|
Brilacidin
Brilacidin (formerly PMX-30063), an investigational new drug (IND), is a polymer-based antibiotic currently in human clinical trials, and represents a new class of antibiotics called host defense protein mimetics, or HDP-mimetics, which are non-peptide synthetic small molecules modeled after host defense peptides (HDPs). 158pages HDPs, also called antimicrobial peptides, some of which are defensins, are part of the innate immune response and are common to most higher forms of life. Accounts of Chemical Research As brilacidin is modeled after a defensin, it is also called a defensin mimetic. Brilacidin is an antibiotic that works by disrupting bacterial cell membranes, mimicking defensins that play a role in innate immunity. Several mimics of antimicrobial peptides, both peptides and non-peptides, have been studied, but none have overcome difficulties to reach the market. Structure and action Brilacidin, a non-peptide chemical mimic, is an arylamide foldamer designed to replica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defensin Mimetic
Defensins are small cysteine-rich cationic proteins across cellular life, including vertebrate and invertebrate animals, plants, and fungi. They are host defense peptides, with members displaying either direct antimicrobial activity, immune signalling activities, or both. They are variously active against bacteria, fungi and many enveloped and nonenveloped viruses. They are typically 18-45 amino acids in length, with three or four highly conserved disulphide bonds. In animals, they are produced by cells of the innate immune system and epithelial cells, whereas in plants and fungi they are produced by a wide variety of tissues. An organism usually produces many different defensins, some of which are stored inside the cells (e.g. in neutrophil granulocytes to kill phagocytosed bacteria), and others are secreted into the extracellular medium. For those that directly kill microbes, their mechanism of action varies from disruption of the microbial cell membrane to metabolic disruption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Bug (bacteria)
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. Protozoa evolve antiprotozoal resistance, and bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance. Those bacteria that are considered extensively drug resistant (XDR) or totally drug-resistant (TDR) are sometimes called "superbugs".A.-P. Magiorakos, A. Srinivasan, R. B. Carey, Y. Carmeli, M. E. Falagas, C. G. Giske, S. Harbarth, J. F. Hinndler ''et al''Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria... Clinical Microbiology and Infection, Vol 8, Iss. 3 first published 27 July 2011 ia Wiley Online Library Retrieved 28 August 2020 Although antimicrobial resistance is a naturally-occurring process, it is often the result of improper usage of the drugs and management of the infections. Antibiotic resistance is a major subset o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intent-to-treat
In medicine an intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis of the results of a randomized controlled trial is based on the initial treatment assignment and not on the treatment eventually received. ITT analysis is intended to avoid various misleading artifacts that can arise in intervention research such as non-random attrition of participants from the study or crossover. ITT is also simpler than other forms of study design and analysis, because it does not require observation of compliance status for units assigned to different treatments or incorporation of compliance into the analysis. Although ITT analysis is widely employed in published clinical trials, it can be incorrectly described and there are some issues with its application. Furthermore, there is no consensus on how to carry out an ITT analysis in the presence of missing outcome data. Rationale Randomized clinical trials analyzed by the intention-to-treat (ITT) approach provide unbiased comparisons among the treatment groups. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
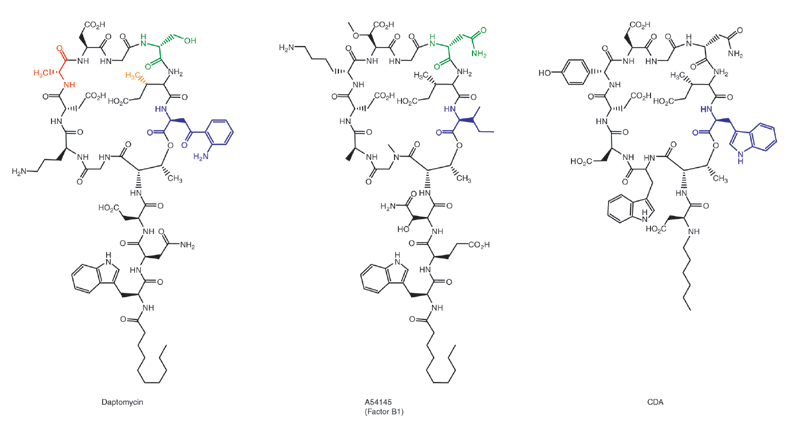
Daptomycin
Daptomycin, sold under the brand name Cubicin among others, is a lipopeptide antibiotic used in the treatment of systemic and life-threatening infections caused by Gram-positive organisms. Daptomycin was removed from the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines in 2019. The World Health Organization classifies daptomycin as critically important for human medicine. Medical uses In the United States, daptomycin is indicated for use in adults for skin and skin structure infections caused by Gram-positive infections, ''S. aureus'' bacteraemia, and right-sided ''S. aureus'' endocarditis. It binds avidly to pulmonary surfactant, so cannot be used in the treatment of pneumonia. There seems to be a difference in working daptomycin on hematogenous pneumonia. Adverse effects Common adverse drug reactions associated with daptomycin therapy include: *Cardiovascular: low blood pressure, high blood pressure, swelling *Central nervous system: insomnia *Dermatological: ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daptomycin
Daptomycin, sold under the brand name Cubicin among others, is a lipopeptide antibiotic used in the treatment of systemic and life-threatening infections caused by Gram-positive organisms. Daptomycin was removed from the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines in 2019. The World Health Organization classifies daptomycin as critically important for human medicine. Medical uses In the United States, daptomycin is indicated for use in adults for skin and skin structure infections caused by Gram-positive infections, ''S. aureus'' bacteraemia, and right-sided ''S. aureus'' endocarditis. It binds avidly to pulmonary surfactant, so cannot be used in the treatment of pneumonia. There seems to be a difference in working daptomycin on hematogenous pneumonia. Adverse effects Common adverse drug reactions associated with daptomycin therapy include: *Cardiovascular: low blood pressure, high blood pressure, swelling *Central nervous system: insomnia *Dermatological: ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staphylococcus Aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although ''S. aureus'' usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. ''S. aureus'' is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as methicillin-resistant ''S. aureu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABSSSI
Skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), also referred to as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSIs), are infections of skin and associated soft tissues (such as loose connective tissue and mucous membranes). Historically, the pathogen involved has most frequently been a bacterial species—always, since redescription of SSSIs as ABSSSIs—and as such, these infections require treatment by antibiotics. Types Until 2008, a distinction was made between two types: complicated SSSIs (cSSSIs) and uncomplicated SSSIs (uSSSIs), which had different regulatory approval requirements. Uncomplicated SSSIs included "simple abscesses, impetiginous lesions, furuncles, and cellulitis." Complicated SSSIs included "infections either involving deeper soft tissue or requiring significant surgical intervention, such as infected ulcers, burns, and major abscesses or a significant underlying disease state that complicates the response t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration Safety And Innovation Act
The Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act of 2012 (FDASIA) is a piece of American regulatory legislation signed into law on July 9, 2012. It gives the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) the authority to collect user fees from the medical industry to fund reviews of innovator drugs, medical devices, generic drugs and biosimilar biologics. It also creates the breakthrough therapy designation program and extends the priority review voucher program to make eligible rare pediatric diseases. The measure was passed by 96 senators voting for and one voting against. Title I: Fees Relating to Drugs Title I extends through FY2017 the authority of the FDA, through the authority of the Secretary of Health and Human Services, to collect drug application and supplement fees, prescription drug establishment fees, and prescription drug product fees to support the FDA process for reviewing human drug applications. It requires the FDA to submit annually to the Hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |