|
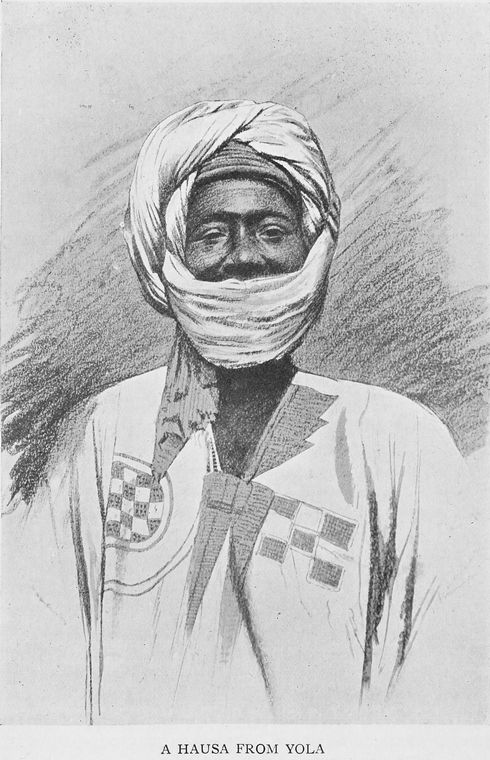
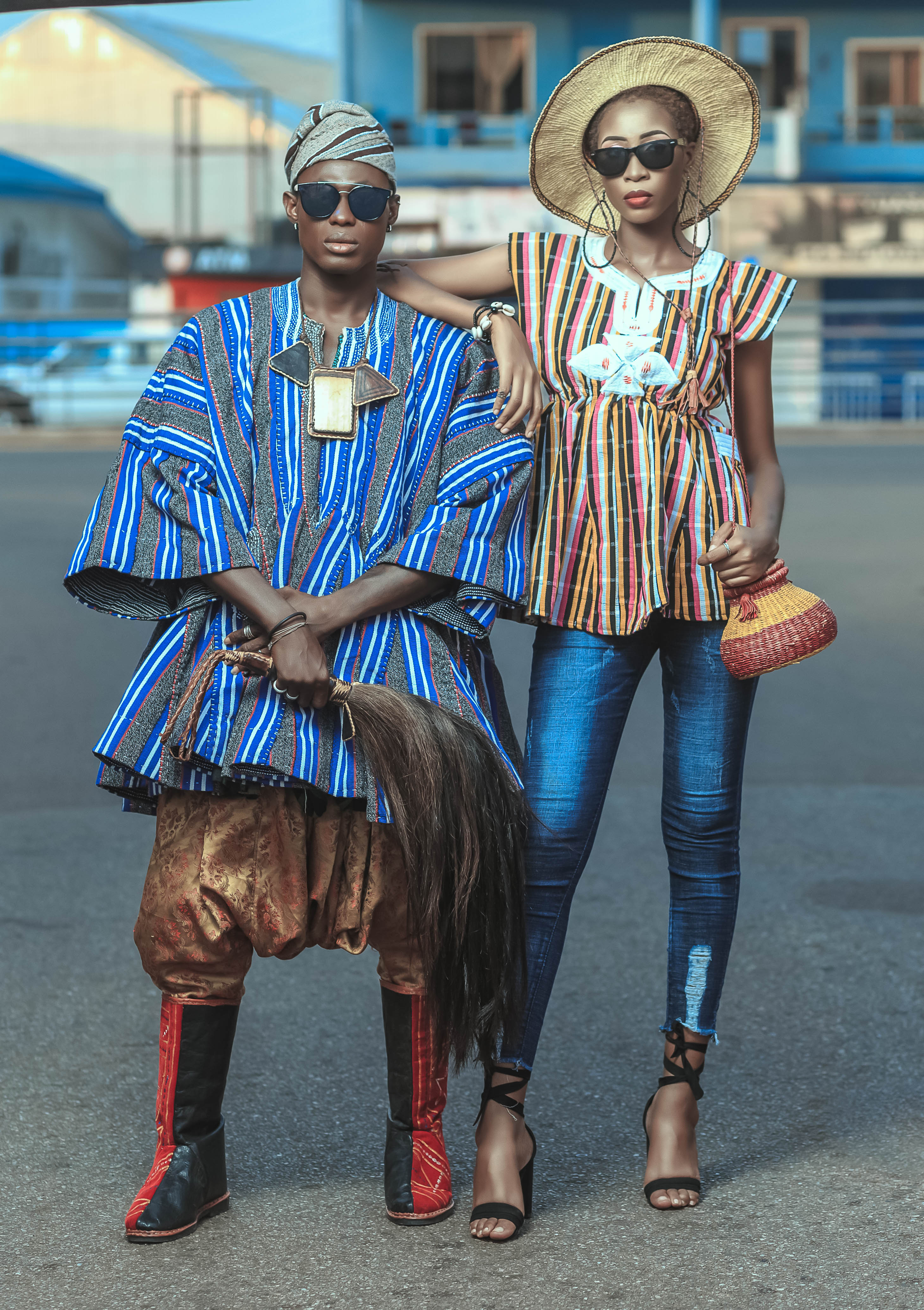
Boubou (clothing)
The boubou or grand boubou from Wolof mboubou is a flowing wide-sleeved robe worn across West Africa, and to a lesser extent in North Africa The garments and its variations are known by various names in different ethnic groups and languages. It is called Kulwu in Kanuri, babban riga in Hausa, boubou, mbubb, mboubou or grand mboubou in Wolof, k'sa or gandora in Tuareg, Kwayi Bèri in Songhai, darra'a in Arabic, grand boubou in various French-speaking West African countries and the English term gown. The Senegalese boubou, also called ''grand boubou'' in French described below, is also known as the Senegalese kaftan. The female version worn in some communities is also known as a m'boubou or kaftan. History Its origin lies with the clothing style of the Wolof, Mande, Songhai- Zarma, Hausa, Kanuri, Toubou, and other trans-Saharan and Sahelian trading groups who used the robe as a practical means of protection from both elements (the harsh sun of the day and sub-freezin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamadou Tandja 2005
Mamadou is a common given name in West Africa among predominantly Muslim ethnic groups such as the Mandé peoples, Mandé and Wolof people, Wolof people. It is a variant of the Arabic name Muhammad (name), Muhammad. In Francophone countries, the name is sometimes uses as a slur towards people of African descent. Academics *Mamadou Diouf (historian), Senegalese professor of West African history at Columbia University Arts and music *Mamadou Diabaté (born 1975), Malian ''kora'' player *Mamadou Diop (musician) (born 1954), Senegalese rhythm guitarist and band leader *Mamadou Konte (died 2007), Senegalese music producer *Jimi Mbaye, Mamadou "Jimi" Mbaye (1957-2025), Senegalese guitarist Government *Mamadou (mansa), ruler of the Mali Empire *Mamadou Blaise Sangaré (born 1954), Malian politician, president of the Social Democratic Convention *Mamadou Boye Bah (1930-2009), Guinean economist and politician *Mamadou Kamara Dékamo (born 1949), Congo-Brazzaville politician and diplomat *M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alasho
Alasho is an indigenous Hausa long turban, worn across the head and neck. It is near identical in length, colour and dimensions to that of the Tuareg The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ... tagelmust, but is wrapped differently to the Tuareg method, leaving the sides of the head and some of the lower neck free. A similar style turban is worn by Songhai men, known as 'fatalaa' in Zarma. Tal Tamari (1998), Les castes de l'Afrique occidentale: Artisans et musiciens endogames, Nanterre: Société d’ethnologie, Once common throughout Hausa society as common male clothing, today it only survives when used for important occasions or ceremonies, rite of passage rituals to the adult age, marriage or in the inauguration of a social leader. The Alasho veil has traditionally be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friday Prayer
Friday prayer, or congregational prayer (), is the meeting together of Muslims for communal prayer and service at midday every Friday. In Islam, the day itself is called ''Yawm al-Jum'ah'' (shortened to ''Jum'ah''), which translated from Arabic means "Day of Meeting", "Day of Assembly" or "Day of Congregation". On this day, all Muslim men are expected to meet and participate at the designated place of meeting and prostration / mosque, with certain exceptions due to distance and situation. Women and children can also participate but do not fall under the same obligation that men do. In many Muslim countries, the Workweek and weekend, weekend is inclusive of Fridays, and in others, Fridays are half-days for schools and some workplaces. It is one of the most exalted Islamic rituals and one of its confirmed obligatory acts. Service The meeting services consists of several parts including ritual washing, chants, recitation of scripture and prayer, and sermons or discussions. Ritual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard. Originally, mosques were simple places of prayer for the early Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than elaborate buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture (650–750 CE), early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets, from which the Adhan, Islamic call to prayer was issued on a daily basis. It is typical of mosque buildings to have a special ornamental niche (a ''mihrab'') set into the wall in the direction of the city of Mecca (the ''qibla''), which Muslims must face during prayer, as well as a facility for ritual cleansing (''wudu''). The pulpit (''minbar''), from which public sermons (''khutbah'') are delivered on the event of Friday prayer, was, in earlier times, characteristic of the central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim Holidays
There are two main holidays in Islam that are celebrated by Muslims worldwide: Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha. The timing of both holidays are set by the lunar Islamic calendar, which is based upon the cycle of the moon, and so is different from the more common, European, solar-based Gregorian calendar. Every year, the Gregorian dates of the Islamic holidays change. Both Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha follow a period of 10 holy days or nights: the last 10 nights of Ramadan for Eid al-Fitr, and the first 10 days of Dhu al-Hijjah for Eid al-Adha. The Night of Power (Arabic: لیلة القدر, Romanization of Arabic, romanized: Laylat al-Qadr), one of the last 10 nights of Ramadan, is the holiest night of the year. Conversely, the Day of Arafah, the day before Eid al-Adha, is the holiest day of the Islamic year. There are a number of other days of note as well as festivals, some common to all Muslims, others specific to Shia Islam or branches thereof. Additionally, Friday is considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
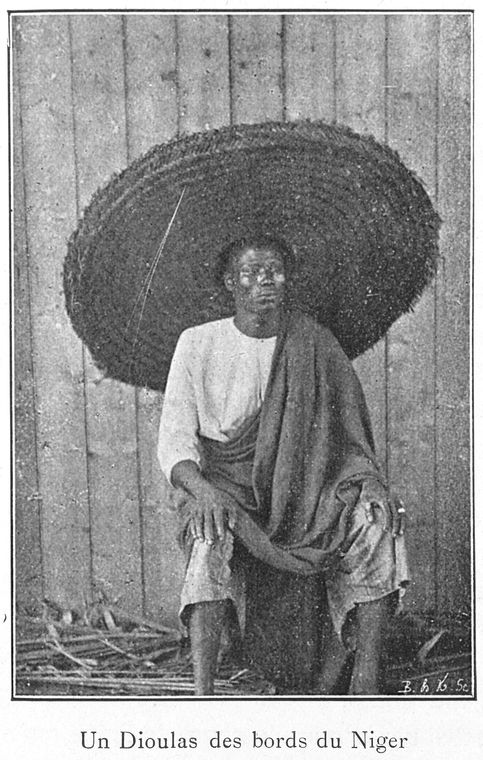
Dyula People
The Dyula (Dioula or Juula) are a Mande people, Mande ethnic group inhabiting several West African countries, including Mali, Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, and Burkina Faso. Characterized as a highly successful merchant caste, ''Dyula'' migrants began establishing trading communities across the region in the fourteenth century. Since business was often conducted under non-Muslim rulers, the ''Dyula'' developed a set of theological principles for Muslim minorities in non-Muslim societies. Their unique contribution of long-distance commerce, Islamic scholarship and religious tolerance were significant factors in the peaceful expansion of Islam in West Africa. The term 'Dyula' is sometimes used interchangeably with Soninke Wangara, Wangara or Jakhanke people, Jakhanke, depending on the historical period and region. Historical background The Mandé embraced Islam during the thirteenth century following introduction to the faith through contact with the North African traders. By the 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulani
The Fula, Fulani, or Fulɓe people are an ethnic group in Sahara, Sahel and West Africa, widely dispersed across the region. Inhabiting many countries, they live mainly in West Africa and northern parts of Central Africa, South Sudan, Darfur, and regions near the Red Sea coast in Sudan. The approximate number of Fula people is unknown, due to clashing definitions regarding Fula ethnicity. Various estimates put the figure between 25 and 40 million people worldwide. A significant proportion of the Fula – a third, or an estimated 7 to 10 million – are pastoralists, and their ethnic group has the largest nomadic pastoral community in the world., Quote: The Fulani form the largest pastoral nomadic group in the world. The Bororo'en are noted for the size of their cattle herds. In addition to fully nomadic groups, however, there are also semisedentary Fulani – Fulbe Laddi – who also farm, although they argue that they do so out of necessity, not choice. The majority of the Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thawb
A thawb, also known as a dishdashah or a kandura in other varieties of Arabic, is a garment traditionally worn by men in the Arab world. It is a long-sleeved, ankle-length robe that has regional variations in name and style. It can be worn in formal or informal settings, depending on the social and cultural norms in question; thawbs are the main formal attire for men in Saudi Arabia. Outside of the Arab world, the garment has been adopted in a number of Muslim-majority areas, particularly in the Indian subcontinent, where it is commonly referred to as a ''jubbah'' and is frequently worn by those who regard it as ''sunnah'' (i.e., something practiced, spoken, or observed by Muhammad, the founding Islamic prophet) due to its modest appearance. Etymology The word ''thawb'' () is a Standard Arabic word for "dress" or "garment". It is also romanized as ''thobe'' or ''thaub'' or ''thob.'' Name by locality Regional variations The ''thawb'' is commonly worn by men in the Arabian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghanaian Smock
The Ghanaian Smock or Tani is a fabric worn by both women and men in Ghana. It is the most popular traditional attire in the country. The fabric is called Tani in Dagbani language, Dagbani, while the male and female wear are respectively called Bin'gmaa and Bin'mangli. The smock is formally worn with a hat (zipligu)/ scarf (bobga), footwear (muɣri), and a trouser (kurugu). The smock was famously worn by The Big Six (Ghana), Ghana's founding fathers when they declared Independence Day (Ghana), Ghana's independence from the British Empire, British on March 6, 1957. Other names The smock is also called Bun-nwↃ or Bana by Mampruli language, Mamprusis, fugu in Mossi people, Mossi, batakari in the Asante dialect, in Farefare language, Frafra, and Banaa in Kusaal language, Kusaal both in the Upper East Region, upper east region. It is worn by Royals and civilians across Dagbon and other northern regions, but popular across Ghana. The smock originated in the northern region o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dashiki
The dashiki (, ) is a colorful garment that covers the top half of the body, worn mostly in West Africa. It has formal and informal versions and varies from simple draped clothing to fully tailored suits. A common form is a loose-fitting pullover garment, with an ornate V-shaped collar, and tailored and embroidered neck and sleeve lines. It is frequently worn with a brimless kufi cap (which is worn in Islamic communities in Africa and the African diaspora) and pants. It has been popularized and claimed by communities in the African diaspora, especially African Americans. The now trademark dashiki design was born from a wax print pattern by Dutch designer Toon van de Mannaker for Netherlands-based Vlisco. Van de Mannaker's print pattern was inspired by the silk embroidered tunics worn by Christian Ethiopian noblewomen in the 19th century. The pattern became known as the Angelina pattern in the West African market after the release of Ghanaian highlife hit song "Angelina" by The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songhai Empire
The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its largest ethnic group and ruling elite, the Songhai people. Sonni Ali established Gao as the empire's capital, although a Songhai state had existed in and around Gao since the 11th century. Other important cities in the kingdom were Timbuktu and Djenné, where urban-centred trade flourished; they were conquered in 1468 and 1475, respectively. Initially, the Songhai Empire was ruled by the Sonni dynasty (–1493), but it was later replaced by the Askia dynasty (1493–1591). During the second half of the 13th century, Gao and the surrounding region had grown into an important trading center and attracted the interest of the expanding Mali Empire. Mali conquered Gao near the end of the 13th century. Gao remained under Malian command until the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa Bakwai
Hausa Kingdoms, also known as Hausa Kingdom or Hausaland, was a collection of states ruled by the Hausa people, before the Fulani jihads. It was situated between the Niger River and Lake Chad (modern day northern Nigeria). Hausaland lay between the Western Sudanic kingdoms of Ancient Ghana, Mali and Songhai and the Eastern Sudanic kingdoms of Kanem-Bornu. Hausaland took shape as a political and cultural region during the first millennium CE as a result of the westward expansion of Hausa peoples. They arrived in Hausaland when the terrain was converting from woodlands to savannah. They started cultivating grains, which led to a denser peasant population. They had a common language, laws and customs. The Hausa were known for fishing, hunting, agriculture, salt-mining, and blacksmithing. By the 14th century, Katsina had become the most powerful city-state. Katsina was the base for the trans-Saharan trade in salt, cloth, leather, and grain. The Hausa oral history is reflected in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |