|
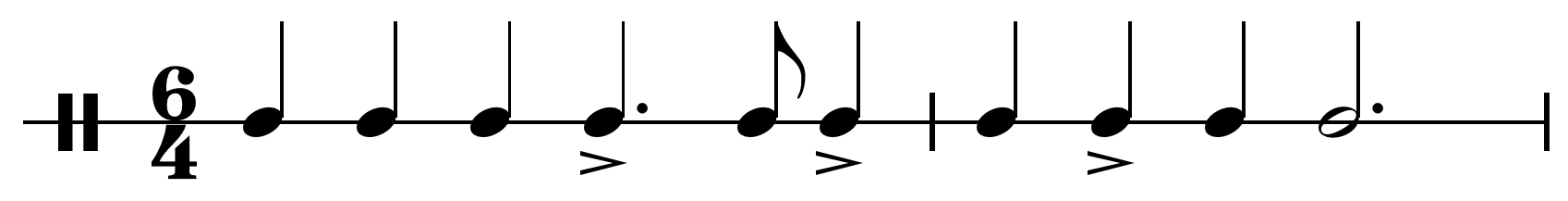
Bransle
A branle ( , ), also bransle, brangle, brawl(e), brall(e), braul(e), brando (in Italy), bran (in Spain), or brantle (in Scotland), is a type of France, French dance popular from the early 16th century to the present, danced by couples in either a Line dance, line or a Circle dance, circle. The term also refers to the music and the characteristic step of the dance. History Beginnings and courtly adoption The name ''branle'' derives from the French verb ''branler'' (to shake, wave, sway, wag, wobble), referring to the side-to-side movement of a circle or chain of dancers holding hands or linking arms. Dances of this name are encountered from about 1500 and the term is used for dances still danced in France today. Before 1500, the only dance-related use of this word is the "swaying" step of the basse danse. The branle was danced by a chain of dancers, usually in couples, with linked arms or holding hands. The dance alternated a number of larger sideways steps to the left (often fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suite (music)
A suite, in Western classical music, is an ordered set of instrumental or orchestral/concert band pieces. It originated in the late 14th century as a pairing of dance tunes; and grew in scope so that by the early 17th century it comprised up to five dances, sometimes with a Prelude (music), prelude. The separate Movement (music), movements were often thematically and tonally linked. The term can also be used to refer to similar forms in other musical traditions, such as the Ottoman Classical Music, Turkish fasıl and the Arab music, Arab nuubaat. In the Baroque music, Baroque era, the suite was an important musical form, also known as ''Suite de danses'', ''Ordre'' (the term favored by François Couperin), ''Partita'', or ''Ouverture'' (after the theatrical "overture" which often included a series of dances) as with the orchestral suites of Christoph Graupner, Georg Philipp Telemann, Telemann and Johann Sebastian Bach, J.S. Bach. During the 18th century, the suite fell out of fav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beauchamp–Feuillet Notation
Beauchamp-Feuillet notation is a system of dance notation used in Baroque dance. The notation was commissioned by Louis XIV (who had founded the Académie Royale de Danse in 1661), and devised in the 1680s by Pierre Beauchamp Pierre Beauchamp or Beauchamps (; 30 October 1631 – February 1705) was a French choreographer, dancer and composer, and the probable inventor of Beauchamp–Feuillet notation. His grand-father was called Christophe (a musician) and his f .... The notation system was first described in detail in 1700 by Raoul-Auger Feuillet in ''Chorégraphie''. Feuillet also then began a programme of publishing complete notated dances. It was used to record dances for the stage and domestic use throughout the eighteenth century, being modified by Pierre Rameau in 1725, and surviving into at least the 1780s in various modified forms. One of the innovations of this notation was to show the music on a staff as a musician would use it, across the top of a page. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suite Française (Poulenc)
''Suite française'' (French Suite), FP 80, is an orchestral suite for wind instruments, percussion and harpsichord (or harp ''ad libitum'') by Francis Poulenc. It was composed in a neoclassical style in 1935 for Édouard Bourdet's ''la Reine Margot'', and it was inspired by Claude Gervaise's dance collection ''Le livre de danceries''. Structure # Bransle de Bourgogne # Pavane The ''pavane'' ( ; , ''padovana''; ) is a slow processional dance common in Europe during the 16th century (Renaissance). The pavane, the earliest-known music for which was published in Venice by Ottaviano Petrucci, in Joan Ambrosio Dalza's ... # Petite marche militaire # Complainte # Bransle de Champagne # Sicilienne # Carillon * A typical performance lasts 14 minutes. References Sources * * * {{italic title Suites by Francis Poulenc 1935 compositions Orchestral suites Chamber music by Francis Poulenc Compositions for orchestra without strings Incidental music Neoclassicis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Poulenc
Francis Jean Marcel Poulenc (; 7 January 189930 January 1963) was a French composer and pianist. His compositions include mélodie, songs, solo piano works, chamber music, choral pieces, operas, ballets, and orchestral concert music. Among the best-known are the piano suite ''Trois mouvements perpétuels'' (1919), the ballet ''Les biches'' (1923), the ''Concert champêtre'' (1928) for harpsichord and orchestra, the Organ Concerto (Poulenc), Organ Concerto (1938), the opera ''Dialogues des Carmélites'' (1957), and the ''Gloria (Poulenc), Gloria'' (1959) for soprano, choir, and orchestra. As the only son of a prosperous manufacturer, Poulenc was expected to follow his father into the family firm, and he was not allowed to enrol at a music college. He studied with the pianist Ricardo Viñes, who became his mentor after the composer's parents died. Poulenc also made the acquaintance of Erik Satie, under whose tutelage he became one of a group of young composers known collectively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galliard
The ''galliard'' (; ; ) was a form of Renaissance dance and Renaissance music, music popular all over Europe in the 16th century. It is mentioned in dance manuals from England, Portugal, France, Spain, Germany, and Italy. Dance form The ''galliard'' is not an improvised dance, but rather, it consists of choreographed patterns of steps, which occupy one or more measures of music. In one measure, a galliard typically has five steps; in French such a basic step is called a ''cinq pas'' and in Italy, ''cinque passi''. This is sometimes written in English sources as ''sinkapace''. These steps are: right, left, right, left, cadence. The galliard is an athletic dance, characterised by leaps, jumps, hops and other similar figures. The main feature that defines a galliard step is a large jump, after which the dancer lands with one leg ahead of the other. This jump is called a ''cadence,'' and the final landing is called the ''posture.'' The cadence is typically preceded by three quick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Marston (poet)
John Marston (baptised 7 October 1576 – 25 June 1634) was an English playwright, poet and satirist during the late Elizabethan era, Elizabethan and early Jacobean era, Jacobean periods. His career as a writer lasted only a decade. His work is remembered for its energetic and often obscure style, its contributions to the development of a distinctively Jacobean style in poetry, and its idiosyncratic vocabulary. Life Marston was born to John and Maria Marston ''née'' Guarsi, and baptised 7 October 1576, at Wardington, Oxfordshire. His father was an eminent lawyer of the Middle Temple who first argued in London and then became the counsel to Coventry and ultimately its steward. John Marston entered Brasenose College, Oxford, in 1592 and received his BA in 1594. By 1595, he was in London, living in the Middle Temple, where he had been admitted a member three years previously. He had an interest in poetry and play writing, although his father's will of 1599 expresses the hope that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Praetorius
Michael Praetorius (probably 28 September 1571 – 15 February 1621) was a German composer, organist, and Music theory, music theorist. He was one of the most versatile composers of his age, being particularly significant in the development of musical forms based on Protestant Reformation, Protestant hymns. Life Praetorius was born Michael Schultze, the youngest son of a Lutheran pastor, in Creuzburg, in present-day Thuringia. After attending school in Torgau and Zerbst, he studied divinity and philosophy at the University of Frankfurt (Oder). He was fluent in a number of languages. After receiving his musical education, from 1587 he served as organist at the Marienkirche in Frankfurt. From 1592/3 he served at the court in Wolfenbüttel, under the employ of Henry Julius, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg. He served in the duke's Staatsorchester Braunschweig, State Orchestra, first as organist and later (from 1604) as ''Kapellmeister'' (court music director). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitzwilliam Virginal Book
The ''Fitzwilliam Virginal Book'' is a primary source of keyboard music from the late Elizabethan and early Jacobean periods in England, i.e., the late Renaissance and very early Baroque. It takes its name from Viscount Fitzwilliam who bequeathed this manuscript collection to Cambridge University in 1816. It is now housed in the Fitzwilliam Museum at Cambridge. The word virginals does not necessarily denote any specific instrument and might refer to any instrument with a keyboard. History It was given no title by its copyist and the ownership of the manuscript before the eighteenth century is unclear. At the time ''The'' ''Fitzwilliam Virginal Book'' was put together most collections of keyboard music were compiled by performers and teachers: other examples include ''Will Forster's Virginal Book'', '' Clement Matchett's Virginal Book'', and ''Anne Cromwell's Virginal Book''. It is possible that the complexities of typesetting music precluded the printing of much keyboard mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Tomkins
Thomas Tomkins (1572 – 9 June 1656) was a Welsh-born composer of the late Tudor and early Stuart period. In addition to being one of the prominent members of the English Madrigal School, he was a skilled composer of keyboard and consort music, and the last member of the English virginalist school. Life Tomkins was born in St David's in Pembrokeshire in 1572. His father, also Thomas, who had moved there in 1565 from the family home of Lostwithiel in Cornwall, was a vicar choral of St David's Cathedral and organist there. Three of Thomas junior's half-brothers, John, Giles and Robert, also became eminent musicians, but none quite attained the fame of Thomas. By 1594, but possibly as early as 1586, Thomas and his family had moved to Gloucester, where his father was employed as a minor canon at the cathedral. Thomas almost certainly studied under William Byrd for a time, for one of his songs bears the inscription: ''To my ancient, and much reverenced Master, William Byrd'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck (music), neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted. More specifically, the term "lute" commonly refers to an instrument from the Family (musical instruments), family of History of lute-family instruments, European lutes which were themselves influenced by India, Indian short-necked lutes in Gandhara which became the predecessor of the Islamic music, Islamic, the Sino-Japanese and the Early music, European lute families. The term also refers generally to any necked string instrument having the strings running in a plane parallel to the Sound board (music), sound table (in the Hornbostel–Sachs system). The strings are attached to pegs or posts at the end of the neck, which have some type of turning mechanism to enable the player to tighten the tension on the string or loosen the tension before playing (which respectively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmanuel Adriaenssen
Emmanuel Adriaenssen (also ''Adriaensen'', ''Adriansen'', ''Hadrianus'', ''Hadrianius''; c. 1554 in Antwerp – buried 27 February 1604 in Antwerp) was a Flemish lutenist, composer and master of music.Godelieve Spiessens, ''Emanuel Adriaenssen'' in: Nationaal Biografisch Woordenboek, Volume 1, Brussels, 1964, col. 3-6 He authored the influential ''Pratum Musicum'', which contains scores for lute solos, and more importantly settings of madrigals for multiple lutes and different ensembles involving lutes and voices. He also had an important influence on the next generation of lutenists through his activity as a teacher of music in his own music school.Facsimile of ''Pratum Musicum'' with an introduction and bibliography by Kwee Him Yong, Frits Knuf, Netherl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |