|
Bubble Snails
''Bulla'' is a genus of medium to large hermaphrodite sea snails, shelled Marine (ocean), marine opisthobranch gastropod Mollusc, molluscs. These herbivorous snails are in the Order (biology), order Cephalaspidea.Gofas, S. (2010). Bulla Linnaeus, 1758. In: Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S.; Rosenberg, G. (2010) World Marine Mollusca database. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=137716 on 2011-05-04 These snails are popularly known as "bubble snails" because the shell of some of the species is very inflated indeed, almost spherical in shape, and is also very thin and light. According to some experts, ''Bulla'' is currently the only genus in the Family (biology), family Bullidae, which in turn is the only member of the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Bulloidea. In addition to its taxonomic interest, ''Bulla'' — particularly ''Bulla gouldiana'' — has served as an important model organism in circadian biology res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod Shell
The gastropod shell is part of the body of many gastropods, including snails, a kind of mollusc. The shell is an exoskeleton, which protects from predators, mechanical damage, and dehydration, but also serves for muscle attachment and calcium storage. Some gastropods appear shell-less (slugs) but may have a remnant within the mantle, or in some cases the shell is reduced such that the body cannot be retracted within it (semi-slug). Some snails also possess an operculum that seals the opening of the shell, known as the Aperture (mollusc), aperture, which provides further protection. The study of mollusc shells is known as conchology. The biological study of gastropods, and other molluscs in general, is malacology. Shell morphology terms vary by species group. Shell layers The gastropod shell has three major layers secreted by the Mantle (mollusc), mantle. The calcareous central layer, ostracum, is typically made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) precipitated into an organic matrix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
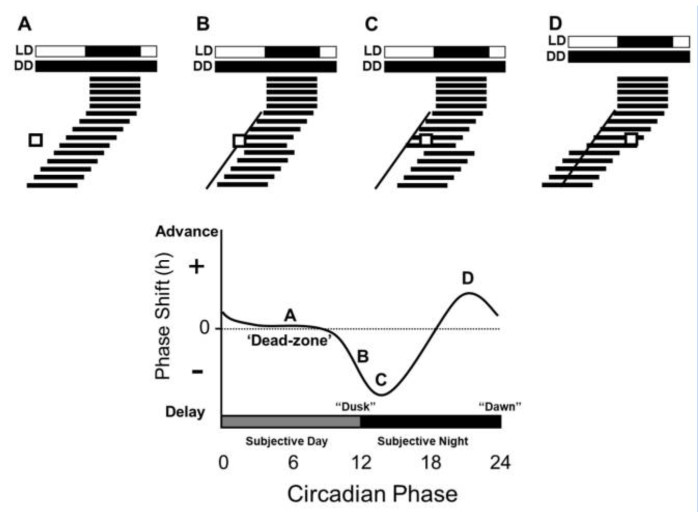
Photoentrainment (chronobiology)
In chronobiology, photoentrainment refers to the process by which an organism's biological clock, or circadian rhythm, synchronizes to daily cycles of light and dark in the environment. The mechanisms of photoentrainment differ from organism to organism. Photoentrainment plays a major role in maintaining proper timing of physiological processes and coordinating behavior within the natural environment. Studying organisms’ different photoentrainment mechanisms sheds light on how organisms may adapt to anthropogenic changes to the environment. Background 24-hour physiological rhythms, known now as circadian rhythms, were first documented in 1729 by Jean Jacques d'Ortous de Mairan, a French astronomer who observed that mimosa plants (''Mimosa pudica'') would orient themselves to be toward the position of the sun despite being in a dark room. That observation spawned the field of chronobiology, which seeks to understand the mechanisms that underlie endogenously expressed daily rhythm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapodia
In invertebrates, the term parapodium ( Gr. ''para'', beyond or beside + ''podia'', feet; : parapodia) refers to lateral outgrowths or protrusions from the body. Parapodia are predominantly found in annelids, where they are paired, unjointed lateral outgrowths that bear the chaetae. In several groups of sea snails and sea slugs, 'parapodium' refers to lateral fleshy protrusions. __TOC__ Annelid parapodia Most species of polychaete annelids have paired, fleshy parapodia which are segmentally arranged along the body axis. Parapodia vary greatly in size and form, reflecting a variety of functions, such as, anchorage, protection and locomotion. General description Parapodia in polychaetes can be uniramous (consisting of one lobe or ramus) but are usually biramous (two lobes or rami). In the latter case, the dorsal lobes are called notopodia and the ventral lobes neuropodia. Both neuropodia and notopodia may possess a bundle of chaetae (neurochaetae and notochaetae respectively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corneous
Corneous is a biological and medical term meaning horny, in other words made out of a substance similar to that of horns and hooves in some mammals. The word is generally used to describe natural or pathological anatomical structures made out of a hard layer of protein. In mammals this protein would usually be keratin. The word corneous is also often used to describe the operculum of a snail, a gastropod mollusc. Not all gastropods have opercula, but in the great majority of those that do have one, the operculum is corneous. (However in several genera within a few families including the marine Naticidae and the terrestrial Pomatiidae, the operculum is primarily calcareous, in other words mostly made of calcium carbonate Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ....) Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat non-vascular autotrophs such as mosses, algae and lichens, but do not include those feeding on decomposed plant matters (i.e. detritivores) or macrofungi (i.e. fungivores). As a result of their plant-based diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouth structures ( jaws or mouthparts) well adapted to mechanically break down plant materials, and their digestive systems have special enzymes (e.g. amylase and cellulase) to digest polysaccharides. Grazing herbivores such as horses and cattles have wide flat- crowned teeth that are better adapted for grinding grass, tree bark and other tougher lignin-containing materials, and many of them evolved rumination or cecotropic behaviors to better extract nutrients from plants. A larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gizzard
The gizzard, also referred to as the ventriculus, gastric mill, and gigerium, is an organ found in the digestive tract of some animals, including archosaurs (birds and other dinosaurs, crocodiles, alligators, pterosaurs), earthworms, some gastropods, some fish, and some crustaceans. This specialized stomach constructed of thick muscular walls is used for grinding up food, often aided by particles of stone or grit. In certain insects and molluscs, the gizzard features chitinous plates or teeth. Etymology The word ''gizzard'' comes from the Middle English ''giser'', which derives from a similar word in Old French ''gésier'', which itself evolved from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''gésier'', which itself evolved from the Latin ''gigeria'', meaning giblets. Structure In birds Birds swallow food and store it in their crop if necessary. Then the food passes into thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operculum (gastropod)
An operculum (; ) is a corneous or calcareous anatomical structure like a trapdoor that exists in many (but not all) groups of sea snails and freshwater snails, and also in a few groups of land snails, including the Helicinidae, Cyclophoridae, Aciculidae, Maizaniidae, Pomatiidae, etc. The operculum is attached to the upper surface of the foot and in its most complete state, it serves as a sort of "trapdoor" to close the aperture (mollusc), aperture of the shell when the soft parts of the animal are retracted. The shape of the operculum varies greatly from one family of gastropods to another. It is fairly often circular, or more or less oval in shape. In species where the operculum fits snugly, its outline corresponds exactly to the shape of the aperture (mollusc), aperture of the shell and it serves to seal the entrance of the shell. Many families have opercula that are reduced in size, and which are not capable of closing the shell aperture. Opercula have sometimes been modifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apex (mollusc)
In anatomy, an apex (adjectival form: apical) is part of the mollusc shell, shell of a mollusk. The apex is the pointed tip (the oldest part) of the shell of a gastropod, scaphopod, or cephalopod. The apex is used in end-blown conch (instrument), conches. Gastropods The word "apex" is most often used to mean the tip of the spire (mollusc), spire of the shell of a gastropod. The apex is the first-formed, and therefore the oldest, part of the shell. To be more precise, the apex would usually be where the tip of the embryonic shell or protoconch is situated, if that is still present in the adult shell (often it is lost or eroded away). Coiled gastropod shells The phrase apical whorls, or protoconch, means the whorls that constitute the embryonic shell at the apex of the shell, especially when this is clearly distinguishable from the later whorls of the shell, otherwise known as the teleoconch. Comparison of the apical part and the whole shell of ''Otukaia kiheiziebisu'': File:Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilicus (mollusk)
The umbilicus of a coiled mollusc shell is the axially aligned, hollow cone-shaped space within its whorls. The term ''umbilicus'' is often used in descriptions of gastropod shells, i.e. it is a feature present on the ventral (or under) side of many (but not all) snail shells, including some species of sea snails, land snails, and freshwater snails. The word is also applied to the depressed central area on the planispiral coiled shells of ''Nautilus'' species and fossil ammonites. (These are not gastropods, but shelled cephalopods.) In gastropods The spirally coiled whorls of gastropod shells frequently connect to each other by their inner sides, during the natural course of its formation. This results in a more or less solid central axial pillar, known as the columella. The more intimate the contact between the concave side of the whorls is, the more solid the columella becomes. On the other hand, if this connection is less intense, a hollow space inside the whorls may result, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coquille De Bulla Vernicosa
Coquille, the French word for "shell" (like an oyster shell), can refer to: People * Coquille people, a Native American tribe in Oregon * Coquille Indian Tribe, a federally recognized Native American tribal entity in Oregon * Guy Coquille (1523–1603), French jurist Places * Coquille, Oregon, a city in the U.S. state of Oregon * La Coquille, a village and commune in the Dordogne département of western France * Coquille River (Oregon), a river in Oregon * Coquille River (Normandin River), a tributary of Nicabau Lake in Quebec, Canada Ships * ''Coquille'' (steamboat), a 1908 propeller-driven steamboat in Oregon, United States * French frigate ''Coquille'' (1794), French Navy ship later renamed HMS ''Coquille'' * French ship ''Astrolabe'' (1811), originally christened ''Coquille'' Other uses * Coquilles st jacques, "Shell of Saint James", in French, the scallop itself, as well as the preparation of scallops in cream sauce * Coquille, a dialect of the Tututni language Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulla Striata
''Bulla striata'', commonly known as the common Atlantic bubble or striate bubble, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Bullidae ''Bulla'' is a genus of medium to large hermaphrodite sea snails, shelled marine opisthobranch gastropod molluscs. These herbivorous snails are in the order Cephalaspidea.Gofas, S. (2010). Bulla Linnaeus, 1758. In: Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S.; Rosen ..., the bubble snails. Bulla striata var. adansoni 01.jpg, var. ''adansoni'' File:Bulla striata 02.jpg, Fossil (Pliocene) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q962379 Bullidae Gastropods described in 1792 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulla Ampulla
''Bulla ampulla'' is a species of gastropods belonging to the family Bullidae. The species has cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, a cosmopolitan distribution is the range of a taxon that extends across most or all of the surface of the Earth, in appropriate habitats; most cosmopolitan species are known to be highly adaptable to a range of climatic and en ... (except the Americas). References Bullidae Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Gastropods described in 1758 {{Heterobranchia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |