|
Breech Presentation
A breech birth is when a baby is born bottom first instead of Cephalic presentation, head first, as is normal. Around 3–5% of pregnant women at term (37–40 weeks pregnant) have a breech baby. Due to their higher than average rate of possible complications for the baby, breech births are generally considered higher risk. Breech births also occur in many other mammals such as dogs and horses, see veterinary obstetrics. Most babies in the breech position are delivered via caesarean section because it is seen as safer than being Vaginal birth, born vaginally. Doctors and Midwife, midwives in the developing world often lack many of the skills required to safely assist women giving birth to a breech baby vaginally. Also, delivering all breech babies by caesarean section in developing countries is difficult to implement as there are not always resources available to provide this service. Cause With regard to the fetal presentation during pregnancy, three periods have been distingu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Smellie (obstetrician)
William Smellie (5 February 1697 – 5 March 1763) was a Scottish people, Scottish Obstetrics, obstetrician and medical instructor who practiced and taught primarily in London. One of the first prominent Midwife#Men in midwifery, male midwives in Britain, he designed an improved version of the obstetrical forceps, established safer delivery practices, and through his teaching and writing helped make obstetrics more scientifically based. He is often called the "father of British midwifery". Early life and education Smellie was born on 5 February 1697 in the town of Lesmahagow, Scotland. He was the only child of Sara Kennedy (1657–1727) and Archibald Smellie (1663/4–1735), a merchant and burgess of the town. Smellie practiced medicine before getting a license, opening an apothecary in 1720 in Lanark. It was not a particularly lucrative venture, as he also sold cloth as a side business to supplement his income, but he began reading medical books and teaching himself obstetrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myotonic Dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is a type of muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle loss and weakness. In DM, muscles are often myotonia, unable to relax after contraction. Other manifestations may include cataracts, intellectual disability and arrhythmia, heart conduction problems. In men, there may be early balding and infertility. While myotonic dystrophy can occur at any age, onset is typically in the 20s and 30s. Myotonic dystrophy is caused by a genetic mutation in one of two genes. Mutation of the ''Myotonin-protein kinase, DMPK'' gene causes myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). Mutation of ''CNBP'' gene causes type 2 (DM2). DM is typically heredity, inherited, following an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, and it generally anticipation (genetics), worsens with each generation. A type of DM1 may be apparent at birth. DM2 is generally milder. Diagnosis is confirmed by genetic testing. There is no cure. Treatments may include braces or wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Agenesis
Sacral may refer to: *Sacred, associated with divinity and considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion *Of the sacrum The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, ..., a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine See also * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
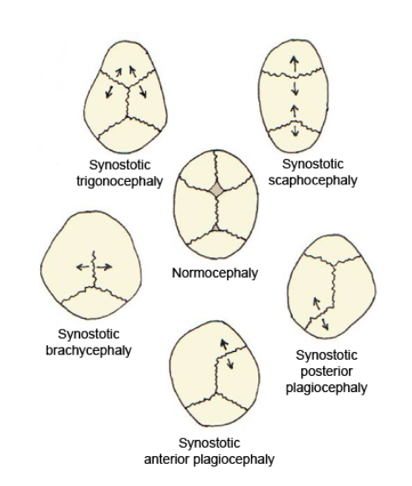
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infant's skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development combined with a significant reduction in IQ. Craniosynostosis occurs in one in 2000 births. Craniosynostosis is part of a syndrome in 15% to 40% of affected patients, but it usually occurs as an isol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amelia (birth Defect)
Amelia is the birth defect of lacking one or more limbs. The term may be modified to indicate the number of legs or arms missing at birth, such as tetra-amelia for the absence of all four limbs. The term is . Symptoms The diagnosis of amelia syndrome is established clinically and can be made on routine prenatal ultrasonography. WNT3 is the only gene known to be associated with tetra-amelia syndrome. Molecular genetic testing on a clinical basis can be used to diagnose the incidence of the syndrome. The mutation detection frequency is unknown as only a limited number of families have been studied. Affected infants are often stillborn or die shortly after birth. Description Amelia may be present as an isolated defect, but it is often associated with major malformations in other organ systems. These frequently include cleft lip and/or palate, body wall defects, malformed head, and defects of the neural tube, kidneys, and diaphragm. Facial clefts may be accompanied by other faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achondrogenesis
Achondrogenesis is a number of disorders that are the most severe form of congenital chondrodysplasia (malformation of bones and cartilage). These conditions are characterized by a small body, short limbs, and other skeletal abnormalities. As a result of their serious health problems, infants with achondrogenesis are usually born prematurely, are stillborn, or die shortly after birth from respiratory failure. Some infants, however, have lived for a while with intensive medical support. Researchers have described at least three forms of achondrogenesis, designated as Achondrogenesis type 1A, achondrogenesis type 1B and achondrogenesis type 2. These types are distinguished by their signs and symptoms, inheritance pattern, and genetic cause. Other types of achondrogenesis may exist, but they have not been characterized or their cause is unknown. Achondrogenesis type 1A is caused by a defect in the microtubules of the Golgi apparatus. In mice, a nonsense mutation in the thyroid hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyoplasia
Amyoplasia is a condition characterized by a generalized lack in the newborn of muscular development and growth, with contracture and deformity that affect at least two joints. It is the most common form of arthrogryposis. It is characterized by the four limbs being involved, and by the replacement of skeletal muscle by dense fibrous and adipose tissue. Studies involving amyoplasia have revealed similar findings of the muscle tissue due to various causes including that seen in sacral agenesis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. So amyoplasia may also include an intermediate common pathway, rather than the primary cause of the contractors. Signs and symptoms Amyoplasia results when a fetus is unable to move sufficiently in the womb. Mothers of children with the disorder often report that their baby was abnormally still during the pregnancy. The lack of movement in utero (also known as fetal akinesia) allows extra connective tissue to form around the joints and, therefore, the joints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Organ (biology), organs—may be mild to severe. Symptoms found in various types of OI include sclera, whites of the eye (sclerae) that are blue instead, short stature, joint hypermobility, loose joints, hearing loss, breathing problems and problems with the teeth (dentinogenesis imperfecta). Potentially life-threatening Complication (medicine), complications, all of which become more common in more severe OI, include: tearing (Dissection (medical), dissection) of the major arteries, such as Aortic dissection, the aorta; pulmonary insufficiency, pulmonary valve insufficiency secondary to distortion of the ribcage; and basilar invagination. The underlying mechanism is usually a problem with connective tissue due to a lack of, or poorly forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds up within the brain, which can cause pressure to increase in the skull. Symptoms may vary according to age. Headaches and double vision are common. Elderly adults with normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) may have poor balance, difficulty controlling urination, or mental impairment. In babies, there may be a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects (primary) or can develop later in life (secondary). Hydrocephalus can be classified via mechanism into communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus. Diagnosis is made by physical examination and medical imaging, such as a CT scan. Hydrocephalus is typically treated through surgery. One option is the placement of a shunt system. A procedure called an endoscopic third ventriculostomy has gained popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spina Bifida
Spina bifida (SB; ; Latin for 'split spine') is a birth defect in which there is incomplete closing of the vertebral column, spine and the meninges, membranes around the spinal cord during embryonic development, early development in pregnancy. There are three main types: spina bifida occulta, meningocele and myelomeningocele. Meningocele and myelomeningocele may be grouped as spina bifida cystica. The most common location is the Lumbar vertebrae, lower back, but in rare cases it may be in the Thoracic vertebrae, middle back or Cervical vertebrae, neck. Occulta has no or only mild signs, which may include a hairy patch, dimple, dark spot or swelling on the back at the site of the gap in the spine. Meningocele typically causes mild problems, with a sac of fluid present at the gap in the spine. Myelomeningocele, also known as open spina bifida, is the most severe form. Problems associated with this form include poor ability to walk, impaired Neurogenic bladder dysfunction, bladder o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anencephalus
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fails to close, usually between the 23rd and 26th day following conception. Strictly speaking, the Greek term translates as "without a brain" (or totally lacking the inside part of the head), but it is accepted that children born with this disorder usually only lack a telencephalon, the largest part of the brain consisting mainly of the cerebral hemispheres, including the neocortex, which is responsible for cognition. The remaining structure is usually covered only by a thin layer of membrane—skin, bone, meninges, etc., are all lacking. With very few exceptions, infants with this disorder do not survive longer than a few hours or days after birth. Anencephaly is a severe neural tube defect typically considered incompatible with prolonged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Lange Syndrome
Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) is a genetic disorder. People with Cornelia de Lange syndrome experience a range of physical, cognitive, and medical challenges ranging from mild to severe. Cornelia de Lange syndrome has a widely varied phenotype, meaning people with the syndrome have varied features and challenges. The typical features of CdLS include thick or long eyebrows, a small nose, small stature, developmental delay, long or smooth philtrum, thin upper lip and downturned mouth. The syndrome is named after Dutch pediatrician Cornelia Catharina de Lange, who described it in 1933. It is often termed Brachmann de Lange syndrome or Bushy syndrome and is also known as Amsterdam dwarfism. Its exact incidence is unknown, but it is estimated at 1 in 10,000 to 30,000. Signs and symptoms The phenotype of CdLS is highly varied and is described as a spectrum; from Classic CdLS (with a greater number of key features) to mild variations with only a few features. Some people will have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |