|
Breath Carbon Monoxide Monitor
Breath carbon monoxide is the level of carbon monoxide in a person's exhalation. It can be measured in a breath carbon monoxide test, generally by using a carbon monoxide breath monitor (breath CO monitor), such as for motivation and education for smoking cessation and also as a clinical aid in assessing carbon monoxide poisoning. The breath carbon monoxide level has been shown to have a close relationship with the level of CO in the blood known as carboxyhaemoglobin (%COHb) or "blood CO". This correlation allows for the level of CO in the blood to be indirectly measured through a breath sample. Breath CO monitor CO monitors measure carbon monoxide in parts per million (ppm) in breath. These monitors have become increasingly popular given that they allow for noninvasive testing and are inexpensive to use. Breath CO monitors function based on the detection of carbon monoxide gas with an electrochemical gas sensor. Monitors typically incorporate an LCD display that provides a conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breath Carbon Monitor Device
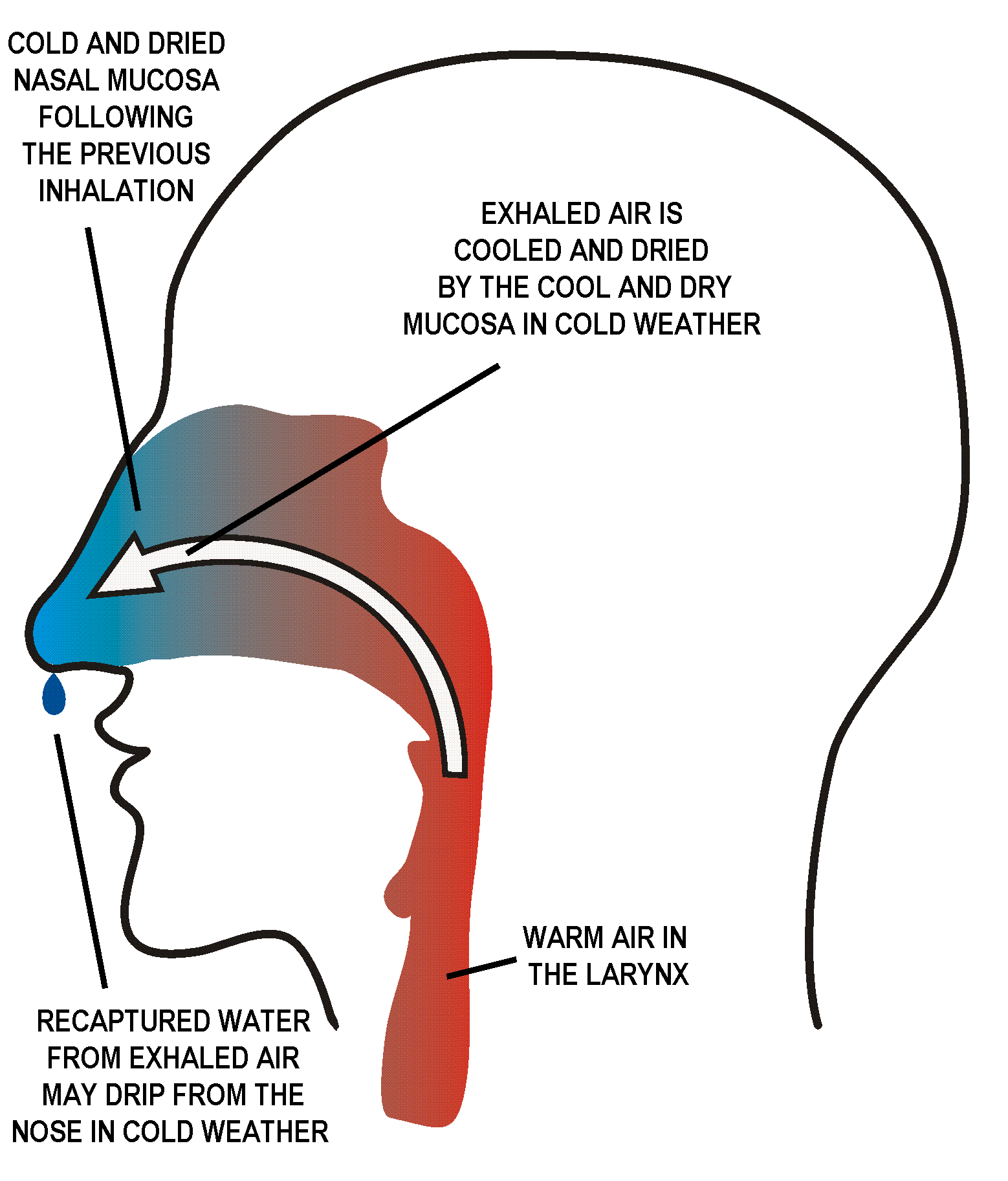
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into (inhalation) and out of (exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or external respiration, brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where cellular respiration takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the four primary v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest oxocarbon, carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called ''metal carbonyl, carbonyl''. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry. The most common source of carbon monoxide is the partial combustion of carbon-containing compounds. Numerous environmental and biological sources generate carbon monoxide. In industry, carbon monoxide is important in the production of many compounds, including drugs, fragrances, and fuels. Indoors CO is one of the most acutely toxic contaminants affecting indoor air quality. CO may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel-burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel-burning heating systems (wood, oil, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking Cessation
Smoking cessation, usually called quitting smoking or stopping smoking, is the process of discontinuing tobacco smoking. Tobacco smoke contains nicotine, which is Addiction, addictive and can cause Substance dependence, dependence. As a result, nicotine withdrawal often makes the process of quitting difficult. Smoking is the Leading causes of preventable death, leading cause of preventable death and a global public health concern. Tobacco use leads most commonly to diseases affecting the heart and lungs, with smoking being a major risk factor for Myocardial infarction, heart attacks, strokes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), emphysema, and various types and subtypes of cancers (particularly lung cancer, Oropharyngeal cancer, cancers of the oropharynx, Laryngeal cancer, larynx, and Oral cancer, mouth, Esophageal cancer, esophageal and pancreatic cancer). Smoking cessation significantly reduces the risk of dying from smoking-rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning typically occurs from breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) at excessive levels. Symptoms are often described as " flu-like" and commonly include headache, dizziness, weakness, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. Large exposures can result in loss of consciousness, arrhythmias, seizures, or death. The classically described "cherry red skin" rarely occurs. Long-term complications may include chronic fatigue, trouble with memory, and movement problems. CO is a colorless and odorless gas which is initially non-irritating. It is produced during incomplete burning of organic matter. This can occur from motor vehicles, heaters, or cooking equipment that run on carbon-based fuels. Carbon monoxide primarily causes adverse effects by combining with hemoglobin to form carboxyhemoglobin (symbol COHb or HbCO) preventing the blood from carrying oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide as carbaminohemoglobin. Additionally, many other hemoproteins such as myoglob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxyhemoglobin
Carboxyhemoglobin (carboxyhaemoglobin BrE) (symbol COHb or HbCO) is a stable complex (chemistry), complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin (Hb) that forms in red blood cells upon contact with carbon monoxide. Carboxyhemoglobin is often mistaken for the compound formed by the combination of carbon dioxide (Carboxylic acid, carboxyl) and hemoglobin, which is actually carbaminohemoglobin. Carboxyhemoglobin terminology emerged when carbon monoxide was known by its historic name, "carbonic oxide", and evolved through Germanic and British English etymological influences; the preferred IUPAC nomenclature is carbonylhemoglobin. The average non-smoker maintains a systemic carboxyhemoglobin level under 3% COHb whereas smokers approach 10% COHb. The biological threshold for carboxyhemoglobin tolerance is 15% COHb, meaning toxicity is consistently observed at levels in excess of this concentration. The FDA has previously set a threshold of 14% COHb in certain clinical trials evaluating the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parts Per Million
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantity, dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction (chemistry), mass fraction. Since these fraction (mathematics), fractions are quantity-per-quantity measures, they are pure numbers with no associated units of measurement. Commonly used are * parts-per-million - ppm, * parts-per-billion - ppb, * parts-per-trillion - ppt, * parts-per-quadrillion - ppq, This notation is not part of the International System of Units - SI system and its meaning is ambiguous. Applications Parts-per notation is often used describing dilute solutions in chemistry, for instance, the relative abundance of dissolved minerals or pollutants in water. The quantity "1 ppm" can be used for a mass fraction if a water-borne pollutant is present at one-millionth of a gram per gram of sample solution. When working with aqueous solutions, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breath CO Monitor
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into (inhalation) and out of (exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or external respiration, brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where cellular respiration takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the four primary v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Clinical Excellence
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Book Store, a bookstore and office supplies chain in the Philippines * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900–1924 * National Radio Company, Malden, Massachusetts, USA 1914–1991 * National Supermark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern Ireland) which was created separately and is often referred to locally as "the NHS". The original three systems were established in 1948 (NHS Wales/GIG Cymru was founded in 1969) as part of major social reforms following the Second World War. The founding principles were that services should be comprehensive, universal and free at the point of delivery. Each service provides a comprehensive range of health services, provided without charge for residents of the United Kingdom apart from dental treatment and optical care. In England, NHS patients have to pay prescription charges; some, such as those aged over 60, or those on certain state benefits, are exempt. Taken together, the four services in 2015–16 employed around 1.6 million people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking And Pregnancy
Tobacco smoking during pregnancy causes many detrimental effects on health and reproduction, in addition to the general health effects of tobacco. A number of studies have shown that tobacco use is a significant factor in miscarriages among pregnant smokers, and that it contributes to a number of other threats to the health of the foetus. Because of the associated risks, people are advised not to smoke before, during or after pregnancy. If this is not possible, however, reducing the daily number of cigarettes smoked can minimize the risks for both the mother and child. This is especially true for people in developing countries, where breastfeeding is essential for the child's overall nutritional status. Smoking before pregnancy Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant are advised to stop smoking. It is important to examine these effects because smoking before, during and after pregnancy is not an unusual behavior among the general population and can have detrimental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Protection Agency
The Health Protection Agency (HPA) was a non-departmental public body in England. It was set up by the UK government in 2003 to protect the public from threats to their health from infectious diseases and environmental hazards. The HPA's role was to provide an integrated approach to protecting public health in the UK. It did this by providing advice and information to the general public, health professionals and local government, and by providing emergency services, support and advice to the National Health Service (NHS) and the Department of Health. The HPA also played a lead role in helping prepare for new and emerging health threats, such as bioterrorism or emerging virulent disease strains. There were four HPA centres – at Porton Down in Salisbury, Chilton in Oxfordshire, South Mimms in Hertfordshire, and Colindale in NW London. In addition, the HPA had regional laboratories across England and administrative headquarters in Central London. On 1 April 2013, the HPA minus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CO-oximeter
A CO-oximeter is a device that measures the oxygen carrying state of hemoglobin in a blood specimen, including oxygen-carrying hemoglobin (O2Hb), non-oxygen-carrying but normal hemoglobin (HHb) (formerly, but incorrectly, referred to as 'reduced' hemoglobin), as well as the dyshemoglobins such as carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) and methemoglobin (MetHb). The use of 'CO' rather than 'Co' or 'co' is more appropriate since this designation represents a device that measures carbon monoxide (CO) bound to hemoglobin, as distinguished from simple oximetry which measures hemoglobin bound to molecular oxygen—O2Hb—or hemoglobin capable of binding to molecular oxygen—HHb. Simpler oximeters may report oxygen saturation alone, i.e. the ratio of oxyhemoglobin to total 'bindable' hemoglobin (i.e. oxyhemoglobin + deoxyhemoglobin-HHb). CO-oximetry is useful in defining the causes for hypoxemia, or hypoxia, (oxygen deficiency at the tissue level). Mechanism A CO-oximeter measures the absorption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |