|
Cabin Pressurization
Cabin pressurization is a process in which conditioned air is pumped into the aircraft cabin, cabin of an aircraft or spacecraft in order to create a safe and comfortable environment for humans flying at high altitudes. For aircraft, this air is usually Bleed air, bled off from the gas turbine, gas turbine engines at the compressor stage, and for spacecraft, it is carried in high-pressure, often liquid oxygen, cryogenic, tanks. The air is cooled, humidified, and mixed with recirculated air by one or more Environmental control system (aircraft), environmental control systems before it is distributed to the cabin. The first experimental pressurization systems saw use during the 1920s and 1930s. In the 1940s, Boeing 307 Stratoliner, the first commercial aircraft with a pressurized cabin entered service. The practice would become widespread a decade later, particularly with the introduction of the British de Havilland Comet jetliner in 1949. However, South African Airways Flight 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing 737 Fuselage Train Hull 3473
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support services. Boeing is among the largest global aerospace manufacturers; it is the fourth-largest defense contractor in the world based on 2022 revenue and is the largest exporter in the United States by dollar value. Boeing was founded by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington, on July 15, 1916. The present corporation is the result of the merger of Boeing with McDonnell Douglas on August 1, 1997. As of 2023, the Boeing Company's corporate headquarters is located in the Crystal City neighborhood of Arlington County, Virginia. The company is organized into three primary divisions: Boeing Commercial Airplanes (BCA), Boeing Defense, Space & Security (BDS), and Boeing Global Services (BGS). In 2021, Boeing recorded $62.3billion in sales. Boei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airbus A350 XWB
The Airbus A350 is a flight length, long-range, wide-body twin-engine airliner developed and produced by Airbus. The initial A350 design proposed in 2004, in response to the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, would have been a development of the Airbus A330 with composite wings, advanced winglets, and new efficient engines. Due to inadequate market support, Airbus switched in 2006 to a clean-sheet "XWB" (eXtra Wide Body) design, powered by two Rolls-Royce Trent XWB high bypass turbofan engines. The prototype first flew on 14 June 2013 from Toulouse, France. Type certification from the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) was obtained in September 2014, followed by certification from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) two months later. The A350 is the first Airbus aircraft largely made of carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers. The fuselage is designed around a 3-3-3 nine-across economy cross-section, an increase from the eight-across A330/A340 2-4-2 configuration. It has a common t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood. The body normally attempts to compensate for this homeostatically, but if this fails or is overridden, the blood pH will rise, leading to respiratory alkalosis. This increases the affinity of oxygen to hemoglobin and makes it harder for oxygen to be released into body tissues from the blood. The symptoms of respiratory alkalosis include dizziness, tingling in the lips, hands, or feet, headache, weakness, fainting, and seizures. In extreme cases, it may cause carpopedal spasms, a flapping and contraction of the hands and feet. Factors that may induce or sustain hyperventilation include: physiological stress, anxiety or panic disorder, high altitude, head injury, stroke, respiratory disorders such as asthma, pneumonia, or hyper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude Sickness
Altitude sickness, the mildest form being acute mountain sickness (AMS), is a harmful effect of high altitude, caused by rapid exposure to low amounts of oxygen at high elevation. People's bodies can respond to high altitude in different ways. Symptoms of altitude sickness may include headaches, vomiting, tiredness, confusion, trouble sleeping, and dizziness. Acute mountain sickness can progress to high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) with associated shortness of breath or high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) with associated confusion. Chronic mountain sickness may occur after long-term exposure to high altitude. Altitude sickness typically occurs only above , though some people are affected at lower altitudes. Risk factors include a prior episode of altitude sickness, a high degree of activity, and a rapid increase in elevation. Being physically fit does not decrease the risk. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and is supported for those who have more than a minor reduction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the total amount of all constituents in a mixture, ''n''tot (also expressed in moles): :x_i = \frac It is denoted ''xi'' (lowercase Roman letter '' x''), sometimes (lowercase Greek letter chi). (For mixtures of gases, the letter ''y'' is recommended.) It is a dimensionless quantity with dimension of \mathsf/\mathsf and dimensionless unit of moles per mole (mol/mol or molmol−1) or simply 1; metric prefixes may also be used (e.g., nmol/mol for 10−9). When expressed in percent, it is known as the mole percent or molar percentage (unit symbol %, sometimes "mol%", equivalent to cmol/mol for 10−2). The mole fraction is called amount fraction by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and amount-of-substance fractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Pressure Of Oxygen
Blood gas tension refers to the partial pressure of gases in blood. There are several significant purposes for measuring gas tension. The most common gas tensions measured are oxygen tension (PxO2), carbon dioxide tension (PxCO2) and carbon monoxide tension (PxCO). The subscript ''x'' in each symbol represents the source of the gas being measured: "''a''" meaning arterial, "''A''" being alveolar, "''v''" being venous, and "''c''" being capillary. Blood gas tests (such as arterial blood gas tests) measure these partial pressures. Oxygen tension ;Arterial blood oxygen tension (normal) PaO2 – Partial pressure of oxygen at sea level ( in the atmosphere, 21% of the standard atmospheric pressure of ) in arterial blood is between . ;Venous blood oxygen tension (normal) PvO2 – Oxygen tension in venous blood at sea level is between . Carbon dioxide tension Carbon dioxide is a by-product of food metabolism and in high amounts has toxic effects including: dyspnea, acidosis and altered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Cannula
The nasal cannula (NC) is a device used to deliver supplemental oxygen or increased airflow to a patient or person in need of respiratory help. This device consists of a lightweight tube which on one end splits into two prongs which are placed in the nostrils curving toward the sinuses behind the nose, and from which a mixture of air and oxygen flows. The other end of the tube is connected to an oxygen supply such as a portable oxygen generator, or a wall connection in a hospital via a flowmeter. The cannula is generally attached to the patient by way of the tube hooking around the patient's ears or by an elastic headband, and the prongs curve toward the paranasal sinuses Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphe .... The earliest, and most widely used form of adult nasal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Mask
An oxygen mask is a mask that provides a method to transfer breathing gas, breathing oxygen gas from a storage tank to the lungs. Oxygen masks may cover only the nose and mouth (oral nasal mask) or the entire face (full-face mask). They may be made of plastic, silicone, or rubber. In certain circumstances, oxygen may be delivered via a nasal cannula instead of a mask. Medical plastic oxygen masks Examples of medical plastic oxygen masks Medical plastic oxygen masks are used primarily by medical care providers for oxygen therapy because they are disposable and so reduce cleaning costs and infection risks. Mask design can determine accuracy of oxygen delivered with many various medical situations requiring treatment with oxygen. Oxygen is naturally occurring in room air at 21% and higher percentages are often essential in medical treatment. Oxygen in these higher percentages is classified as a drug with too much oxygen being potentially harmful to a patient's health, resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
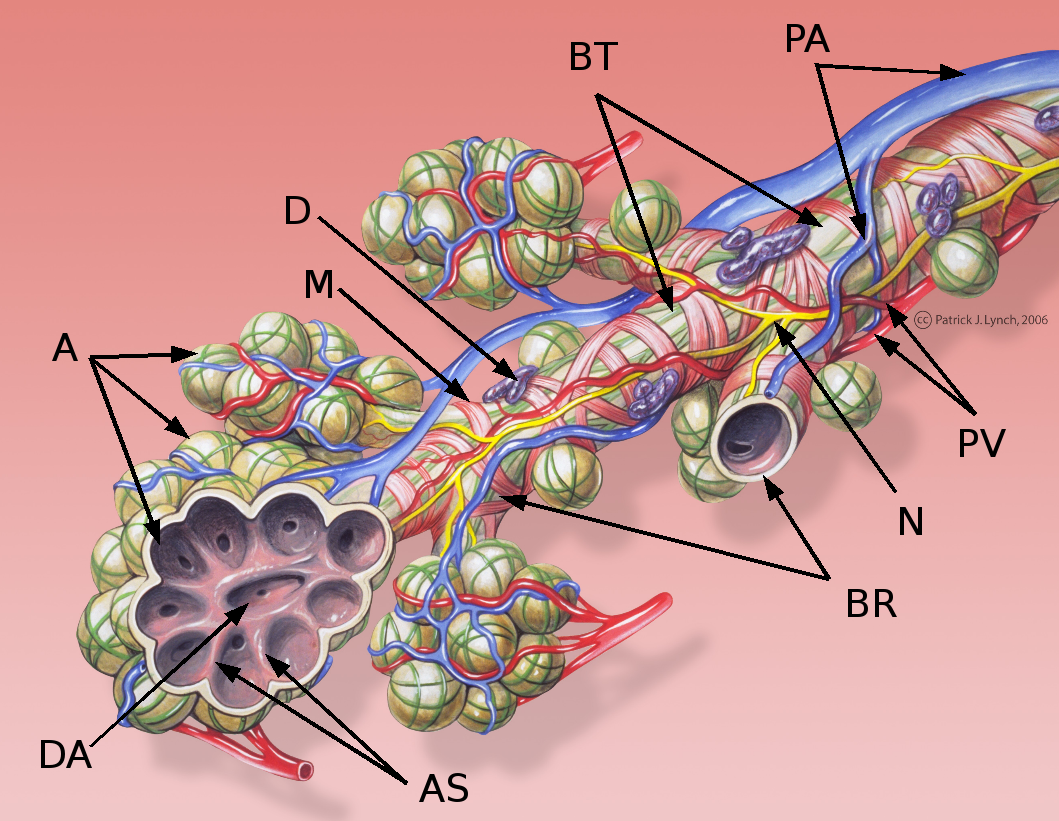
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (; ), also called an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where pulmonary gas exchange takes place. Oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide at the blood–air barrier between the alveolar air and the pulmonary capillary. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Oxygen is diffused across the membrane into the capillaries and carbon dioxide is released fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). In respiratory physiology, the partial pressure of a dissolved gas in liquid (such as oxygen in arterial blood) is also defined as the partial pressure of that gas as it would be undissolved in gas phase yet in equilibrium with the liquid. This concept is also known as blood gas tension. In this sense, the diffusion of a gas liquid is said to be driven by differences in partial pressure (not concentration). In chemistry and thermodynamics, this concept is generalized to non-ideal gases and instead called fugacity. The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of its Thermodynamic activity, thermodynamic activity. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia is a condition in which the body or a region of the body is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply at the tissue (biology), tissue level. Hypoxia may be classified as either ''Generalized hypoxia, generalized'', affecting the whole body, or ''local'', affecting a region of the body. Although hypoxia is often a pathological condition, variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise. Hypoxia differs from hypoxemia and anoxemia, in that hypoxia refers to a state in which oxygen present in a tissue or the whole body is insufficient, whereas hypoxemia and anoxemia refer specifically to states that have low or no Oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygen in the blood. Hypoxia in which there is complete absence of oxygen supply is referred to as anoxia. Hypoxia can be due to external causes, when the breathing gas is hypoxic, or internal causes, such as reduced effectiveness of gas transfer in the lung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabin Altitude
Cabin may refer to: Buildings * Beach cabin, a small wooden hut on a beach * Log cabin, a house built from logs * Cottage, a small house * Chalet, a wooden mountain house with a sloping roof * Cabin, small free-standing structures that serve as individual lodging spaces of a motel Films * ''The Cabin'', 2018 Swedish-American horror film * ''The Cabin Movie'', 2005 Canadian comedy-drama film Places * Cabin, Shropshire, England * Cabins, West Virginia, US * Cabin Bluff, Georgia, in the List of places in Georgia (U.S. state) (A–D), US Transportation * Cabin (aircraft) * Cabin (ship) * Cabin (truck), an enclosed space where the driver is seated * Cabin car or caboose, a crewed rail transport vehicle at the end of a freight train * Cabin cruiser, a boat with enclosed accommodation * Cabin motorcycle, a fully or semi-enclosed motorcycle Other uses * Cabin (Ferris wheel), a passenger compartment * Cabin rights, an American frontier claim to land * Cabin (band), an American indie roc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |