|
Brachydactyly-mesomelia-intellectual Disability-heart Defects Syndrome
Heart-hand syndromes are a group of rare diseases that manifest with both heart and limb deformities. , known heart-hand syndromes include Holt–Oram syndrome, Berk–Tabatznik syndrome, brachydactyly-long thumb syndrome, patent ductus arteriosus-bicuspid aortic valve syndrome, heart hand syndrome, Slovenian type and Heart-hand syndrome, Spanish type. Types Heart-hand syndrome type 1 Heart-hand syndrome type 1 is more commonly known as Holt–Oram syndrome. Is the most prevalent form of heart-hand syndrome. It is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands (the upper limbs) and may also cause heart problems. The syndrome includes an absent radial bone in the arms, an atrial septal defect, and a first degree heart block. Heart-hand syndrome type 2 Heart-hand syndrome type 2 is also known as Berk–Tabatznik syndrome. Berk–Tabatznik syndrome is a condition with an unknown cause that shows symptoms of short stature, congenital optic atro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holt–Oram Syndrome
Holt–Oram syndrome (also called atrio-digital syndrome, atriodigital dysplasia, cardiac-limb syndrome, heart-hand syndrome type 1, HOS, ventriculo-radial syndrome) is an autosomal dominant disorder that affects bones in the arms and hands (the upper limbs) and often causes heart problems. The syndrome may include an absent radial bone in the forearm, an atrial septal defect in the heart, or heart block. It affects approximately 1 in 100,000 people. Presentation All people with Holt-Oram syndrome have at least one abnormal wrist bone, which can often only be detected by X-ray. Other bone abnormalities are associated with the syndrome. These vary widely in severity, and include a missing thumb, a thumb that looks like a finger, upper arm bones of unequal length or underdeveloped, partial or complete absence of bones in the forearm, and abnormalities in the collar bone or shoulder blade. Bone abnormalities may affect only one side of the body or both sides; if both sides ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern and Western European populations, exhibiting a high degree of continuity with other Indo-European-derived ethnic groups in the region. Spain is also home to a diverse array of national and regional identities, shaped by its complex history. These include various languages and dialects, many of which are direct descendants of Latin, the language imposed during Roman rule. Among them, Spanish (also known as Castilian) is the most widely spoken and the only official language across the entire country. Commonly spoken regional languages include, most notably, the sole surviving indigenous language of Iberia, Basque, as well as other Latin-descended Romance languages like Spanish itself, Catalan and Galician. Many populations outside Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Limb Deformities
Congenital limb deformities are congenital musculoskeletal disorders which primarily affect the upper and lower limbs. An example is polydactyly, where a foot or hand has more than 5 digits. Clubfoot, one of the most common congenital deformities of the lower limbs, occurs approximately 1 in 1000 births. It can be treated by physical therapy, or by a combination of physical therapy and surgery. One class of congenital limb deformities, limb reduction defects, occurs when one or more limbs are undersized or missing parts. The prevalence of these defects in the United States is approximately 1 in 1900 births. This category includes amelia, ectrodactyly, radial dysplasia, and phocomelia among others. These defects are more likely to be unilateral than bilateral, more likely to affect the upper limbs than lower limbs, and are associated with complex genetic syndromes about 10% of the time. A wide variety of abnormalities of the hands and feet, including the nails and the creases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015, they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births, depending upon how they are diagnosed. In about 6 to 19 per 1,000 they cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximately 13% of CVD deaths, while tobacco accounts for 9%, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia (; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Dictionary of Cell and Molecular Biology (11 March 2008) Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells.Hypoplasia Stedman's Medical Dictionary. lww.com Hypoplasia is similar to aplasia, but less severe. It is technically ''not'' the opposite of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones ( wrist bones), which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Char Syndrome
Char syndrome is an autosomal dominant congenital disease caused by mutations in TFAP2B gene which affects the development of the bones of the face as well as the heart and limbs. During embryo development, TFAP2B regulates the production of the protein AP-2β, a transcription factor that is active in the neural crest and helps regulate genes that control cell division and apoptosis. There are at least 10 mutations of this gene that have been identified in people presenting Char syndrome, which alters specific regions of the gene preventing production of the transcription factor and disrupting normal development of embryo structures. People with this condition present a very distinct facial appearance with flattened cheek bones, flat and broad tip nose, shortened distance between the nose and upper lip, triangular-shaped mouth with tick lips and strabismus. It is also characterized by a patent ductus arteriosus, which is the failure to close the ductus that connects the aorta and pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
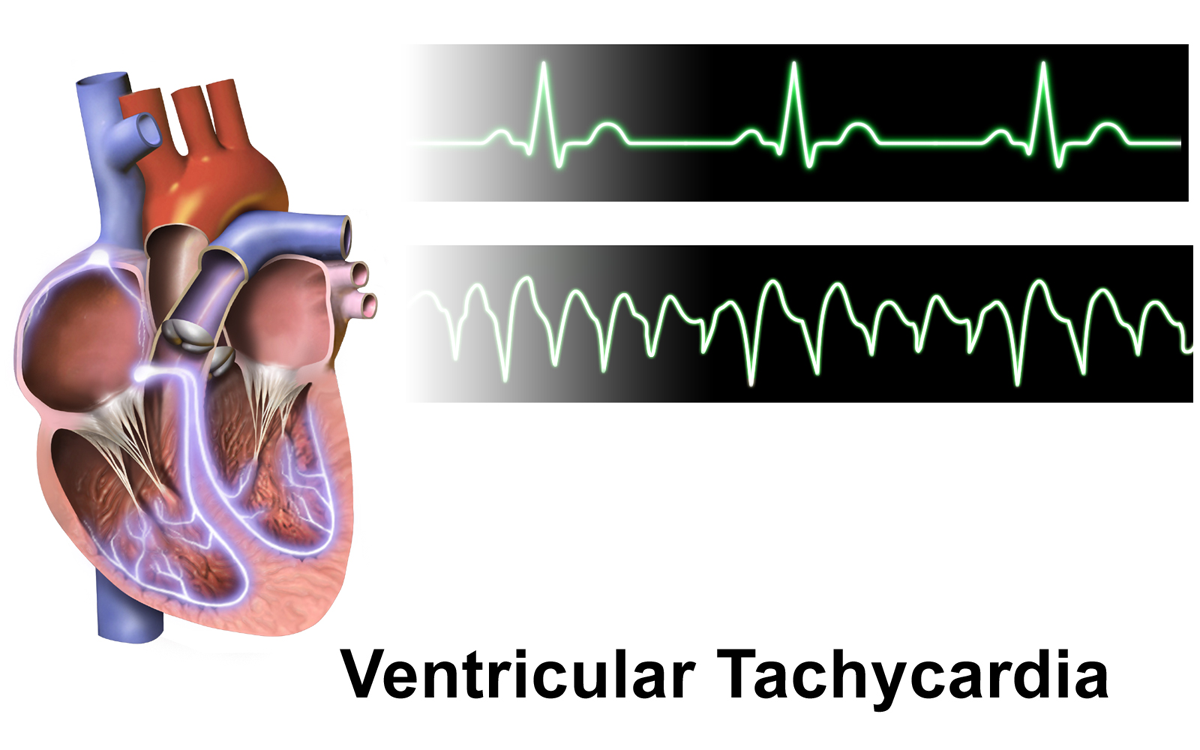
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and decreased level of consciousness. Ventricular tachycardia may lead to coma and persistent vegetative state due to lack of blood and oxygen to the brain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte imbalance, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudden Cardiac Death
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest ''SCA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly circulate around the body and the blood flow to the brain and other organs is decreased. When the brain does not receive enough blood, this can cause a person to lose consciousness and brain cells can start to die due to lack of oxygen. Coma and persistent vegetative state may result from cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is also identified by a lack of central pulses and abnormal or absent breathing. Cardiac arrest and resultant hemodynamic collapse often occur due to arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms). Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia are most commonly recorded. However, as many incidents of cardiac arrest occur out-of-hospital or when a person is not having their cardiac activity monitored, it is difficult to identify the specific mechanism in each case. Structural heart disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachytelephalangy
Brachydactyly () is a medical term denoting the presence of abnormally short digits (fingers or toes) at birth. The shortness is relative to the length of other long bones and other parts of the body. Brachydactyly is an inherited, dominant trait. It most often occurs as an isolated dysmelia, but can also occur with other anomalies as part of many congenital syndromes. Brachydactyly may also be a signal that one is at risk for congenital heart disease due to the association between congenital heart disease and Carpenter syndrome and the link between Carpenter syndrome and brachydactyly. Nomograms for normal values of finger length as a ratio to other body measurements have been published. In clinical genetics, the most commonly used index of digit length is the dimensionless ratio of the length of the third (middle) finger to the hand length. Both are expressed in the same units (centimeters, for example) and are measured in an open hand from the fingertip to the principal cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |