|
Borole
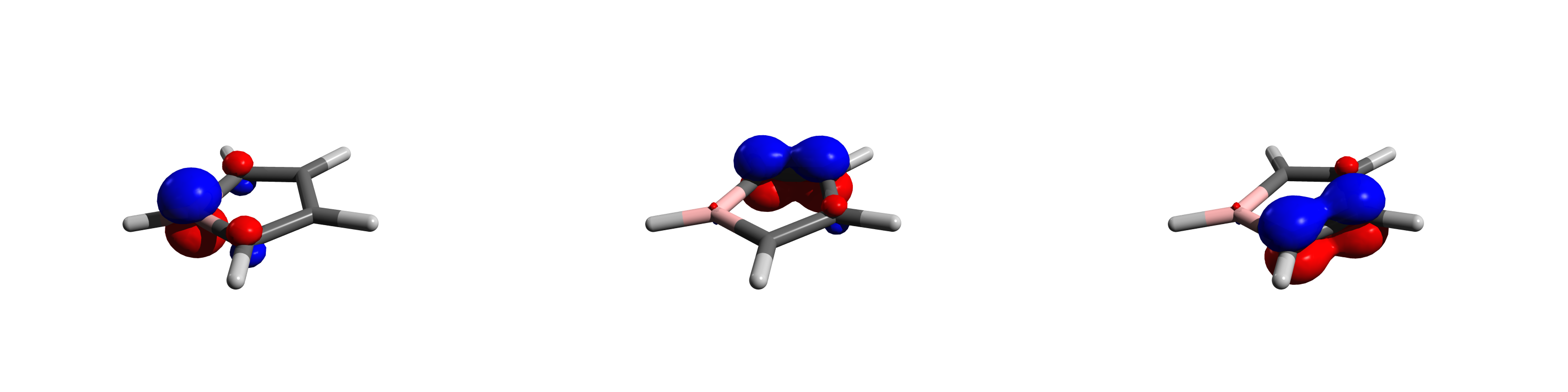
Boroles represent a class of molecules known as metalloles, which are heterocyclic 5-membered rings. As such, they can be viewed as structural analogs of cyclopentadiene, pyrrole or furan, with boron replacing a carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atom respectively. They are isoelectronic with the cyclopentadienyl cation or abbreviated as and comprise four π electrons. Although Hückel's rule cannot be strictly applied to borole, it is considered to be antiaromatic due to having 4 π electrons. As a result, boroles exhibit unique electronic properties not found in other metalloles. The parent unsubstituted compound with the chemical formula has yet to be isolated outside a coordination sphere of transition metals. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, can have various substituents at the 4 carbons and boron. The high electron deficiency leads to various reactivities such as metal free hydrogen activation and rearrangements upon cycloaddition which are unobserved in othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borole Homolumo
Boroles represent a class of molecules known as metalloles, which are heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic 5-membered rings. As such, they can be viewed as structural analogs of cyclopentadiene, pyrrole or furan, with boron replacing a carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atom respectively. They are Isoelectronicity, isoelectronic with the cyclopentadienyl cation or abbreviated as and comprise four π electrons. Although Hückel's rule cannot be strictly applied to borole, it is considered to be antiaromaticity, antiaromatic due to having 4 π electrons. As a result, boroles exhibit unique electronic properties not found in other metalloles. The parent unsubstituted compound with the chemical chemical formula, formula has yet to be isolated outside a coordination sphere of transition metals. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, can have various substituents at the 4 carbons and boron. The high electron deficiency leads to various reactivities such as metal free hydrogen a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallole
Metalloles are metallacycle derivatives of cyclopentadiene in which the carbon atom at position 5, the saturated carbon, is replaced by a heteroatom. In contrast to its parent compound, the numbering of the metallole starts at the heteroatom. Some of these compounds are described as organometallic compounds, but in the list below quite a number of metalloids are present too. Some metalloles are fluorescent. Polymeric derivatives of pyrrole and thiophene are of interest in molecular electronics. Metalloles, which can also be viewed as structural analogs of pyrrole, include: * Arsole, a moderately-aromatic arsenic analog * Bismole, a bismuth analog * Borole, a boron analog * Furan (oxole), an oxygen analog * Gallole, a gallium analog * Germole, a germanium analog * Phosphole, a phosphorus analog * Pyrrole (azole), a nitrogen analog * Selenophene, a selenium analog * Silole, a silicon analog * Stannole, a tin analog * Stibole, an antimony analog * Tellurophene, a tel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic Compound
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic organic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of organic heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of organic heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on organic unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained organic 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of organic heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthesis Of Boroles
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to: Science Chemistry and biochemistry *Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors **Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organic compounds ***Total synthesis, the complete organic synthesis of complex organic compounds, usually without the aid of biological processes ***Convergent synthesis or linear synthesis, a strategy to improve the efficiency of multi-step chemical syntheses **Dehydration synthesis, a chemical synthesis resulting in the loss of a water molecule *Biosynthesis, the creation of an organic compound in a living organism, usually aided by enzymes **Photosynthesis, a biochemical reaction using a carbon molecule to produce an organic molecule, using sunlight as a catalyst **Chemosynthesis, the synthesis of biological compounds into organic waste, using methane or an oxidized molecule as a catalyst **Amino acid synthesis, the synthesis of an amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Gordon Albert Stone
Francis Gordon Albert Stone CBE, FRS, FRSC (19 May 1925 – 6 April 2011), always known as Gordon, was a British chemist who was a prolific and decorated scholar. He specialized in the synthesis of main group and transition metal organometallic compounds. He was the author of more than 900 academic publications resulting in an h-index of 72 in 2011. Early life Gordon Stone was born in Exeter, Devon in 1925, the only child of Sidney Charles Stone, a civil servant, and Florence Beatrice Stone (née Coles).Bristol University ObituaryF Gordon A Stone retrieved 08/03/2012 He received his B.A. in 1948 and Ph.D. in 1951, both from Christ's College, Cambridge (Cambridge University), England, where he studied under Harry Julius Emeléus. Academic life After graduating from Cambridge, he was a Fulbright Scholar at the University of Southern California for two years, before being appointed as an instructor in the Chemistry Department at Harvard University, and was appointed assis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stannole
Stannole is an organotin compound with the chemical formula, formula (carbon, Chydrogen, H)4tin, SnH2. It is classified as a metallole, i.e. an unsaturated five-membered ring containing a heteroatom. It is a structural analog of cyclopentadiene, with tin replacing the saturated carbon atom. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are also called stannoles. Examples 1,1-Dibutylstannole is a pale yellow oil prepared from 1,4-dilithio-1,3-butadiene and dibutyltin dichloride. : 1,1-Dimethyl-2,3,4,5-tetraphenyl-1''H''-stannole, for example, can be formed by the double displacement, displacement reaction of 1,4-dilithio-1,2,3,4-tetraphenyl-1,3-butadiene and dimethyltin dichloride. 1,1-Disubstituted stannoles can be formed in the [2+2+1] cycloaddition reaction of two acetylene molecules with an organotin molecule SnR2. Related compounds 1λ2-Stannole has formula C4H4Sn, with no hydrogen on the tin atom, which is in the +2 oxidation state. See also *Organotin chemistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
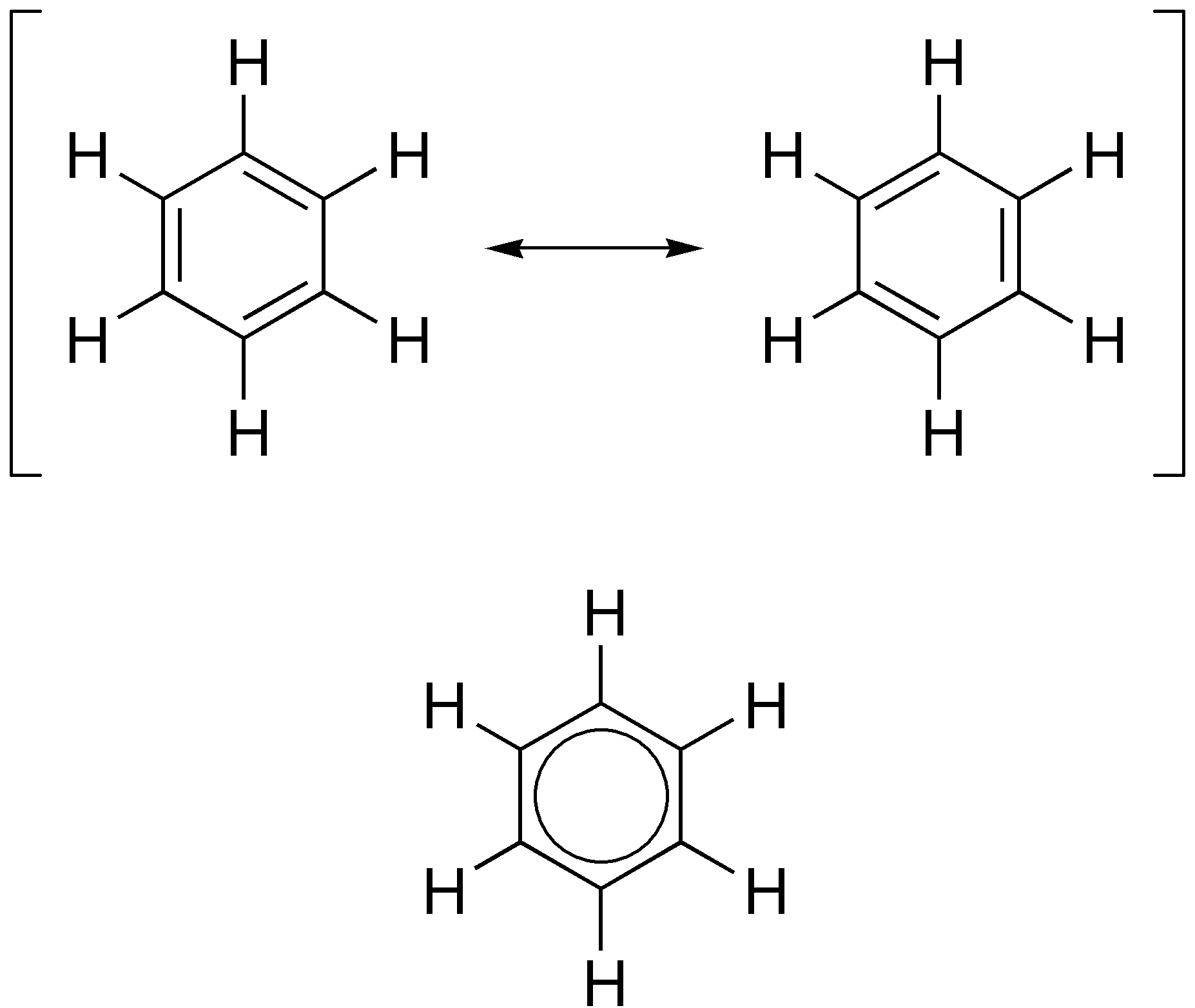
Resonance In Borole 2-
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximum amplitude response in the system. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases. All systems, including molecular systems and particles, tend to vibrate at a natural frequency depending upon their structure; when there is very little damping this frequency is approximately equal to, but slightly above, the resonant frequency. When an oscillating force, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance (chemistry)
In chemistry, resonance, also called mesomerism, is a way of describing Chemical bond, bonding in certain molecules or polyatomic ions by the combination of several contributing structures (or ''forms'', also variously known as ''resonance structures'' or ''canonical structures'') into a resonance hybrid (or ''hybrid structure'') in valence bond theory. It has particular value for analyzing delocalized electrons where the bonding cannot be expressed by one single Lewis structure. The resonance hybrid is the accurate structure for a molecule or ion; it is an average of the theoretical (or hypothetical) contributing structures. Overview Under the framework of valence bond theory, resonance is an extension of the idea that the bonding in a chemical species can be described by a Lewis structure. For many chemical species, a single Lewis structure, consisting of atoms obeying the octet rule, possibly bearing formal charges, and connected by bonds of positive integer order, is suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis Acids And Bases
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane CH3)3Bis a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis. From p. 142: "We are inclined to think of substances as po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |