|
Bujeo
Bujeo is a type of soil found on the countryside of Andalusia, mainly the area of the Guadalquivir The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from Seville ... valley. The color ranges from yellowish brown to olive brown gray and dark gray to almost black, depending on their composition. One of its main features is its columnar structure, strong and deep cracks in the dry state when dealing with materials rich in clays expansive. The texture is silty clay to clay. Their pH ranges from neutral to moderately alkaline, and organic matter content is generally low. Because of the way these loamy clay soils "swell in winter and crack deeply in summer", they are called "tierras de bujeo", which literally means "land that moves". References {{reflist Agriculture in Spain Andalusia Soil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognized as a nationalities and regions of Spain, historical nationality and a national reality. The territory is divided into eight provinces of Spain, provinces: Province of Almería, Almería, Province of Cádiz, Cádiz, Province of Córdoba (Spain), Córdoba, Province of Granada, Granada, Province of Huelva, Huelva, Province of Jaén (Spain), Jaén, Province of Málaga, Málaga, and Province of Seville, Seville. Its capital city is Seville, while the seat of High Court of Justice of Andalusia, its High Court of Justice is the city of Granada. Andalusia is immediately south of the autonomous communities of Extremadura and Castilla-La Mancha; west of the autonomous community of Region of Mur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
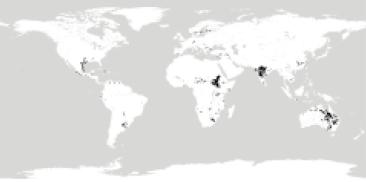
Vertisol
A vertisol is a Soil Order in the USDA soil taxonomy and a Reference Soil Group in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB). It is also defined in many other soil classification systems. In the Australian Soil Classification it is called vertosol. The natural vegetation of vertisols is grassland, savanna, or grassy woodland. The heavy texture and unstable behaviour of the soil makes it difficult for many tree species to grow, and forest is uncommon. Composition Vertisols have a high content of expansive clay minerals (many of them belonging to the montmorillonites) that form deep cracks in drier seasons or years. In a phenomenon known as argillipedoturbation, alternate shrinking and swelling causes ''self-ploughing'', where the soil material consistently mixes itself, causing some vertisols to have an extremely deep A horizon and no B horizon. (A soil with no B horizon is called an ''A/C soil''). This heaving of the underlying material to the surface often create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalquivir
The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from Seville to the Gulf of Cádiz, but in Roman times it was navigable from Córdoba. Geography The river is long and drains an area of about . It flows through Córdoba and Seville and reaches the sea at Sanlúcar de Barrameda, flowing into the Gulf of Cádiz in the Atlantic Ocean. Course The course of the Guadalquivir is divided into three parts. This division is based on the main course of the river and its confluence with other rivers. The Guadalquivir originates at an elevation of about 1,350 meters above sea level in a place known as Cañada de las Fuentes, in the Sierra de Cazorla mountain range. The upper course of the river runs from the source of the Guadalquivir roughly to Mengíbar. It includes its junction with the Guadali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture In Spain
Agriculture in Spain is important to the national economy. The primary sector activities accounting for agriculture, husbandry, fishing and silviculture represented a 2.7% of the Spanish GDP in 2017, with an additional 2.5% represented by the agrofood industry. Geography and climate of Spain Viewed in terms of land mass, Spain is one of the largest countries in Western Europe, and it ranks second in terms of its elevation, after Switzerland. Most of the territory experiences a dry summer climate (mediterranean or semiarid) with scarce rainfall in the summer and high potential evaporation, as well as a total annual rainfall ranging from 400 to 600 mm. Longer droughts also occur. Although average minimum winter temperatures are often above 0 °C in a large part of the agricultural land, frosts are not uncommon in the interior of the country during the Winter. 20.6 million of Spain's 50.5 million hectares of land, or about 40 percent, is suitable for cultivation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |