|
Calendar Spread
In finance, a calendar spread (also called a time spread or horizontal spread) is a spread trade involving the simultaneous purchase of futures or options expiring on a particular date and the sale of the same instrument expiring on another date. These individual purchases, known as the legs of the spread, vary only in expiration date; they are based on the same underlying market and strike price. The usual case involves the purchase of futures or options expiring in a more distant month--the far leg--and the sale of futures or options in a more nearby month--the near leg. Uses The calendar spread can be used to attempt to take advantage of a difference in the implied volatilities between two different months' options. The trader will ordinarily implement this strategy when the options they are buying have a distinctly lower implied volatility than the options they are writing (selling). In the typical version of this strategy, a rise in the overall implied volatility of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into Personal finance, personal, Corporate finance, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as Currency, currencies, loans, Bond (finance), bonds, Share (finance), shares, stocks, Option (finance), options, Futures contract, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, Investment, invested, and Insurance, insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, Financial risk, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spread Trade
In finance, a spread trade (also known as a relative value trade) is the simultaneous purchase of one security and sale of a related security, called legs, as a unit. Spread trades are usually executed with options or futures contracts as the legs, but other securities are sometimes used. They are executed to yield an overall net position whose value, called the spread, depends on the difference between the prices of the legs. Common spreads are priced and traded as a unit on futures exchanges rather than as individual legs, thus ensuring simultaneous execution and eliminating the execution risk of one leg executing but the other failing. Spread trades are executed to attempt to profit from the widening or narrowing of the spread, rather than from movement in the prices of the legs directly. Spreads are either "bought" or "sold" depending on whether the trade will profit from the widening or narrowing of the spread. Margin The volatility of the spread is typically much lower th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futures Contract
In finance, a futures contract (sometimes called futures) is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The item transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the ''forward price'' or ''delivery price''. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the ''delivery date''. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a Derivative (finance), derivative. Contracts are traded at futures exchanges, which act as a marketplace between buyers and sellers. The buyer of a contract is said to be the Long (finance), long position holder and the selling party is said to be the Short (finance), short position holder. As both parties risk their counter-party reneging if the price goes against them, the contract may involve both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset (or contingent liability) and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in '' over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
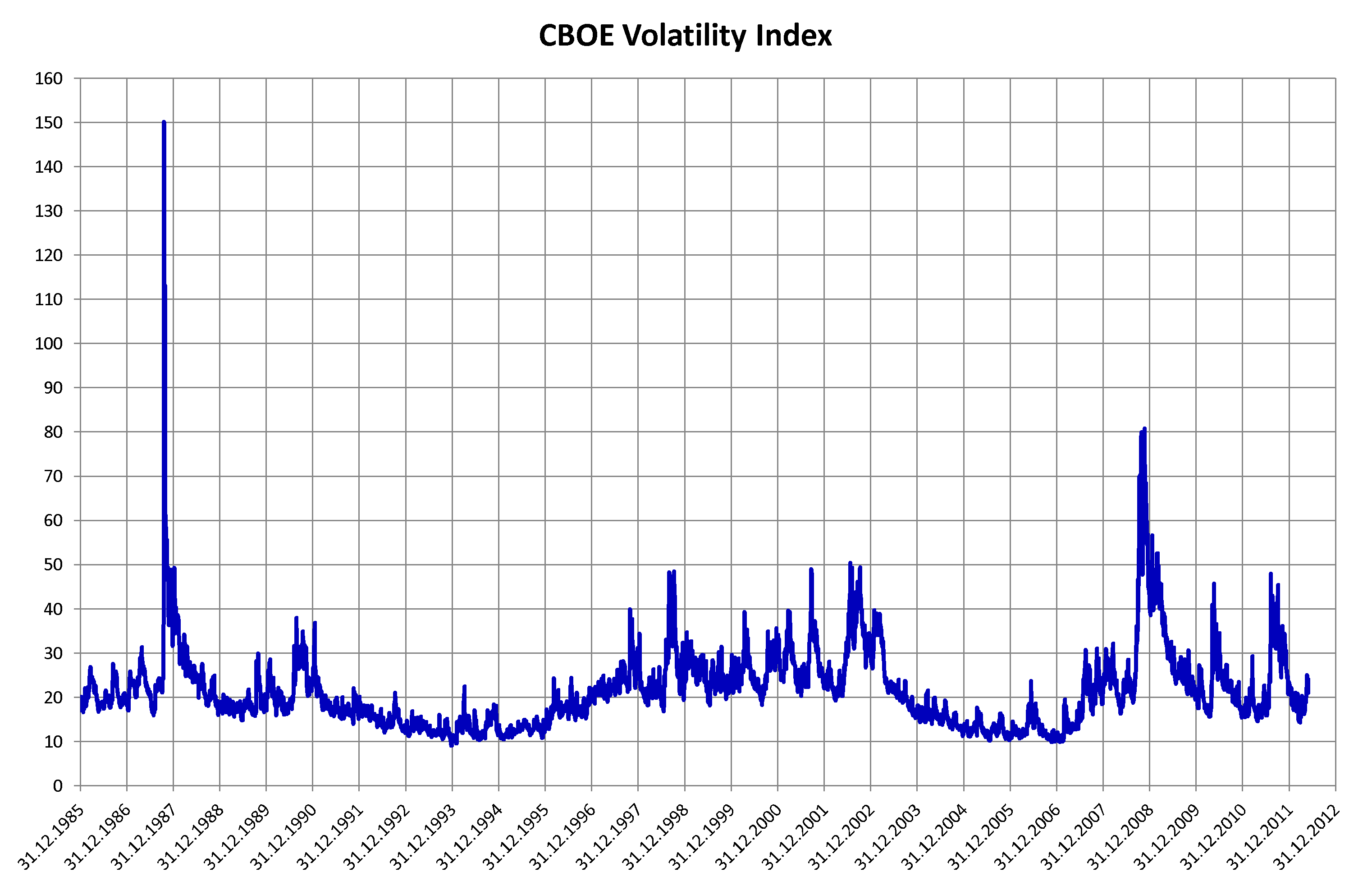
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
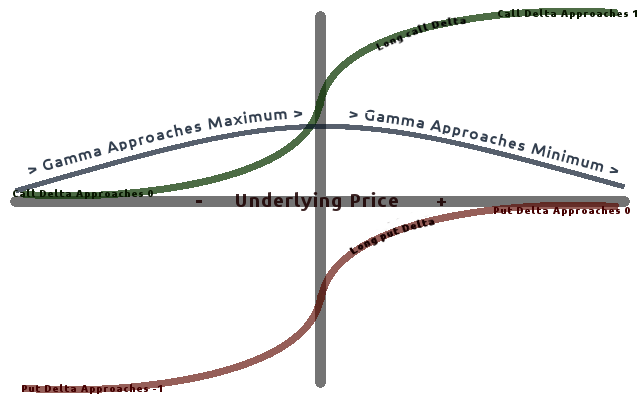
Greeks (finance)
In mathematical finance, the Greeks are the quantities (known in calculus as partial derivatives; first-order or higher) representing the sensitivity of the price of a derivative instrument such as an option to changes in one or more underlying parameters on which the value of an instrument or portfolio of financial instruments is dependent. The name is used because the most common of these sensitivities are denoted by Greek letters (as are some other finance measures). Collectively these have also been called the risk sensitivities, risk measures or hedge parameters. Use of the Greeks The Greeks are vital tools in risk management. Each Greek measures the sensitivity of the value of a portfolio to a small change in a given underlying parameter, so that component risks may be treated in isolation, and the portfolio rebalanced accordingly to achieve a desired exposure; see for example delta hedging. The Greeks in the Black–Scholes model (a relatively simple idealised mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolling (finance)
Rolling a contract is an investment concept meaning trading out of a contract and then buying the contract with next longest maturity (finance), maturity, so as to maintain a position with constant maturity. Motivation One may roll a contract because one has a special preference for a specific maturity—for example, the five-year Credit default swap, CDS rate of a given name—or because a given on-the-run security is more liquid than off-the-run securities. Examples While holding United States Treasury security, US Treasuries, one may wish to hold only the most recently issued security of a given maturity, the so-called On the run (finance), on-the-run security. Thus, if one has purchased the on-the-run 30-year treasury and a new 30-year auction occurs, one may sell the old treasury, which is now off-the-run, and purchase the new on-the-run treasury. There is generally very high trading activity on these dates, as contracts whose maturity falls on them are rolled. Index roll con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Options (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset (or contingent liability) and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in '' over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |