|
Breakwaters
A breakwater is a permanent structure constructed at a coastal area to protect against tides, currents, waves, and storm surges. Breakwaters have been built since antiquity to protect anchorages, helping isolate vessels from marine hazards such as wind-driven waves. A breakwater, also known in some contexts as a jetty or a mole, may be connected to land or freestanding, and may contain a walkway or road for vehicle access. Part of a coastal management system, breakwaters are installed parallel to the shore to minimize erosion. On beaches where longshore drift threatens the erosion of beach material, smaller structures on the beach may be installed, usually perpendicular to the water's edge. Their action on waves and current is intended to slow the longshore drift and discourage mobilisation of beach material. In this usage they are more usually referred to as groynes. Purposes Breakwaters reduce the intensity of wave action in inshore waters and thereby provide safe har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Armour
Riprap (in North American English), also known as rip rap, rip-rap, shot rock, rock armour (in British English) or rubble, is human-placed rock or other material used to protect shoreline structures against scour and water, wave, or ice erosion. Riprap is used to armor shorelines, streambeds, bridge abutments, foundational infrastructure supports and other shoreline structures against erosion. Common rock types used include granite and modular concrete blocks. Rubble from building and paving demolition is sometimes used, as well as specifically designed structures called ''tetrapods'' or similar concrete blocks. Riprap is also used underwater to cap immersed tubes sunken on the seabed to be joined into an undersea tunnel. Environmental effects Sediment effects Riprap causes morphological changes in the riverbeds they surround. One such change is the reduction of sediment settlement in the river channel, which can lead to scouring of the river bed as well as coarser sedime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (architecture)
A mole is a massive structure, usually of stone, used as a pier, breakwater, or a causeway separating two bodies of water. A mole may have a wooden structure built on top of it that resembles a wooden pier. The defining feature of a mole, however, is that water cannot freely flow underneath it, unlike a true pier. The oldest known mole is at Wadi al-Jarf, an ancient Egyptian harbor complex on the Red Sea, constructed . The word comes from Middle French ''mole'', ultimately from Latin ''mōlēs'', meaning a large mass, especially of rock; it has the same root as molecule and mole, the chemical unit of measurement. Heptastadion Notable in antiquity was the Heptastadion, a giant mole built in the 3rd century BC in the city of Alexandria, Egypt to join the city to ''Pharos Island'' where the Pharos lighthouse stood. The causeway formed a barrier separating Alexandria's oceanfront into two distinct harbours, an arrangement which had the advantage of protecting the harbours fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Overtopping
Wave overtopping is the time-averaged amount of water that is discharged (in liters per second) per structure length (in meters) by wind waves, waves over a structure such as a breakwater (structure), breakwater, revetment or levee, dike which has a crest height above still water level. When waves break over a dike, it causes water to flow onto the land behind it. Excessive overtopping is undesirable because it can compromise the integrity of the structure or result in a safety hazard, particularly when the structure is in an area where people, infrastructure or vehicles are present, such as in the case of a dike fronting an esplanade or densely populated area. Wave overtopping typically transpires during extreme weather events, such as intense storms, which often elevate water levels beyond average due to wind setup. These effects may be further intensified when the storm coincides with a high spring tide. Excessive overtopping may cause damage to the inner slope of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xbloc
An Xbloc is a wave-dissipating concrete block (or "armour unit") designed to protect shores, harbour walls, seawalls, breakwaters and other coastal structures from the direct impact of incoming waves. The Xbloc model was designed and developed in 2001 by the Dutch firm Delta Marine Consultants, now called BAM Infraconsult, a subsidiary of the Royal BAM Group. Xbloc has been subjected to extensive research by several universities. Benefits vs other systems Concrete armour units are generally applied in breakwaters and shore protections. The units are placed in a single layer as the outer layer of the coastal structure. This layer is called the armour layer. Its function is twofold: (1) to protect the finer material below it against severe wave action; (2) to dissipate the wave energy to reduce the wave run-up, overtopping and reflection. These functions require a heavy, but porous armour. Common factors to apply single layer concrete armour units are: * natural rock is unavail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Management
Coastal management is defence against flooding and erosion, and techniques that stop erosion to claim lands. Protection against rising sea levels in the 21st century is crucial, as sea level rise accelerates due to climate change. Changes in sea level damage beaches and coastal systems are expected to rise at an increasing rate, causing coastal sediments to be disturbed by tidal energy. Coastal zones occupy less than 15% of the Earth's land area, while they host more than 40% of the world population. Nearly 1.2 billion people live within of a coastline and of sea level, with an average density three times higher than the global average for population. With three-quarters of the world population expected to reside in the coastal zone by 2025, human activities originating from this small land area will impose heavy pressure on coasts. Coastal zones contain rich resources to produce goods and services and are home to most commercial and industrial activities. History Coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Engineering
Coastal engineering is a branch of civil engineering concerned with the specific demands posed by constructing at or near the coast, as well as the development of the coast itself. The fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic impact of especially wind wave, waves, tides, storm surges and tsunamis and (often) the harsh environment of salt seawater are typical challenges for the coastal engineer – as are the morphodynamics, morphodynamic changes of the coastal topography, caused both by the autonomous development of the system and human-made changes. The areas of interest in coastal engineering include the coasts of the oceans, seas, marginal seas, estuary, estuaries and big lakes. Besides the design, building and maintenance of coastal structures, coastal engineers are often interdisciplinary involved in integrated coastal zone management, also because of their specific knowledge of the hydro- and morphodynamics of the coastal system. This may include providing input and technology for e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
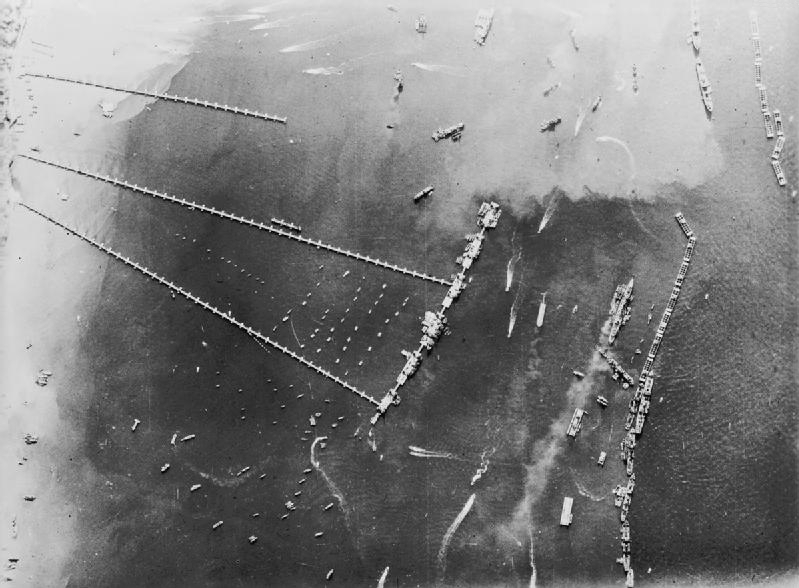
Mulberry Harbour
The Mulberry harbours were two temporary portable harbours developed by the Admiralty (United Kingdom), British Admiralty and War Office during the Second World War to facilitate the rapid offloading of cargo onto beaches during the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Normandy in June 1944. They were designed in 1942 then built in under a year in great secrecy; within hours of the Allies creating beachheads after D-Day, sections of the two prefabricated harbours were towed across the English Channel from southern England and placed in position off Omaha Beach (Mulberry "A") and Gold Beach (Mulberry "B"), along with old ships to be sunk as breakwater (structure), breakwaters. The Mulberry harbours solved the problem of needing deepwater jetties and a harbour to provide the invasion force with the necessary reinforcements and supplies, and were to be used until major French ports could be captured and brought back into use after repair of the inevitable sabotage by German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherbourg
Cherbourg is a former Communes of France, commune and Subprefectures in France, subprefecture located at the northern end of the Cotentin peninsula in the northwestern French departments of France, department of Manche. It was merged into the commune of Cherbourg-Octeville on 28 February 2000,Décret 23 February 2000 which was merged into the new commune of Cherbourg-en-Cotentin on 1 January 2016. Cherbourg is protected by Cherbourg Harbour, between La Hague and Val de Saire, and the city has been a strategic position over the centuries, disputed between the English and French. Cited as one of the "keys to the kingdom" by Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Vauban, it became, by colossal maritime development work, a first-rate military port under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolos
A dolos (plural: dolosse) is a wave-dissipating concrete block used in great numbers as a form of coastal management. It is a type of tetrapod. Weighing up to , dolosse are used to build revetments for protection against the erosive force of waves from a body of water. The dolos was invented in 1963, and was first deployed in 1964 on the breakwater of East London, a South African port city. Construction Dolosse are normally made from un-reinforced concrete, poured into a steel mould. The concrete will sometimes be mixed with small steel fibers to strengthen it in the absence of reinforcement. They are used to protect harbour walls, breakwaters and shore earthworks. In Dania Beach, Florida, dolosse are used as an artificial reef known as the Dania Beach Erojacks. They are also used to trap sea-sand to prevent erosion. Roughly 10,000 dolosse are required for a kilometre of coastline. They work by dissipating, rather than blocking, the energy of waves. Their design deflects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
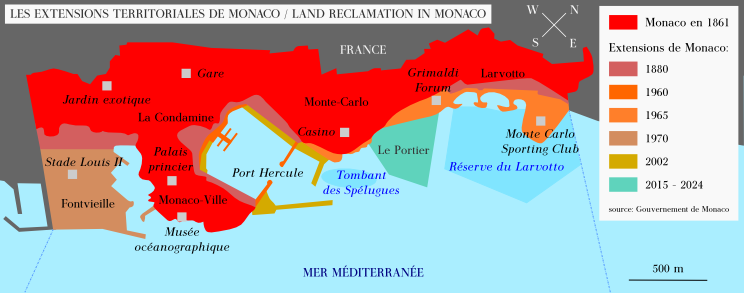
Le Portier
Le Portier (), sometimes referred to as Portier Cove or Mareterra, is a residential area opened in December 2024. It is part of the traditional ''Quartier'' of Monte Carlo in the Principality of Monaco, and constitutes the eleventh modern administrative Monégasque ward. History The project, started in the early 2000s and scheduled for 2014, was abandoned in 2009 at the command of Prince Albert II due to the state of the nation's finances. In 2011, new funds were acquired and the project resumed construction. In addition to a new residential area, there were plans to build new administrative buildings, museums and a theatre. On July 18, 2019, the last of the 18 interlocking concrete caisson was placed, closing the belt that delimits the offshore extension, thus specifically modifying the physical limits of Monaco. On December 16 of that year, construction of the new six-hectare strip was completed. By the year 2020, work had been completed to reclaim land from the sea in the Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Reclamation In Monaco
Land reclamation is done in Monaco through a policy of building land in the sea with concrete blocks because land is very scarce, as the country is comparatively tiny, at . To solve this problem and to continue economic development, for years the country has added to its total land area by reclaiming land from the sea. Geography The entire district of Fontvieille, Monaco, Fontvieille was constructed on land reclaimed from the sea in the western part of Monaco in the 1970s. It is the newest of the four traditional quartiers (districts) in the principality of Monaco, and one of ten wards for modern administrative purposes. Land has also been added to areas of La Condamine and Larvotto, Larvotto/Bas Moulins. History Prince Albert II, Prince Albert's father, Rainier III, was known as the "Builder Prince". In an attempt to further develop the economy of Monaco, he first supported the idea of land reclamation. Since it was impossible to extend into France, the only solution was to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corniche Beirut
The Corniche Beirut is a seaside promenade in the Central District of Beirut, Lebanon. Lined with palm trees, the waterfront esplanade has views of the Mediterranean Sea and the summits of Mount Lebanon to the east. Corniche Beirut has its foundation in the Avenue des Français, which was built during the period of the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon along the seafront that extended from the old town. Location The Corniche, which is long, encircles the Beirut promontory from the Saint George Bay on the northern coast of the city, turning west into Place Rafic Hariri, then into Avenue de Paris and the Raouché, and then into Avenue General de Gaulle before it ends on Rafic Hariri Avenue. Usage The Corniche is a common destination for walkers, joggers and bikers. Push cart vendors offer various local snacks and drinks. A number of the trunks of the palm trees that line the Corniche are pockmarked with bullet holes from the Lebanese Civil War The Lebanese Civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |