|
Buko Pie
Buko pie, sometimes anglicized as coconut pie, is a traditional Cuisine of the Philippines, Filipino baked young coconut (malauhog) pie. It is considered a specialty in the municipality of Los Baños, Laguna, located on the island of Luzon. Buko pie is made with young coconuts (''buko'' in Tagalog language, Tagalog), and uses sweetened condensed milk, which makes it denser than cream-based custard pies. There are also variations of the pie, which are similar but use slightly different ingredients, such as macapuno pie, that uses ''macapuno'', a special type of coconut that is thick and sticky. The pie was originally a delicacy only available in the Philippines, but Flash freezing, blast freezing technology has allowed buko pie-makers the ability to export. As it has become easier to transport and more accessible around the world, people are able to buy it as a ''pasalubong'' or homecoming present after having visited the Philippines. Buko pie is traditionally plain, but nowadays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laguna (province)
Laguna , officially the Province of Laguna (), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon Regions of the Philippines, region in Luzon. Its capital is Santa Cruz, Laguna, Santa Cruz while its largest city is the Calamba, Laguna, City of Calamba (the regional center of Calabarzon) and the province is situated southeast of Metro Manila, south of the province of Rizal (province), Rizal, west of Quezon, north of Batangas and east of Cavite. Laguna hugs the southern shores of Laguna de Bay, the largest lake in the country. As of the 2020 census, the total population of Laguna is 3,382,193. Among all 82 provinces in the Philippines, Laguna accounted for the largest share (5%) of the national Gross Domestic Product (GDP) with a total of Php 990.69 billion in 2022. Laguna is notable as the birthplace of José Rizal, the country's ''de facto'' national hero. It has numerous natural and cultural attractions such as Cavinti Falls aka Pagsanjan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Pie
An apple pie is a pie in which the principal filling is apples. Apple pie is often served with whipped cream, ice cream ("apple pie à la mode"), custard or cheddar cheese. It is generally double-crusted, with pastry both above and below the filling; the upper crust may be solid or latticed (woven of crosswise strips). The bottom crust may be baked separately ("Blind-baking, blind") to prevent it from getting soggy. Tarte Tatin is baked with the crust on top, but served with it on the bottom. Originating in the 14th century in England, apple pie recipes are now a standard part of cuisines in many countries where apples grow. Apple pie is a significant dessert in many countries, including the United Kingdom, Eire, Sweden, Norway, Australia, Germany, New Zealand, and the US. Ingredients Apple pie can be made with many different sorts of apples. The more popular cooking apples include Braeburn, Gala (apple), Gala, Cortland (apple), Cortland, Bramley (apple), Bramley, Empire (ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, biscuits, breakfast cereals, Snack, snack foods, bagels, teas, hot chocolate and traditional foods. The aroma and flavour of cinnamon derive from its essential oil and principal component, cinnamaldehyde, as well as numerous other constituents, including eugenol. Cinnamon is the name for several species of trees and the commercial spice products that some of them produce. All are members of the genus ''Cinnamomum'' in the family Lauraceae. Only a few ''Cinnamomum'' species are grown commercially for spice. ''Cinnamomum verum'' (alternatively ''C. zeylanicum''), known as "Ceylon cinnamon" after its origins in Sri Lanka (formerly Ceylon), is considered to be "true cinnamon", but most cinnamon in international commerce is derived from four other speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
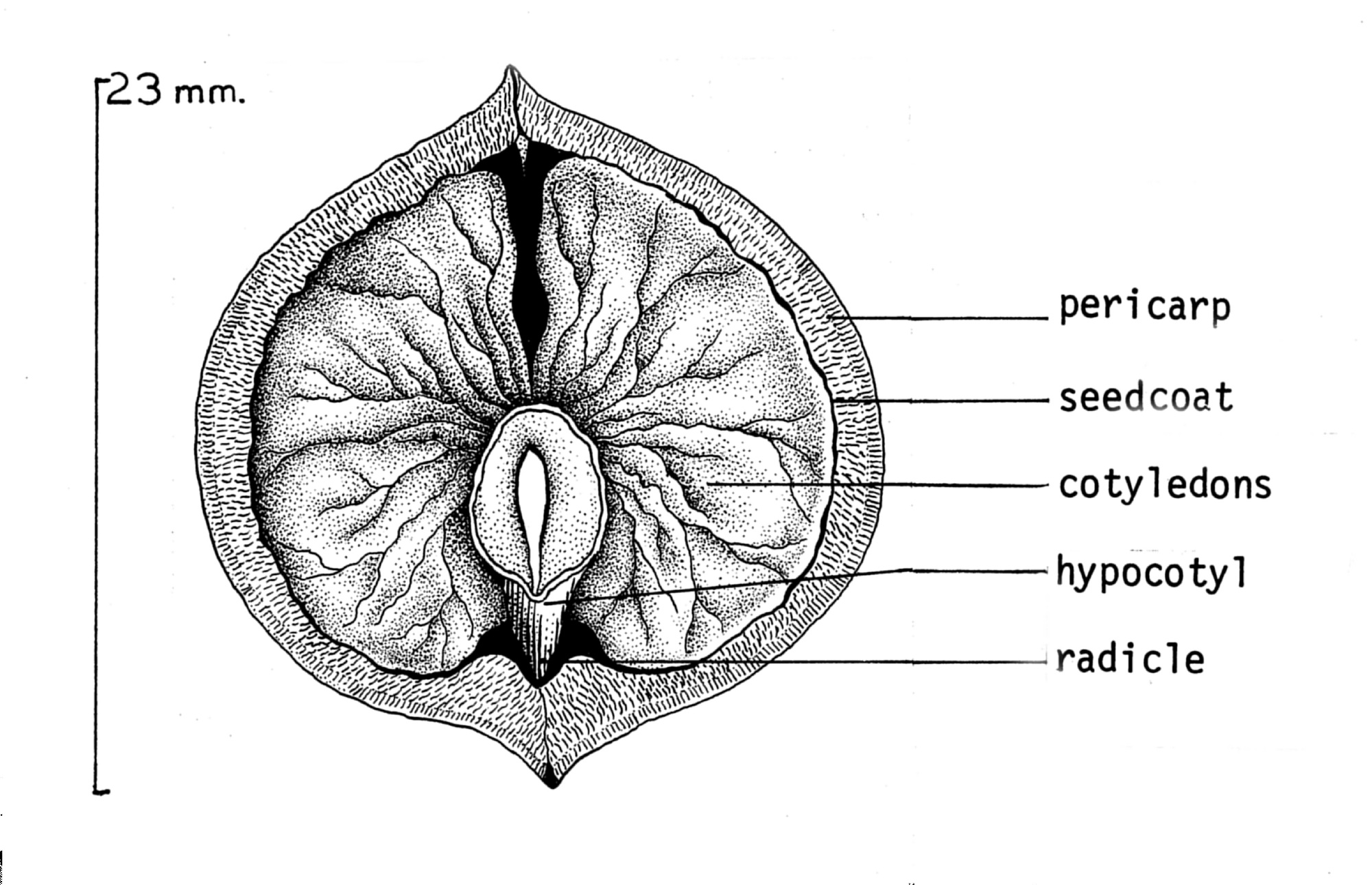
Nut (fruit)
A nut is a fruit consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, many dry seeds are called nuts, but in a botanical context, "nut" implies that the shell does not open to release the seed (Dehiscence (botany), indehiscent). Most seeds come from fruits that naturally free themselves from the shell, but this is not the case in nuts such as hazelnuts, chestnuts, and acorns, which have hard shell walls and originate from a compound ovary. Definition A seed is the mature fertilised ovule of a plant; it consists of three parts, the embryo which will develop into a new plant, stored food for the embryo, and a protective seed coat. Botany, Botanically, a nut is a fruit with a woody pericarp developing from a syncarpous gynoecium. Nuts may be contained in an Bract#Involucral bracts, involucre, a cup-shaped structure formed from the flower bracts. The involucre may be scaly, spiny, leafy or tubular, depending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raisins
A raisin is a dried grape. Raisins are produced in many regions of the world and may be eaten raw or used in cooking, baking, and brewing. In the United Kingdom, Ireland, New Zealand, Australia and South Africa, the word ''raisin'' is reserved for the dark-colored dried large grape, with '' sultana'' being a golden- or green-colored dried grape, and '' currant'' being a dried small Black Corinth seedless grape. Varieties Raisin varieties depend on the types of grapes used and appear in a variety of sizes and colors, including green, black, brown, purple, blue, and yellow. Seedless varieties include sultanas (the common American type is known as Thompson Seedless in the United States), Zante currants (black Corinthian raisins, ''Vitis vinifera'' L. var. Apyrena), and Flame grapes. Raisins are traditionally sun-dried but may also be artificially dehydrated. Golden raisins are created with a treatment of sulfur dioxide rather than purely drying them. They are sometimes dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klappertaart
Klappertaart is a Dutch-influenced Indonesian cake originating from Manado, North Sulawesi. ''Klappertaart'' is "coconut cake" or "coconut tart" and it is made from flour, sugar, milk, butter, and the flesh and juice of coconuts. See also * *Coconut cake
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, th ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blind-baking
Baking blind (sometimes called pre-baking) is the process of baking a pie crust or other pastry without the filling. Blind baking a pie crust is necessary when it will be filled with an unbaked filling (such as with pudding or cream pies), in which case the crust must be fully baked. It is also called for if the filling has a shorter bake time than the crust, in which case the crust is partly baked. Blind baking is also used to keep pie crust from becoming soggy due to a wet filling. Blind baking can be accomplished by different methods. In one technique, the pie crust is lined with aluminium foil or parchment paper, then filled with pastry- or pie weights (sometimes called "baking beans") to ensure the crust retains its shape while baking. Pie-weights are available as ceramic or metal beads, but rice, dried peas, lentils, beans or other Pulse (legume), pulses can be used instead. When using this method for a fully baked crust, the weights are removed before the pre-baking is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Carbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (from Greek language, Greek ''wikt:μόνος, monos'': single, ''wikt:σάκχαρ, sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built. Chemically, monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehydes with the formula or polyhydroxy ketones with the formula with three or more carbon atoms. They are usually Transparency and translucency, colorless, water-soluble, and crystalline organic solids. Contrary to their name (sugars), only some monosaccharides have a sweetness, sweet taste. Most monosaccharides have the formula (CH2O)''x'' (though not all molecules with this formula are monosaccharides). Examples of monosaccharides include glucose (dextrose), fructose (levulose), and galactose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose, lactose and maltose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch). The white sugar, table sugar used in ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrates
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' may differ). This formula does not imply direct covalent bonding between hydrogen and oxygen atoms; for example, in , hydrogen is covalently bonded to carbon, not oxygen. While the 2:1 hydrogen-to-oxygen ratio is characteristic of many carbohydrates, exceptions exist. For instance, uronic acids and deoxy-sugars like fucose deviate from this precise Stoichiometry, stoichiometric definition. Conversely, some compounds conforming to this definition, such as formaldehyde and acetic acid, are not classified as carbohydrates. The term is predominantly used in biochemistry, functioning as a synonym for saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and storage. Folate is required for the body to make DNA and RNA and metabolise amino acids necessary for cell division and maturation of blood cells. As the human body cannot make folate, it is required in the diet, making it an essential nutrient. It occurs naturally in many foods. The recommended adult daily intake of folate in the U.S. is 400 micrograms from foods or dietary supplements. Folate in the form of folic acid is used to treat anemia caused by folate deficiency. Folic acid is also used as a supplement by women during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs) in the baby. NTDs include anencephaly and spina bifida, among other defects. Low levels in early pregnancy are believed to be the cause of more tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niacin (nutrient)
Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms, or vitamers: nicotinic acid (niacin), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without either vitamin B3 or tryptophan. Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004. Niacin (the nutrient) can be manufactured by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variety of whole and processed foods, with highest contents in fortified packaged foods, meat, poultry, red fish such as tuna and salmon, lesser amounts in nuts, legumes and seeds. Niacin as a dietary supplement is used to treat pellagra, a disease caused by niacin deficiency. Signs and symptoms of pellagra include skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |