|
Calibration Curve
In analytical chemistry, a calibration curve, also known as a standard curve, is a general method for determining the concentration of a substance in an unknown sample by comparing the unknown to a set of standard samples of known concentration. A calibration curve is one approach to the problem of instrument calibration; other standard approaches may mix the standard into the unknown, giving an internal standard. The calibration curve is a plot of how the instrumental response, the so-called analytical signal, changes with the concentration of the analyte (the substance to be measured). General use In more general use, a calibration curve is a Graph of a function, curve or Table (information), table for a measuring instrument which measures some parameter indirectly, giving values for the desired quantity as a function of values of sensor output. For example, a calibration curve can be made for a particular pressure transducer to determine applied pressure from transducer output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonogenic Assay
A clonogenic assay is a cell biology technique for studying the effectiveness of specific agents on the survival and proliferation of cells. It is frequently used in cancer research laboratories to determine the effect of drugs or radiation on proliferating tumor cells as well as for titration of Cell-killing Particles (CKPs) in virus stocks. It was first developed by T.T. Puck and Philip I. Marcus at the University of Colorado in 1955. Although this technique can provide accurate results, the assay is time-consuming to set up and analyze and can only provide data on tumor cells that can grow in culture. The word "clonogenic" refers to the fact that these cells are clones of one another. Procedure The experiment involves three major steps: # The treatment is applied to a sample of cells. # The cells are "plated" in a tissue culture vessel and allowed to grow. # The colonies produced are fixed, stained, and counted. At the conclusion of the experiment, the percentage of cells t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Selective Electrode
An ion-selective electrode (ISE), also known as a specific ion electrode (SIE), is a simple membrane-based potentiometric device which measures the activity of ions in solution. It is a transducer (or sensor) that converts the change in the concentration of a specific ion dissolved in a Solution (chemistry), solution into an electrical potential. ISE is a type of sensor device that senses changes in signal based on the surrounding environment through time. This device will have an input signal, a property that we wish to quantify, and an output signal, a quantity we can register. In this case, ion selective electrode are electrochemical sensors that give potentiometric signals. The voltage is theoretically dependent on the logarithm of the ionic activity, according to the Nernst equation. Analysis with ISEs expands throughout a range of technological fields such as biology, chemistry, environmental science and other industrial workplaces like agriculture. Ion-selective electrodes are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal. In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends the information to other electronics, frequently a computer processor. Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons ( tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base, and in innumerable applications of which most people are never aware. With advances in micromachinery and easy-to-use microcontroller platforms, the uses of sensors have expanded beyond the traditional fields of temperature, pressure and flow measurement, for example into MARG sensors. Analog sensors such as potentiometers and force-sensing resistors are still widely used. Their applications include manufacturing and machinery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
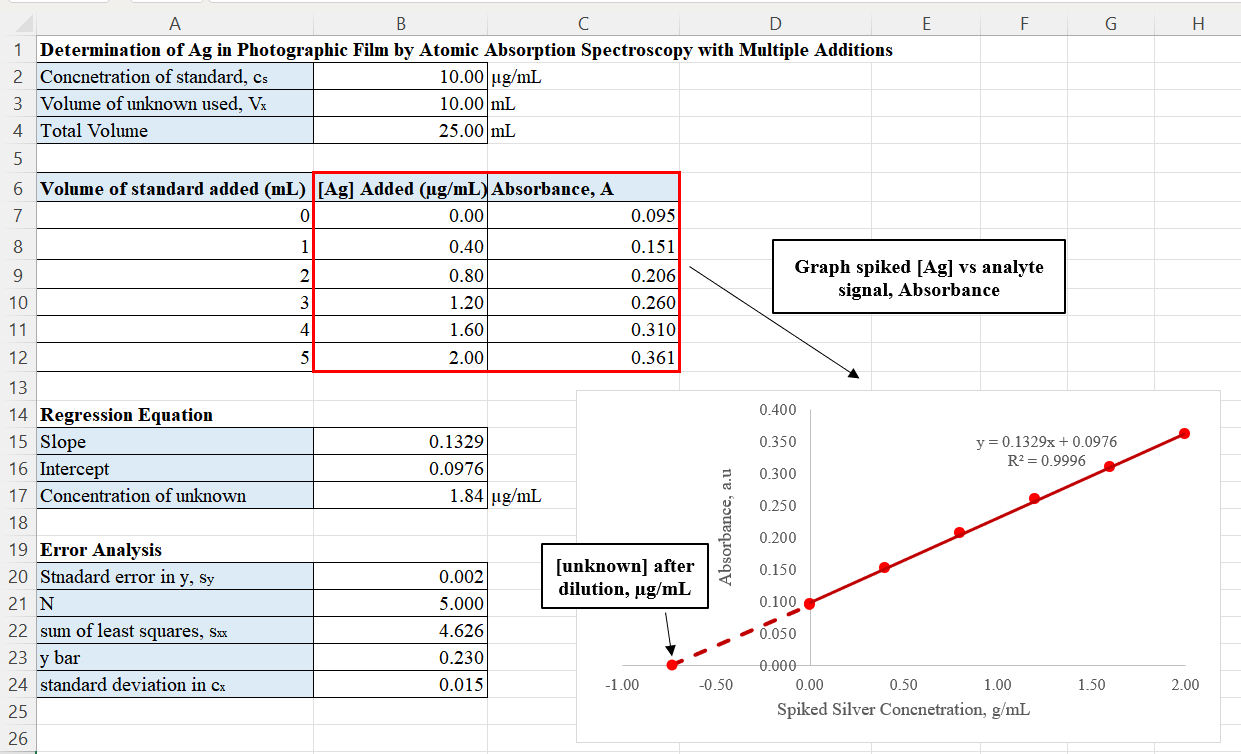
Standard Addition
The Standard addition method, also called known addition, often used in analytical chemistry, quantifies the analyte present in an unknown. This method is useful for analyzing complex samples where a matrix effect interferes with the analyte signal. In comparison to the calibration curve method, the standard addition method has the advantage of the matrices of the unknown and standards being nearly identical. This minimizes the potential bias arising from the matrix effect when determining the concentration. Variations Standard addition involves adding known amounts of analyte to an unknown sample, a process known as ''spiking''. By increasing the number of spikes, the analyst can extrapolate for the analyte concentration in the unknown that has not been spiked. There are multiple approaches to the standard addition. The following section summarize each approach. Single standard addition used in polarography In classic polarography, the standard addition method involves creati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with colored visible light. The color of the light emitted depends on the chemical composition of the substance. Fluorescent materials generally cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops. This distinguishes them from the other type of light emission, phosphorescence. Phosphorescent materials continue to emit light for some time after the radiation stops. This difference in duration is a result of quantum spin effects. Fluorescence occurs when a photon from incoming radiation is absorbed by a molecule, exciting it to a higher energy level, followed by the emission of light as the molecule returns to a lower energy state. The emitted light may have a longer wavelength and, therefore, a lower photon energy than the absorbed radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for Chemical polarity#Polarity of molecules, polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a Cell (biology), cell are dissolved in water within the cell. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for Organic compound, organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents (D-limonene, citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least Squares
The method of least squares is a mathematical optimization technique that aims to determine the best fit function by minimizing the sum of the squares of the differences between the observed values and the predicted values of the model. The method is widely used in areas such as regression analysis, curve fitting and data modeling. The least squares method can be categorized into linear and nonlinear forms, depending on the relationship between the model parameters and the observed data. The method was first proposed by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1805 and further developed by Carl Friedrich Gauss. History Founding The method of least squares grew out of the fields of astronomy and geodesy, as scientists and mathematicians sought to provide solutions to the challenges of navigating the Earth's oceans during the Age of Discovery. The accurate description of the behavior of celestial bodies was the key to enabling ships to sail in open seas, where sailors could no longer rely on la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorbance
Absorbance is defined as "the logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted radiant power through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls)". Alternatively, for samples which scatter light, absorbance may be defined as "the negative logarithm of one minus absorptance, as measured on a uniform sample". The term is used in many technical areas to quantify the results of an experimental measurement. While the term has its origin in quantifying the absorption of light, it is often entangled with quantification of light which is "lost" to a detector system through other mechanisms. What these uses of the term tend to have in common is that they refer to a logarithm of the ratio of a quantity of light incident on a sample or material to that which is detected after the light has interacted with the sample. The term absorption refers to the physical process of absorbing light, while absorbance does not always measure only absorption; it may measure attenuation (of transmitted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |