|
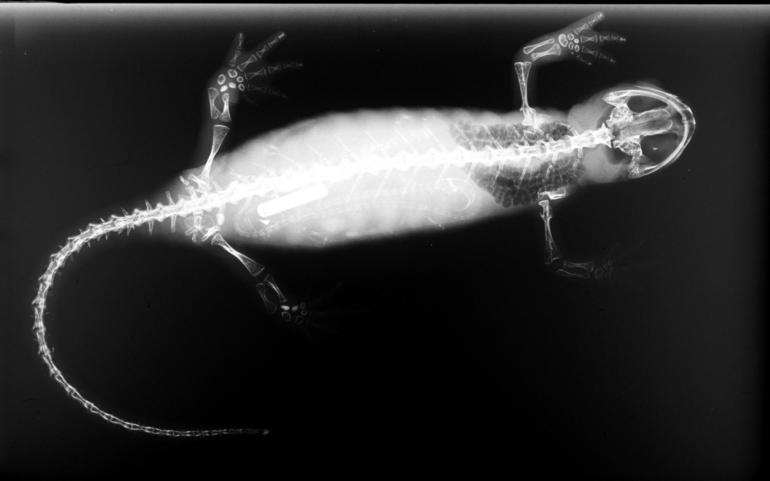
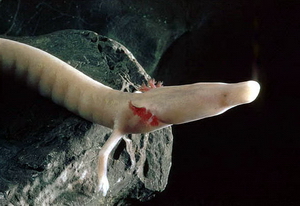
Brown Cave Salamander
The brown cave salamander (''Speleomantes genei''), also known as Gene's cave salamander, Sardinian cave salamander, or simply Sardinian salamander, is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to Sardinia (Italy). Its natural habitats are temperate forests, rocky areas, caves, and subterranean habitats (other than caves). It is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease .... References Speleomantes Cave salamanders Fauna of Sardinia Amphibians of Europe Endemic fauna of Italy Amphibians described in 1838 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Habitats Directive species {{Plethodontidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenraad Jacob Temminck
Coenraad Jacob Temminck (; 31 March 1778 – 30 January 1858) was a Dutch people, Dutch patrician, Zoology, zoologist and museum director. Biography Coenraad Jacob Temminck was born on 31 March 1778 in Amsterdam in the Dutch Republic. From his father, Jacob Temminck, who was treasurer of the Dutch East India Company with links to numerous travellers and collectors, he inherited a large collection of bird specimens. His father was a good friend of Francois Levaillant who also guided Coenraad. Temminck's ''Manuel d'ornithologie, ou Tableau systématique des oiseaux qui se trouvent en Europe'' (1815) was the standard work on European birds for many years. He was also the author of ''Histoire naturelle générale des Pigeons et des Gallinacées'' (1813–1817), illustrated by Pauline Rifer de Courcelles, Pauline Knip. He wrote ''Nouveau Recueil de Planches coloriées d'Oiseaux'' (1820–1839), and contributed to the mammalian sections of Philipp Franz von Siebold's ''Fauna jap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela, the sole surviving order from the group Caudata. ''Urodela'' is a scientific Latin term based on the Ancient Greek : ourà dēlē "conspicuous tail". ''Caudata'' is the Latin for "tailed ones", from : "tail". Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders never have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plethodontidae
Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. With over 500 species, lungless salamanders are by far the largest family of salamanders in terms of their diversity. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil. Only two extant genera occur in the Eastern Hemisphere: '' Speleomantes'' (native to Sardinia and mainland Europe south of the Alps) and '' Karsenia'' (native to South Korea). Biology Adult lungless salamanders have four limbs, with four toes on the fore limbs, and usually with five on the hind limbs. Within many species, mating and reproduction occur solely on land. Accordingly, many species also lack an aquatic larval stage, a phenomenon known as direct development in which the offspring hatch as fully-formed, miniature adults. Direct development is correlated with changes in the developmental characteristics of plethodontids compared to other families of salamanders including increases in egg size and durat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia and 16.45 km south of the French island of Corsica. It has over 1.5 million inhabitants as of 2025. It is one of the five Italian regions with some degree of Autonomous administrative division, domestic autonomy being granted by a Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, special statute. Its official name, Autonomous Region of Sardinia, is bilingual in Italian language, Italian and Sardinian language, Sardinian: / . It is divided into four provinces of Italy, provinces and a Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city. Its capital (and largest city) is Cagliari. Sardinia's indigenous language and Algherese dialect, Algherese Catalan language, Catalan are referred to by both the regional and national law as two of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as Biophysical environment, environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and Luminous intensity, light intensity. Biotic index, Biotic factors include the availability of food and the presence or absence of Predation, predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, habitat generalist species are able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species require a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a Canopy (biology), canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, ''Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA), Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the largest Terrestrial ecosystem, terrestrial ecosystems of Earth by area, and are found around the globe. 45 percent of forest land is in the Tropical forest, trop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave
Caves or caverns are natural voids under the Earth's Planetary surface, surface. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. Exogene caves are smaller openings that extend a relatively short distance underground (such as rock shelters). Caves which extend further underground than the opening is wide are called endogene caves. Speleology is the science of exploration and study of all aspects of caves and the cave environment. Visiting or exploring caves for recreation may be called Caving, ''caving'', ''potholing'', or ''spelunking''. Formation types The formation and development of caves is known as ''speleogenesis''; it can occur over the course of millions of years. Caves can range widely in size, and are formed by various geological processes. These may involve a combination of chemical processes, erosion by water, tectonic forces, microorganisms, pressure, and atmospheric influences. Isotopic dating techniques can be applied to cave sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease in biodiversity and Abundance (ecology), species numbers. Habitat destruction is in fact the leading cause of biodiversity loss and species extinction worldwide. Humans contribute to habitat destruction through the Exploitation of natural resources, use of natural resources, agriculture, industrial production and urbanization (urban sprawl). Other activities include mining, logging and trawling. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introduced species, introduction of invasive species, ecosystem nutrient depletion, water pollution, water and noise pollution are some examples. Loss of habitat can be preceded by an initial habitat fragmentation. Fragmentation and lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speleomantes
''Speleomantes'', or European cave salamanders, are a genus of salamander in the family Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders. It is one of two genera in the family to inhabit the Old World (the other being ''Karsenia''), with the remaining 250 or so species being found in North, Central and South America. The genus is endemic to Italy and a few nearby areas (San Marino, Monaco, and eastern Provence). Characteristics Until recently, ''Speleomantes'' was combined with the web-toed salamander genus ''Hydromantes'' from the Sierra Nevada (U.S.), Sierra Nevada range of California, which are their closest relatives, and are still combined by some herpetologists. They lack lungs; respiration takes place through the skin, which must be kept moist, and the lining of the mouth. The head is broad and distinct with prominent eyes. There are characteristic deep nasolabial grooves between the nostrils and the edge of the lips. The tongue has a broad tip and is extensible, being shot forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cave Salamanders
A cave salamander is a type of salamander that primarily or exclusively inhabits caves, a group that includes several species. Some of these animals have developed special, even extreme, adaptations to their subterranean environments. Some species have only rudimentary (or even absent) eyes (''blind salamanders''). Others lack pigmentation, rendering them a pale yellowish or pinkish color (e.g., '' Eurycea rathbuni''). With the notable exception of the olm (''Proteus anguinus''), all "cave salamanders" are members of the family Plethodontidae ("lungless salamanders"). Almost all of them are paedomorphic and therefore never undergo metamorphosis, but it is not clear if this happened before or after they adapted to an existence in caves, as some species that don't live in caves are also paedomorphic. History The first dedicated scientific study of a cave animal was focused upon a cave salamander, '' Proteus anguinus''. It was originally identified as a "dragon's larva" by Johann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna Of Sardinia
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and ''funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Modern Greek equivalent of fauna (πανίς or rather πανίδα). ''Fauna'' is also the word for a boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |