|
Brown Greater Galago
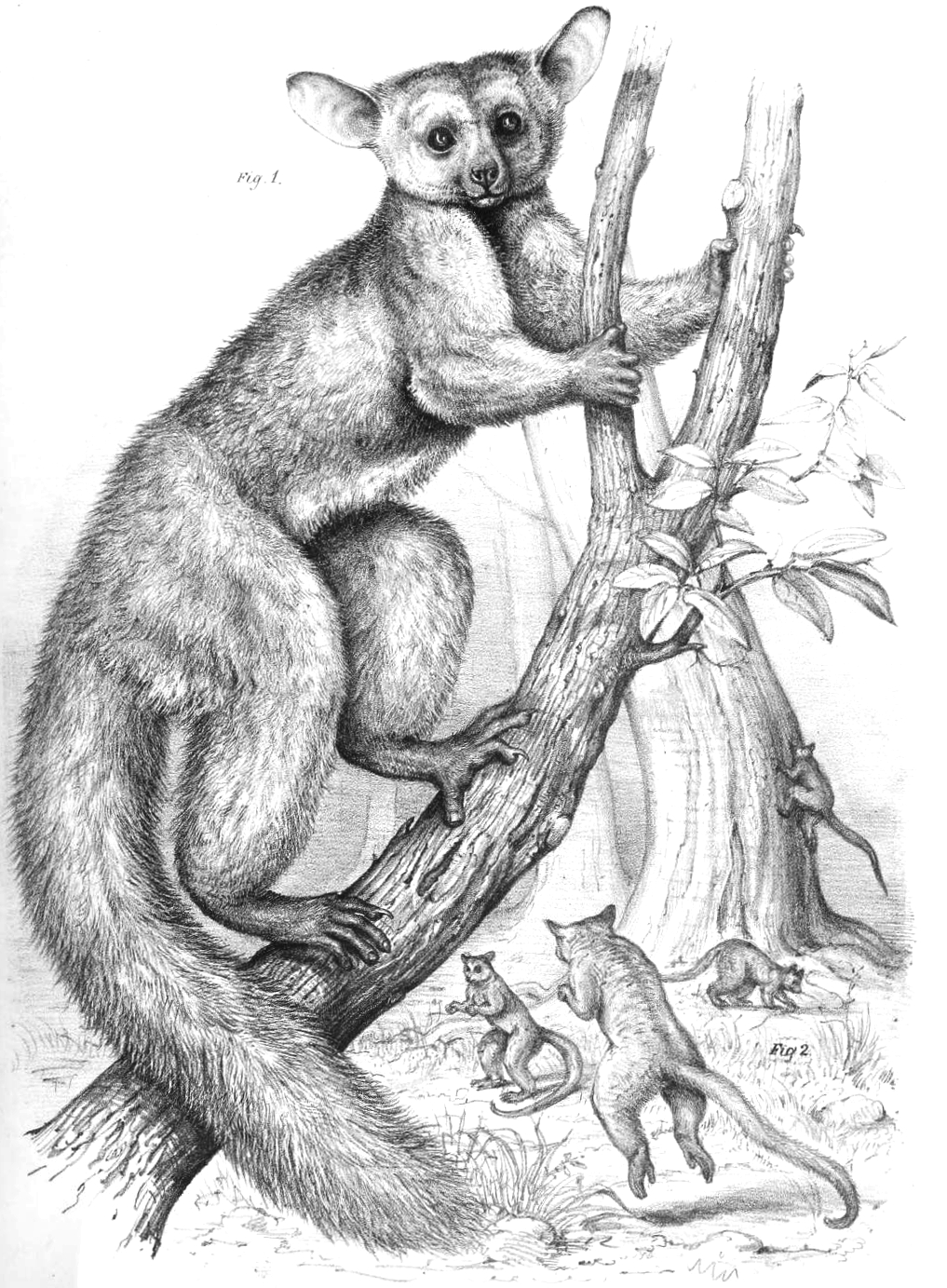
The brown greater galago (''Otolemur crassicaudatus''), also known as the large-eared greater galago or thick-tailed galago, is a nocturnal primate, the largest in the family of galagos. As opposed to smaller galago species it would climb, walk or run rather than leap. Taxonomy Two subspecies of ''Otolemur crassicaudatus'' are recognised: *''O. c. crassicaudatus'' *''O. c. kirkii'' The IUCN considers the silvery greater galago as a third subspecies, ''O. c. monteiri''. Other sources treat it as a separate species, though with "misgivings". The IUCN Red List assesses all three forms individually as Least Concern. Physical characteristics This species has a rounded head with a short, wide snout, very large ears that can be moved independently and relatively large forward binocular eyes. They possess flat thickened skin pads at the ends of their fingers and toes for grasping limbs. The fingers are long and toes are flattened with flattened nails. The dentition formula is I 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
√Čtienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire
√Čtienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire (; 15 April 177219 June 1844) was a French naturalist who established the principle of "unity of composition". He was a colleague of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and expanded and defended Lamarck's evolutionary theories. Geoffroy's scientific views had a transcendental flavor (unlike Lamarck's materialistic views) and were similar to those of German morphologists like Lorenz Oken. He believed in the underlying unity of organismal design, and the possibility of the transmutation of species in time, amassing evidence for his claims through research in comparative anatomy, paleontology, and embryology. He is considered as a predecessor of the evo-devo evolutionary concept. Life and early career Geoffroy was born at √Čtampes (in present-day Essonne), and studied at the Coll√®ge de Navarre, in Paris, where he studied natural philosophy under M. J. Brisson. He then attended the lectures of Louis-Jean-Marie Daubenton at the College de France and Fourcroy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN) is a Provinces of South Africa, province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the government merged the Zulu people, Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu language, Zulu) and Natal Province. It is located in the southeast of the country, with a long shoreline on the Indian Ocean. It shares borders with three other provinces and the countries of Mozambique, Eswatini and Lesotho. Its capital is Pietermaritzburg, and its largest city is Durban, which is also the Port of Durban, city with the largest port in sub-saharan Africa. It is the second-most populous province in South Africa, after Gauteng. Two areas in KwaZulu-Natal have been declared UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the iSimangaliso Wetland Park and the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park. These areas are important to the surrounding ecosystems. During the 1830s and early 1840s, the northern part of what is now KwaZulu-Natal was established as the Zulu Kingdom. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
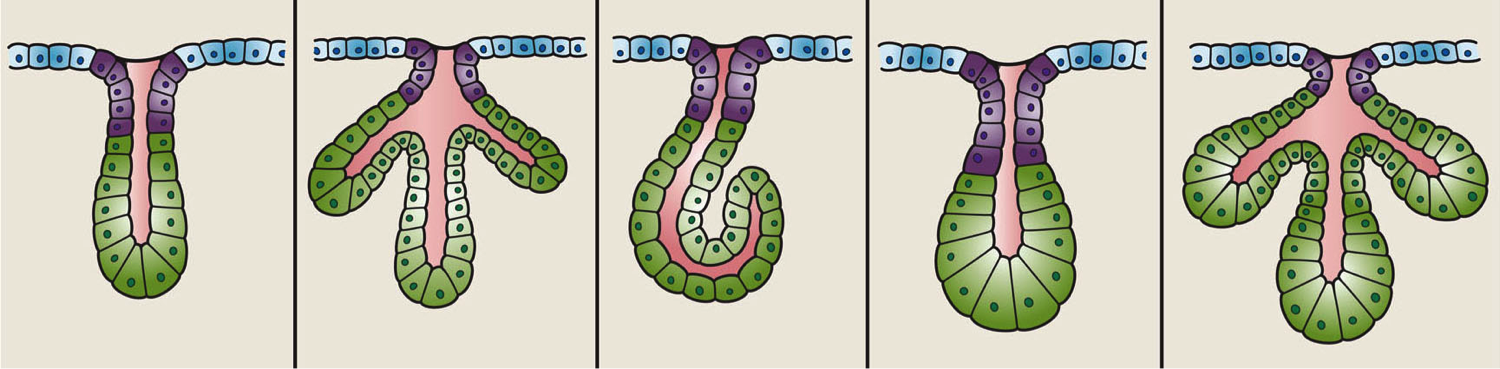
Gland
A gland is a Cell (biology), cell or an Organ (biology), organ in an animal's body that produces and secretes different substances that the organism needs, either into the bloodstream or into a body cavity or outer surface. A gland may also function to remove unwanted substances such as urine from the body. There are two types of gland, each with a different method of secretion. Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete their products, hormones, directly into interstitial spaces to be taken up into the bloodstream. Exocrine glands secrete their products through a duct into a body cavity or outer surface. Glands are mostly composed of epithelium, epithelial tissue, and typically have a supporting framework of connective tissue, and a capsule. Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelium, epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Territory (animal)
In ethology, territory is the sociographical area that an animal consistently defends against conspecificity, conspecific competition (biology), competition (or, occasionally, against animals of other species) using agonistic behaviors or (less commonly) real physical aggression. Animals that actively defend territories in this way are referred to as being territorial or displaying territorialism. Territoriality is only shown by a minority of species. More commonly, an individual or a group of animals occupies an area that it habitually uses but does not necessarily defend; this is called its home range. The home ranges of different groups of animals often overlap, and in these overlap areas the groups tend to avoid each other rather than seeking to confront and expel each other. Within the home range there may be a ''core area'' that no other individual group uses, but, again, this is as a result of avoidance. Function The ultimate function of animals inhabiting and defendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Greater Galago (Otolemur Crassicaudatus) (31812658647)
The brown greater galago (''Otolemur crassicaudatus''), also known as the large-eared greater galago or thick-tailed galago, is a nocturnal primate, the largest in the family of galagos. As opposed to smaller galago species it would climb, walk or run rather than leap. Taxonomy Two subspecies of ''Otolemur crassicaudatus'' are recognised: *''O. c. crassicaudatus'' *''O. c. kirkii'' The IUCN considers the silvery greater galago as a third subspecies, ''O. c. monteiri''. Other sources treat it as a separate species, though with "misgivings". The IUCN Red List assesses all three forms individually as Least Concern. Physical characteristics This species has a rounded head with a short, wide snout, very large ears that can be moved independently and relatively large forward binocular eyes. They possess flat thickened skin pads at the ends of their fingers and toes for grasping limbs. The fingers are long and toes are flattened with flattened nails. The dentition formula is I 2/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slug
Slug, or land slug, is a common name for any apparently shell-less Terrestrial mollusc, terrestrial gastropod mollusc. The word ''slug'' is also often used as part of the common name of any gastropod mollusc that has no shell, a very reduced shell, or only a small internal shell, particularly sea slugs and semi-slugs (this is in contrast to the common name ''snail'', which applies to gastropods that have a coiled shell large enough that they can fully retract their soft parts into it). Various Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic families of land slugs form part of several quite different evolutionary lineages, which also include snails. Thus, the various families of slugs are not closely related, despite the superficial similarity in overall body form. The shell-less condition has arisen many times independently as an example of convergent evolution, and thus the category "slug" is Polyphyly, polyphyletic. Taxonomy Of the six orders of Pulmonata, two ‚Äď the Onchidiacea and Soleoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Australasia, but is now reserved for species mainly from Australia, with others from New Guinea, Southeast Asia, and the Indian Ocean. The genus name is Neo-Latin, borrowed from Koine Greek (), a term used in antiquity to describe a preparation extracted from '' Vachellia nilotica'', the original type species. Several species of ''Acacia'' have been introduced to various parts of the world, and two million hectares of commercial plantations have been established. Description Plants in the genus ''Acacia'' are shrubs or trees with bipinnate leaves, the mature leaves sometimes reduced to phyllodes or rarely absent. There are 2 small stipules at the base of the leaf, but sometimes fall off as the leaf matures. The flowers are borne in spik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilization, fertilized by Pollen, sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The formation of the seed is the defining part of the process of reproduction in seed plants (spermatophytes). Other plants such as ferns, mosses and marchantiophyta, liverworts, do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological Ecological niche, niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. In the flowering plants, the ovary ripens into a fruit which contains the seed and serves to disseminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family (biology), family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berry
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone or pit although many pips or seeds may be present. Common examples of berries in the culinary sense are strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries, white currants, blackcurrants, and redcurrants. In Britain, soft fruit is a horticultural term for such fruits. The common usage of the term "berry" is different from the scientific or botanical definition of a berry, which refers to a fleshy fruit produced from the ovary of a single flower where the outer layer of the ovary wall develops into an edible fleshy portion( pericarp). The botanical definition includes many fruits that are not commonly known or referred to as berries, such as grapes, tomatoes, cucumbers, eggplants, bananas, and chili peppers. Fruits commonly considered berries but excluded by the botanical definition include strawberries, raspber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |