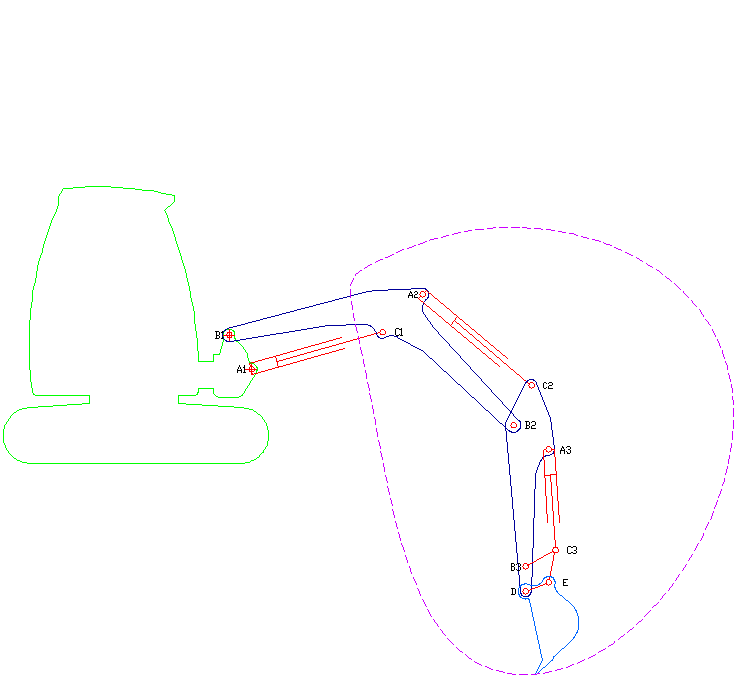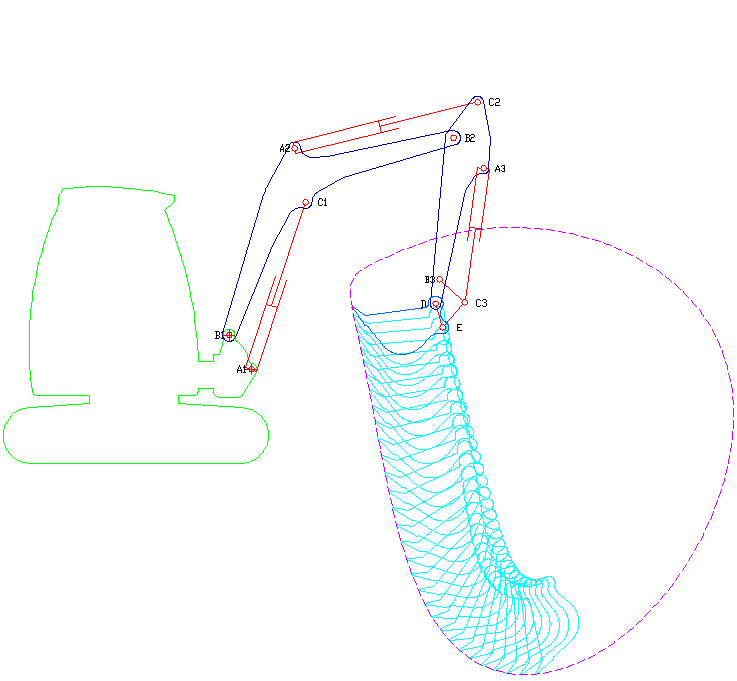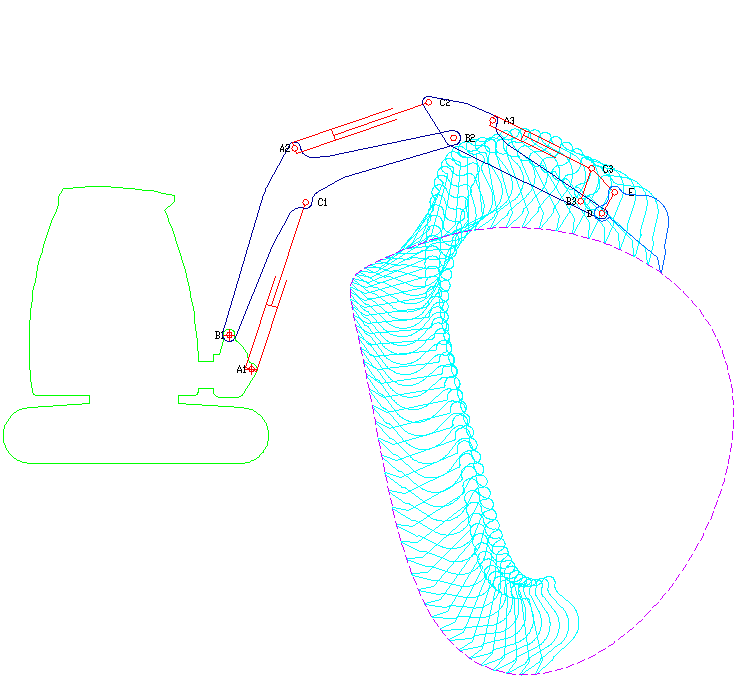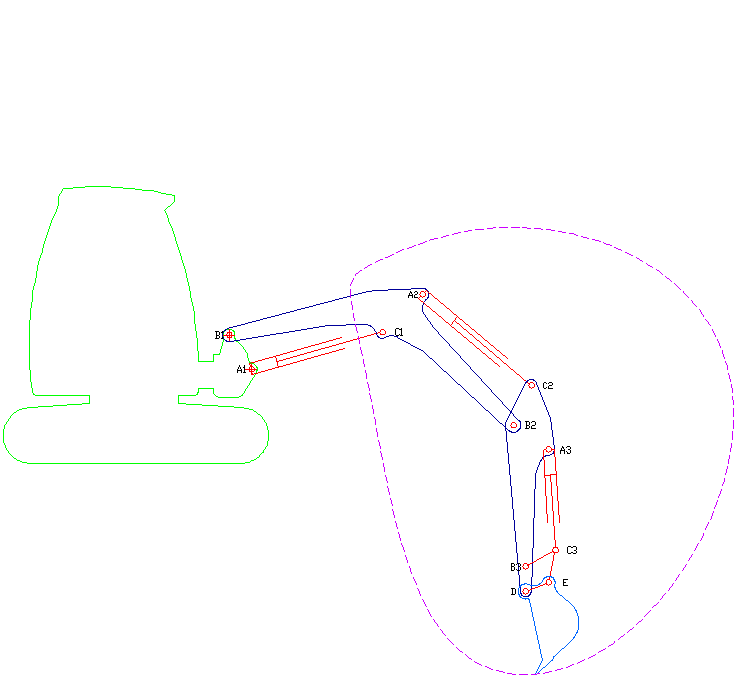
|
Bucket-wheel Excavator
A bucket-wheel excavator (BWE) is a large heavy equipment machine used in surface mining. Their primary function is that of a continuous digging machine in large-scale open-pit mining operations, removing thousands of tons of overburden a day. What sets them apart from other large-scale mining equipment, such as bucket chain excavators, is their use of a large wheel consisting of a continuous pattern of buckets which scoop material as the wheel turns. They are among the largest land or sea vehicles ever produced. The 14,200-ton Bagger 293 holds the Guinness World Record for the heaviest land-based vehicle ever built. History Bucket-wheel excavators have been used in mining for the past century, with some of the first being manufactured in the 1920s. They are used in conjunction with many other pieces of mining machinery (conveyor belts, spreaders, crushing stations, heap-leach systems, etc.) to move and mine massive amounts of overburden (waste). While the overall concepts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garzweiler Tagebau-1230
The Tagebau Garzweiler () is a surface mine () in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is operated by RWE and used for mining lignite. The mine currently has a size of and got its name from the village of which previously existed at this location. The community was moved to a section of Jüchen with the same name. The open-pit mine The mine is located west of Grevenbroich and exploitation is progressing towards Erkelenz. Mining was originally limited to the Garzweiler I area located east of the A 44 motorway. Mining in the Garzweiler II area started in 2006 and is estimated to take until around 2045 to fully exploit both sectors. The lignite is used for power generation at nearby power plants such as Neurath and Niederaußem. In 2015, 1500 protesters took part in civil disobedience against the mine on the basis that it is Europe’s biggest source of CO2 emissions. Around 1000 people entered the coal mine and all of the diggers in its pit were brought to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Track
Continuous track or tracked treads are a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle better than steel or rubber tyres on an equivalent vehicle, enabling continuous tracked vehicles to traverse soft ground with less likelihood of becoming stuck due to sinking. Modern continuous tracks can be made with soft belts of synthetic rubber, reinforced with steel wires, in the case of lighter agricultural machinery. The more common classical type is a solid chain track made of steel plates (with or without rubber pads), also called caterpillar tread or tank tread, which is preferred for robust and heavy construction vehicles and military vehicles. The prominent treads of the metal plates are both hard-wearing and damage resistant, especially in comparison to rubber tyres. The aggressive treads of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagger 1473
Bagger 1473 (christened as ''The Blue Wonder'') is a Type SRs 1500-series bucket-wheel excavator prototype left abandoned in a field in the municipality of Schipkau in Germany. Technical data The bucket wheel excavator had a power of 5555 kW during operation and was supplied with a 6 kV power cable. Overall, the bucket wheel excavator is about 50 meters high and about 171.5 meters long. The six-section crawler undercarriage, with a maximum travel speed of 6 meters per minute, carries the total mass of 3850 tons. With 10 buckets of 1.5 cubic meters each and 57 pours per minute (known as the pour rate), the excavator achieves a theoretical mining capacity of 5130 cubic meters per hour. The bucket wheel diameter is 12.5 meters and the cutting speed is 3.73 meters per second. The design of the wheel boom, with a length of 67 meters, enables an excavation height of up to 35 meters and an excavation depth of up to 15 meters. History The excavator was used at the Meuro mine, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagger 288
Bagger 288 (Excavator 288), previously known as the MAN TAKRAF RB288 built by the German company Krupp for the energy and mining firm Rheinbraun, is a bucket-wheel excavator or mobile strip mining machine. When its construction was completed in 1978, Bagger 288 superseded Big Muskie as the heaviest land vehicle in the world, at 13,500 tons. It took five years to design and manufacture and five years to assemble, with total cost reaching $100 million. In 1995, it was itself superseded by the slightly heavier Bagger 293 (14,200 tons). XCMG's XGC88000 Crawler Crane remains the largest self-propelled land vehicle in the world, since bucket-wheel excavators are powered by an external power source, and the Overburden Conveyor Bridge F60s hold the title of largest land vehicle of any type by physical dimensions. Like its siblings, the Bagger 288 require a disproportionately small number of people to operate, at just five total. Whilst Bagger 288 is considered a "sibling vehicle" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reclaimer
A reclaimer is a large machine used in bulk material handling applications. A reclaimer's function is to recover bulk material such as ores and cereals from a stockpile. A stacker is used to stack the material. Reclaimers are volumetric machines and are rated in m3/h (cubic meters per hour) for capacity, which is often converted to t/h (tonnes per hour) based on the average bulk density of the material being reclaimed. Reclaimers normally travel on a rail between stockpiles in the stockyard. A bucket wheel reclaimer can typically move in three directions: horizontally along the rail; vertically by "luffing" its boom and rotationally by slewing its boom. Reclaimers are generally electrically powered by means of a trailing cable. Reclaimer types Bucket wheel reclaimers use "bucket wheels" to remove material from the pile they are reclaiming. Scraper reclaimers use a series of scrapers on a chain to reclaim the material. The reclaimer structure can be of a number of types, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Excavator
Excavators are heavy construction equipment primarily consisting of a boom, dipper (or stick), bucket, and cab on a rotating platform known as the "house". The modern excavator's house sits atop an undercarriage with tracks or wheels, being an evolution of the steam shovel (which itself evolved into the power shovel when steam was replaced by diesel and electric power). All excavation-related movement and functions of a hydraulic excavator are accomplished through the use of hydraulic fluid, with hydraulic cylinders and hydraulic motors, which replaced winches, chains, and steel ropes. Another principle change was the direction of the digging action, with modern excavators pulling their buckets toward them like a dragline rather than pushing them away to fill them the way the first powered shovels did. Terminology Excavators are also called diggers, scoopers, mechanical shovels, or 360-degree excavators (sometimes abbreviated simply to "360"). Tracked excavators are someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
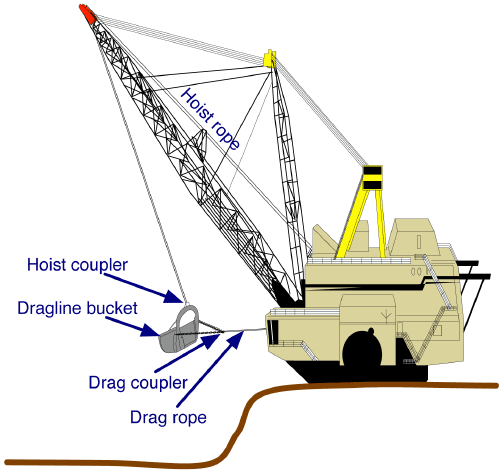
Dragline
A dragline excavator is a heavy-duty excavator used in civil engineering and surface mining. It was invented in 1904, and presented an immediate challenge to the steam shovel and its diesel and electric powered descendant, the power shovel. Much more efficient than even the largest of the latter, it enjoyed a heyday in extreme size for most of the 20th century, first becoming challenged by more efficient rotary excavators in the 1950s, then superseded by them on the upper end from the 1970s on. The largest ever walking dragline was Big Muskie, a Bucyrus-Erie 4250-W put online in 1969 that swung a , 325 ton capacity bucket, had a boom, and weighed 13,500 tons. The largest walking dragline produced as of 2014 was Joy Global’s digital AC drive control P&H 9020XPC, which has a bucket capacity of and boom lengths ranging from ; working weights vary between 7,539 and 8,002 tons. Types Draglines fall into two broad categories: those that are based on standard, lifting cran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Shovel
A steam shovel is a large steam engine, steam-powered excavating machine designed for lifting and moving material such as Rock (geology), rock and soil. It is the earliest type of power shovel or excavator. Steam shovels played a major role in public works in the 19th and early 20th century, being key to the construction of railroads and the Panama Canal. The development of simpler, cheaper Diesel fuel, diesel, gasoline and Electricity, electric Power shovel, shovels caused steam shovels to fall out of favor in the 1930s. History Origins and development Grimshaw of Boulton & Watt devised the first steam-powered excavator in 1796. In 1833 William Brunton patented another steam-powered excavator which he provided further details on in 1836. The steam shovel was invented by William Otis, who received a patent for his design in 1839. The first machines were known as 'partial-swing', since the boom could not rotate through 360 degrees. They were built on a railway chassis, on whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Acquisition
Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acronyms ''DAS,'' ''DAQ,'' or ''DAU,'' typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems include: * Sensors, to convert physical parameters to electrical signals. * Signal conditioning circuitry, to convert sensor signals into a form that can be converted to digital values. * Analog-to-digital converters, to convert conditioned sensor signals to digital values. Data acquisition applications are usually controlled by software programs developed using various general purpose programming languages such as Assembly, BASIC, C, C++, C#, Fortran, Java, LabVIEW, Lisp, Pascal, etc. Stand-alone data acquisition systems are often called data loggers. There are also ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slewing
Slewing is the rotation of an object around an axis, usually the z axis. An example is a radar scanning 360 degrees by slewing around the z axis. This is also common terminology in astronomy. The process of rotating a telescope to observe a different region of the sky is referred to as slewing. The term slewing is also found in motion control applications. Often the slew axis is combined with another axis to form a motion profile. In crane terminology, slewing is the angular movement of a crane boom or crane jib in a horizontal plane. The term is also used in the computer game Microsoft Flight Simulator ''Microsoft Flight Simulator'' is a series of Flight simulation video game, flight simulator programs for MS-DOS, Classic Mac OS, and Microsoft Windows operating systems. It was an early product in the Microsoft application portfolio and diff ... wherein the user presses a key and he or she can rotate and move the virtual aircraft along all three spatial planes. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonnes
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United States customary units) and the long ton ( British imperial units). It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (Mg), a less common way to express the same amount. Symbol and abbreviations The BIPM symbol for the tonne is t, adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.Table 6 . BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10. Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States |