|
Brachycera
The Brachycera are a suborder of the order Diptera. It is a major suborder consisting of around 120 families. Their most distinguishing characteristic is reduced antenna segmentation. Description A summary of the main physical characteristics is: * Antenna size (with eight or fewer flagellomeres) is reduced. In many species the third segment, the flagellum, is fused, except from a bristle called the arista that is sticking out from the fused flagellum. The arista consist of no more than three segments called aristomeres. * The maxillary palp (an elongated appendage near the mouth) has two segments or fewer. * The back portions of the larval head capsule extend into the prothorax (the anterior part of the thorax, which bears the first pair of legs). * Two distinct parts make up of the larval mandible (lower jaw). * The epandrium and hypandrium of the genitalia are separated in males. * No premandible is present on the lower surface of the labrum (the roof of the mout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diptera
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing more than 150,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies, mosquitoes and others. Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great manoeuvrability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the larval food-source and the larvae, which lack true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachycera
The Brachycera are a suborder of the order Diptera. It is a major suborder consisting of around 120 families. Their most distinguishing characteristic is reduced antenna segmentation. Description A summary of the main physical characteristics is: * Antenna size (with eight or fewer flagellomeres) is reduced. In many species the third segment, the flagellum, is fused, except from a bristle called the arista that is sticking out from the fused flagellum. The arista consist of no more than three segments called aristomeres. * The maxillary palp (an elongated appendage near the mouth) has two segments or fewer. * The back portions of the larval head capsule extend into the prothorax (the anterior part of the thorax, which bears the first pair of legs). * Two distinct parts make up of the larval mandible (lower jaw). * The epandrium and hypandrium of the genitalia are separated in males. * No premandible is present on the lower surface of the labrum (the roof of the mout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archisargoidea
} Archisargoidea is an extinct superfamily of brachyceran flies known from the late Middle Jurassic (Callovian) to early Late Cretaceous (Turonian). Most flies in the superfamily have large eyes and an elongated abdomen, preserved females have a sharp, piercing oviscapt used for injecting eggs into host matter. Their relationships with other members of Brachycera is controversial, they are usually considered close relatives of either Stratiomyomorpha or Muscomorpha. Internal relationships between the families are uncertain and the topology of the only cladistic analysis of the family was weakly supported, finding that Archisargidae was paraphyletic with respect to Eremochaetidae and miniaturized Tethepomyiidae. The sharp piercing oviscaps possessed by the group had alternatively been suggested to represent evidence of being parasitoids, injecting their eggs into hosts similar to parasitic wasps, or to inject eggs into plant material like rotting wood or fruit, similar to membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larger Brachycera
The larger brachycera is a name which refers to flies in the following families of the suborder Brachycera: * Acroceridae – hunch-back flies * Asilidae – robber flies * Athericidae – water snipe flies * Bombyliidae – bee flies * Rhagionidae – snipe flies * Scenopinidae – window flies * Stratiomyidae – soldier flies * Tabanidae – horse flies * Therevidae The Therevidae are a family of flies of the superfamily Asiloidea commonly known as stiletto flies. The family contains about 1,600 described species worldwide, most diverse in arid and semiarid regions with sandy soils. The larvae are predators ... – stiletto flies * Xylomyidae – wood soldier flies * Xylophagidae – awl-flies References Brachycera {{Brachycera-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arista (insect Anatomy)
In insect anatomy, the arista is a simple or variously modified apical or subapical bristle, arising from the third antennal segment. It is the evolutionary remains of antennal segments, and may sometimes show signs of segmentation. These segments are called aristameres. The arista may be bare and thin, sometime appearing no more than a simple bristle; pubescent, covered in short hairs; or plumose, covered in long hairs. The presence of an arista is a feature of the Diptera (flies) suborder Brachycera and may be especially well-developed in some species. It is also present in some members of Hemiptera Hemiptera (; ) is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising more than 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from ... (true bugs), specifically in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha. The arista is often covered in multiple kinds of sensilla, or sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genitalia
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting gametes, as well as facilitating fertilization and supporting the development and birth of offspring. Sex organs are found in many species of animals and plants, with their features varying depending on the species. Sex organs are typically differentiated into male and female types. In animals (including humans), the male sex organs include the testicles, epididymides, and penis; the female sex organs include the clitoris, ovaries, oviducts, and vagina. The testicle in the male and the ovary in the female are called the ''primary sex organs''. All other sex-related organs are known as ''secondary sex organs''. The outer parts are known as the genitals or external genitalia, visible at birth in both sexes, while the inner parts are refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
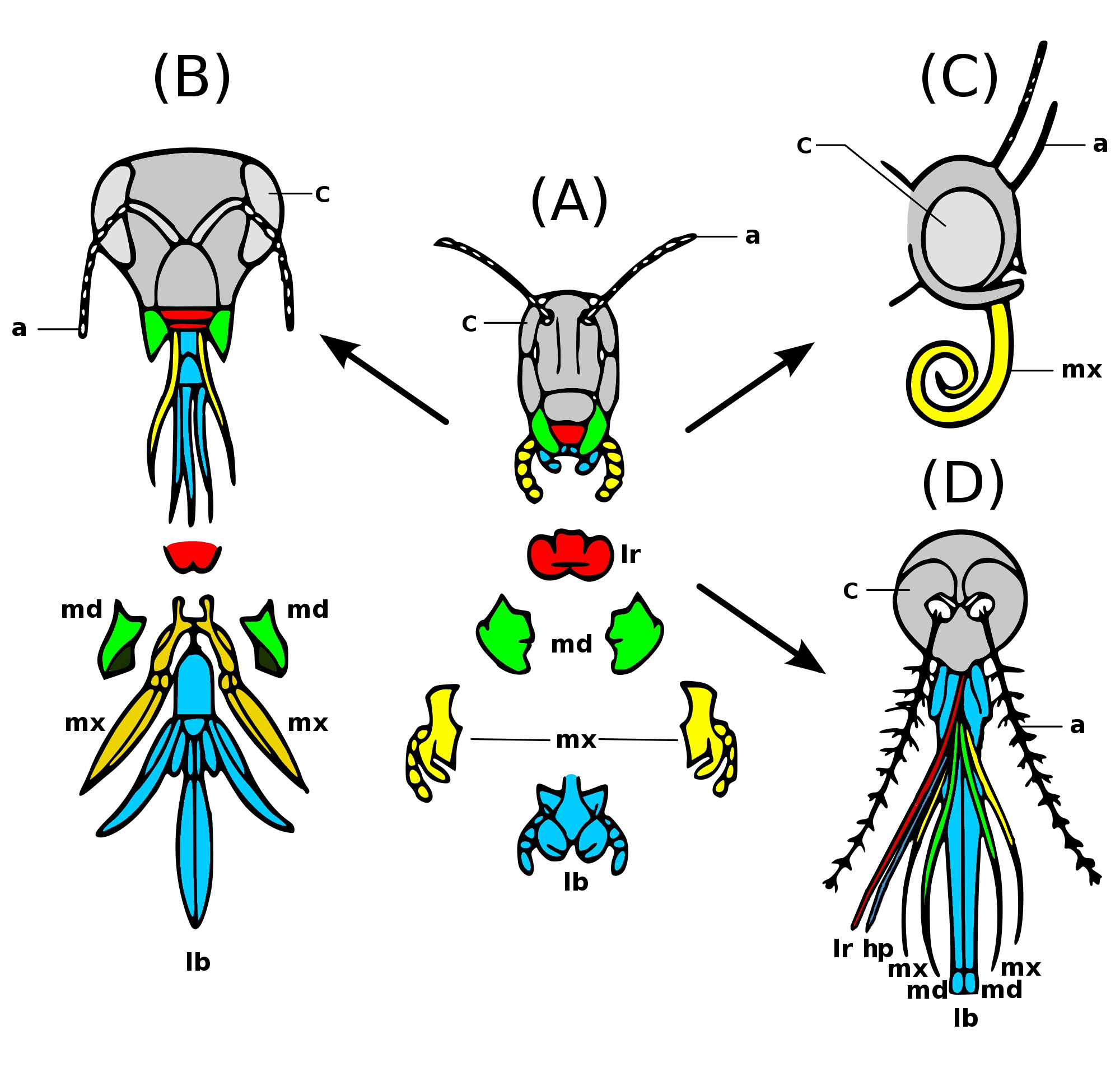
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times independently. For example, mosquitoes (which are true flies) and aphids (which are Hemiptera, true bugs) both pierce and suck, though female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant Homology (biology), homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching Primordium, primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-drag ratio, which compares the benefit of lift with the air resistance of a given wing shape, as it flies. Aerodynamics is the study of wing performance in air. Equivalent Foil (fluid mechanics), foils that move through water are found on Hydrofoil, hydrofoil power vessels and Sailing hydrofoil, foiling sailboats that lift out of the water at speed and on submarines that use diving planes to point the boat upwards or downwards, while running submerged. Hydrodynamics is the study of foil performance in water. Etymology and usage The word "wing" from the Old Norse ''vængr'' for many centuries referred mainly to the foremost limb (anatomy), limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachina Praeceps
''Tachina praeceps'' is a species of fly in the genus ''Tachina'' of the family Tachinidae that can be found in such European countries as Austria, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Greece (including Crete), Hungary, Italy, Malta, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Spain, Switzerland, Ukraine, and all states of former Yugoslavia (except for Bosnia and Herzegovina Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...). References Insects described in 1824 Diptera of Europe praeceps {{Tachina-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Vein
Insect wings are adult outgrowths of the insect exoskeleton that enable insects to fly. They are found on the second and third thoracic segments (the mesothorax and metathorax), and the two pairs are often referred to as the forewings and hindwings, respectively, though a few insects lack hindwings, even rudiments. The wings are strengthened by a number of longitudinal veins, which often have cross-connections that form closed "cells" in the membrane (extreme examples include the dragonflies and lacewings). The patterns resulting from the fusion and cross-connection of the wing veins are often diagnostic for different evolutionary lineages and can be used for identification to the family or even genus level in many orders of insects. Physically, some insects move their flight muscles directly, others indirectly. In insects with direct flight, the wing muscles directly attach to the wing base, so that a small downward movement of the wing base lifts the wing itself upward. Thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |