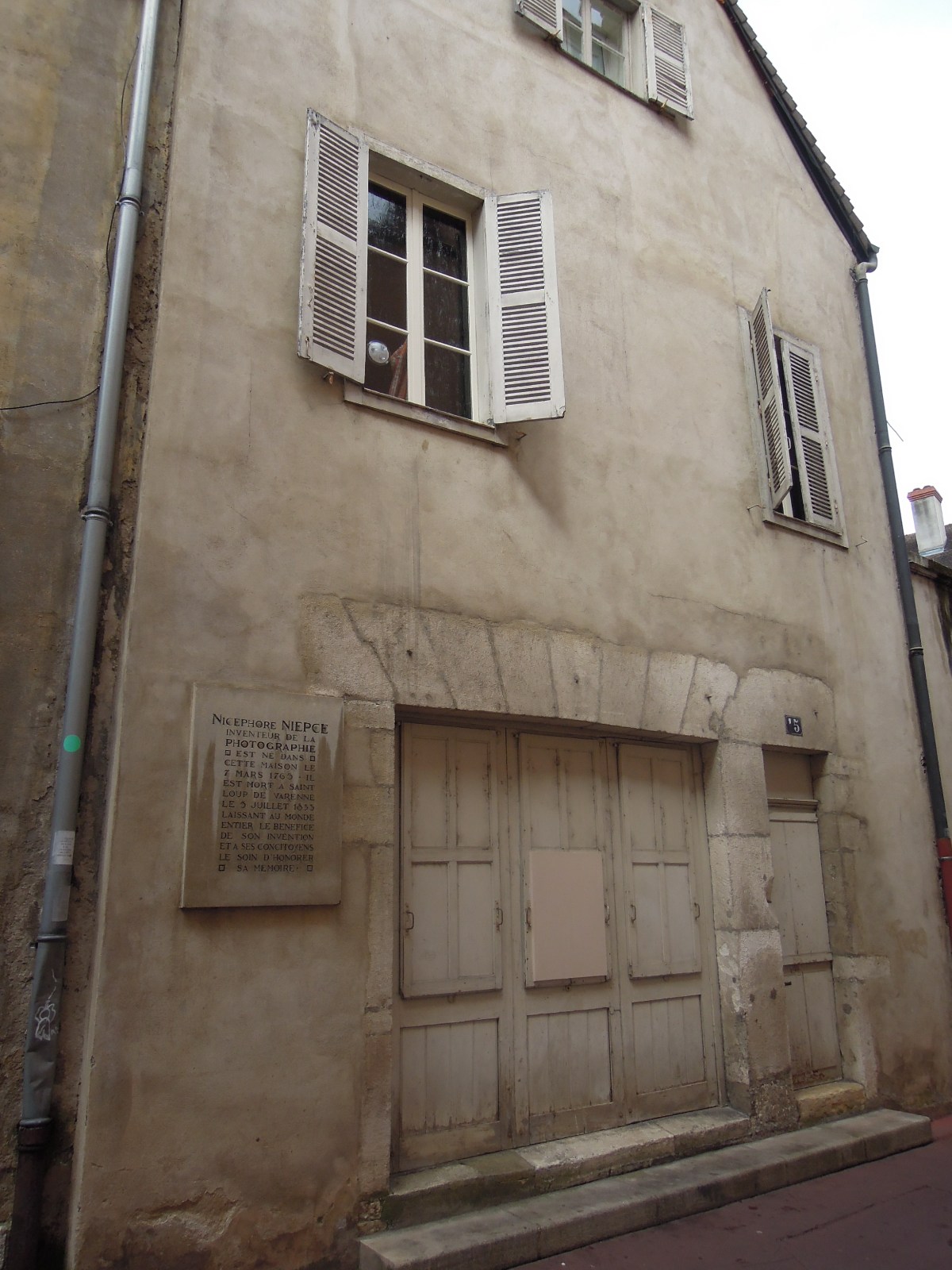
Nicéphore Niépce
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce (; 7 March 1765 – 5 July 1833), commonly known or referred to simply as Nicéphore Niépce, was a French inventor, usually credited with the invention of photography. Niépce developed heliography, a technique he used to create the world's oldest surviving product of a photographic process: a print made from a photoengraved printing plate in 1825. In 1826 or 1827, he used a primitive camera to produce the oldest surviving photograph of a real-world scene. Among Niépce's other inventions was the Pyréolophore, one of the world's first internal combustion engines, which he conceived, created, and developed with his older brother Claude Niépce. Biography Early life Niépce was born in Chalon-sur-Saône, Saône-et-Loire, where his father was a wealthy lawyer. His older brother Claude (1763–1828) was also his collaborator in research and invention, but died half-mad and destitute in England, having squandered the family wealth in pursuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)