|
Boreosphenida
Tribosphenida is a clade of mammals that includes the ancestor of ''Hypomylos'', Aegialodontia and Theria (the last common ancestor of marsupials and placentals plus all of its descendants). It belongs to the group Zatheria. The current definition of Tribosphenida is more or less synonymous with Boreosphenida. Characteristics Tribosphenid mammals were originally grouped on the basis of triangular or V-shaped (Molar (tooth)#Tribosphenic, tribosphenic) molars. The relationship of the also tribosphenic australosphenidans, a group of mammals from the Jurassic-Cretaceous of the Southern Hemisphere often suggested to be close relatives of living Monotreme, monotremes, has been questioned, and it has been argued that they developed tribosphenic molars independently from those of "true" tribosphenidans. Some authors have alternatively continued to argue that non-monotreme australosphenidans are in fact true tribosphenidans unrelated to monotremes. "True" unambiguous members of Tribospheni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambondro Mahabo
''Ambondro mahabo'' is a mammal from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) Isalo III Formation (about 167 million years ago) of Madagascar. The only described species of the genus ''Ambondro'', it is known from a fragmentary mandible, lower jaw with three teeth, interpreted as the last premolar and the first two molar (tooth), molars. The premolar consists of a central cusp (dentistry), cusp with one or two smaller cusps and a cingulum (dentistry), cingulum (shelf) on the inner, or lingual, side of the tooth. The molars also have such a lingual cingulum. They consist of two groups of cusps: a trigonid of three cusps at the front and a talonid with a main cusp, a smaller cusp, and a crest at the back. Features of the talonid suggest that ''Ambondro'' had tribosphenic molars, the basic arrangement of molar features also present in marsupial and placental mammals. It is the oldest known mammal with putatively tribosphenic teeth; at the time of its discovery it antedated the second oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australosphenida
The Australosphenida are a clade of mammals, containing mammals with tribosphenic molars, known from the Jurassic to Mid-Cretaceous of Gondwana. Although they have often been suggested to have acquired tribosphenic molars independently from those of Tribosphenida, this has been disputed. Fossils of australosphenidans have been found from the Jurassic of Madagascar and Argentina, and Cretaceous of Australia and Argentina. Monotremes have also been considered a part of this group in its original definition and in many subsequent studies, but its relationship with other members has been disputed by some scholars. Taxonomy This grouping includes the following taxa: *† Henosferidae, including the genera '' Ambondro'', '' Asfaltomylos'', and '' Henosferus'' from the Jurassic of Argentina and Madagascar. *† Ausktribosphenidae known from the Early Cretaceous of Australia *† Bishopidae including ''Bishops'' from the Lower Cretaceous of Australia and an unnamed genus from the Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
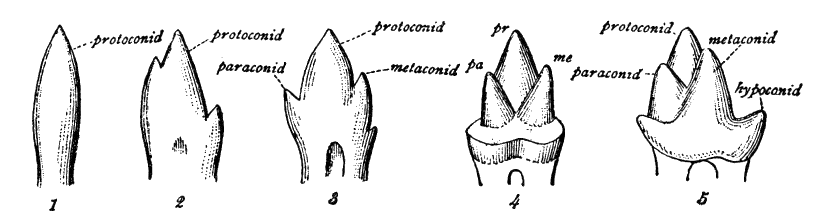
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zatheria
Cladotheria is a clade (sometimes ranked as a Legion (taxonomy), legion) of mammals. It contains modern therian mammals (marsupials and Placentalia, placentals) and several extinct groups, such as the "dryolestoids", amphitheriids and peramurids. The clade was named in 1975 by Malcolm McKenna. In 2002, it was defined as a node-based taxon containing "the common ancestor of dryolestids and living therians, plus all its descendants". A different, stem-based taxon, stem-based definition was given in 2013, in which Cladotheria contains all taxa that are closer to ''Mus musculus'' (the house mouse) than to the "symmetrodont" ''Spalacotherium tricuspidens''. Cladotheria incorporates a set of nested mammal clades culminating in Tribosphenida (also known as Boreosphenida), mammals with fully Tribosphenic molar, tribosphenic teeth such as therians and a few of their closest relatives. The clade Prototribosphenida includes "the common ancestor of ''Vincelestes'' and living therians, plus al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegialodontia
Aegialodontia is a clade of extinct early mammals, close to the origin of Boreosphenida. The clade includes some of the oldest known tribosphenic taxa, until the discovery of '' Tribactonodon'' from the Berriasian Durlston Formation in 2001, '' Aegialodon'' from the Valanginian Wadhurst Clay Formation was the oldest taxon with the tooth form. The Aptian to Albian The Albian is both an age (geology), age of the geologic timescale and a stage (stratigraphy), stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early Cretaceous, Early/Lower Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch/s ... taxon '' Kielantherium'' from Mongolia, formerly a synonym of ''Aegialodon'', is also within the group, sister to ''Aegialodon'' within Aegialodontidae. References Prehistoric mammals Tribosphenida {{Cretaceous-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammaliaformes
Mammaliaformes ("mammalian forms") is a clade of synapsid tetrapods that includes the crown group mammals and their closest extinct relatives; the group radiated from earlier probainognathian cynodonts during the Late Triassic. It is defined as the clade originating from the most recent common ancestor of Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals; the latter is the clade originating with the most recent common ancestor of extant Monotremata, Marsupialia and Placentalia. Besides Morganucodonta and the crown group mammals, Mammaliaformes also includes Docodonta and ''Hadrocodium''. Mammaliaformes is a term of phylogenetic nomenclature. In contrast, the assignment of organisms to class Mammalia has traditionally been founded on traits and, on this basis, Mammalia is slightly more inclusive than Mammaliaformes. In particular, trait-based taxonomy generally includes ''Adelobasileus'' and '' Sinoconodon'' in Mammalia, though they fall outside the Mammaliaformes definition. These ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotreme
Monotremes () are mammals of the order Monotremata. They are the only group of living mammals that lay eggs, rather than bearing live young. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and the four species of echidnas. Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brains, jaws, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and other body parts, compared to the more common mammalian types. Although they are different from other living mammals in that they lay eggs, female monotremes are like other mammals in that they nurse their young with milk. Monotremes have been considered by some authors to be members of Australosphenida, a clade that contains extinct mammals from the Jurassic and Cretaceous of Madagascar, South America, and Australia, but this categorization is disputed and their taxonomy is under debate. All extant species of monotremes are indigenous to Australia and New Guinea, although they were also present during the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene epochs in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm McKenna
Malcolm Carnegie McKenna (1930–2008) was an American paleontologist and author on the subject. Paleontologist McKenna began his paleontology career at the Webb School of California (grades 9-12) in Claremont, California, under noted paleontologist and teacher, Raymond Alf. He attended the California Institute of Technology and Pomona College, then graduated in paleontology at the University of California, Berkeley, where he also earned his Ph.D. He was the curator of vertebrate paleontology at the American Museum of Natural History in New York City. Through most of his four decades at the museum, he held a professorship in geosciences at Columbia University. From 1975 to 1976 he served as president of the Society of Vertebrate Paleontology. With Susan K. Bell, he co-authored the 1997 book ''Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level,'' a comprehensive work genealogy of Mammalia, including the systematics, relationships, and occurrences of all Mammal taxa, living and ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalia
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals). Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and birds), constitut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar Tooth (human), teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the Canine tooth, canine and Molar (tooth), molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per dental terminology#Quadrant, quadrant in the permanent teeth, permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two Cusp (dentistry), cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie Posterior (anatomy), posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |