|
Bollard Pull
Bollard pull is a conventional measure of the pulling (or towing) power of a watercraft. It is defined as the force (usually in tonnes-force or kilonewtons (kN)) exerted by a vessel under full power, on a shore-mounted bollard through a tow-line, commonly measured in a practical test (but sometimes simulated) under test conditions that include calm water, no tide, level trim, and sufficient depth and side clearance for a free propeller stream. Like the horsepower or mileage rating of a car, it is a convenient but idealized number that must be adjusted for operating conditions that differ from the test. The bollard pull of a vessel may be reported as two numbers, the ''static'' or ''maximum'' bollard pull – the highest force measured – and the ''steady'' or ''continuous'' bollard pull, the average of measurements over an interval of, for example, 10 minutes. An equivalent measurement on land is known as drawbar pull, or tractive force, which is used to measure the total hori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Watercraft
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine. Types Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories. *Rafts, which gain their buoyancy from the fastening together of components that are each buoyant in their own right. Generally, a raft is a "flow through" structure, whose users would have difficulty keeping dry as it passes through waves. Consequently, apart from short journeys (such as a river crossing), their use is confined to warmer regions (roughly 40° N to 40° S). Outside this area, use of rafts at sea is impracticable due to the risks of exposure to the crew. *Boats and ships, which float by having the submergeable part of their structure exclude water with a waterproof surface, so creating a space that contains air, as well as cargo, passengers, crew, etc. In total, this structure weighs less than the water that would occupy the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ballast Tractor
A ballast tractor is a specially weighted tractor unit of a heavy hauler combination. It is designed to utilize a drawbar to pull or push heavy or exceptionally large trailer loads which are loaded in a hydraulic modular trailer. When feasible, lowboy-style semi-trailers are used to minimize the height of a load's center of mass. Typical drivetrains are 6×4 and 6×6, but 8×6 and 8×8 are also available. Typical ballast tractor loads include oil rig modules, bridge sections, buildings, ship sections, and industrial machinery such as generators and turbines. Only a handful of manufacturers produce dedicated ballast tractors. Extra-heavy-duty chassis versions of mass-production tractor units are fitted with drawbar hitches and a separate ballast box as an alternative. These units are classified as N3 Category of large goods vehicle. Ballast tractors can be traced back to the 1940s when heavy haulers from the UK started employing purpose-built Scammell Showtracs, a short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Course (navigation)
In navigation, the course of a watercraft or aircraft is the cardinal direction in which the craft is to be Steering, steered. The course is to be distinguished from the ''Heading (navigation), heading'', which is the direction where the watercraft's Bow (watercraft), bow or the aircraft's Nose cone, nose is pointed. The path that a vessel follows is called a track or, in the case of aircraft, ground track (also known as ''course made good'' or ''course over the ground''). The intended track is a route. Discussion For ships and aircraft, routes are typically Great-circle distance, straight-line segments between Waypoint, waypoints. A navigator determines the ''bearing'' (the compass direction from the craft's current position) of the next waypoint. Because water currents or wind can cause a craft to drift off course, a navigator sets a ''course to steer'' that compensates for drift. The helmsman or pilot points the craft on a ''heading'' that corresponds to the course to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catenary
In physics and geometry, a catenary ( , ) is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or wire rope, cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends in a uniform gravitational field. The catenary curve has a U-like shape, superficially similar in appearance to a parabola, which it is not. The curve appears in the design of certain types of Catenary arch, arches and as a cross section of the catenoid—the shape assumed by a soap film bounded by two parallel circular rings. The catenary is also called the alysoid, chainette,#MathWorld, MathWorld or, particularly in the materials sciences, an example of a funicular curve, funicular. Rope statics describes catenaries in a classic statics problem involving a hanging rope. Mathematically, the catenary curve is the Graph of a function, graph of the hyperbolic cosine function. The surface of revolution of the catenary curve, the catenoid, is a minimal surface, specifically a minimal surface of revolution. A ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementary particle, elementary particles, theoretically with the same amount of matter, have nonetheless different masses. Mass in modern physics has multiple Mass in special relativity, definitions which are conceptually distinct, but physically equivalent. Mass can be experimentally defined as a measure (mathematics), measure of the body's inertia, meaning the resistance to acceleration (change of velocity) when a net force is applied. The object's mass also determines the Force, strength of its gravitational attraction to other bodies. The SI base unit of mass is the kilogram (kg). In physics, mass is Mass versus weight, not the same as weight, even though mass is often determined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensionless and equal to per mille, ‰). Salinity is an important factor in determining many aspects of the chemistry of natural waters and of biological processes within it, and is a state function, thermodynamic state variable that, along with temperature and pressure, governs physical characteristics like the density and heat capacity of the water. A contour line of constant salinity is called an ''isohaline'', or sometimes ''isohale''. Definitions Salinity in rivers, lakes, and the ocean is conceptually simple, but technically challenging to define and measure precisely. Conceptually the salinity is the quantity of dissolved salt content of the water. Salts are compounds like sodium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium nitrate, and sod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
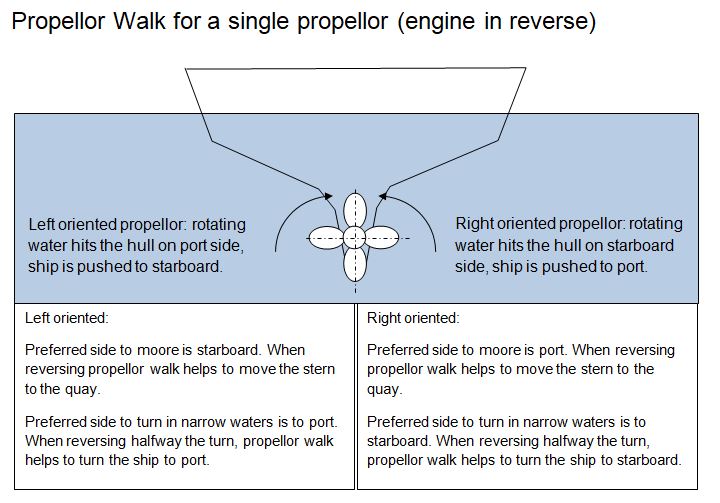
Propeller Walk
Propeller walk (also known as propeller effect, wheeling effect, Paddle steamer, paddle wheel effect, asymmetric thrust, asymmetric blade effect, transverse thrust, prop walk) is the term for a propeller's tendency to rotate about a vertical axis (also known as Ship motions, yaw motion). The rotation is in addition to the forward or backward acceleration. Knowing of and understanding propeller walk is important when maneuvering in small spaces. It can be used to one's advantage while mooring off, or it can complicate a maneuver if the effect works against the pilot. Effect A propeller is called right-handed if it rotates clockwise in forward gear (when viewed from the stern). A right-handed propeller in forward gear will tend to push the stern of the boat to starboard (thereby pushing the bow to Port (direction), port and turning the boat counter-clockwise) unless the rotation is corrected for. In reverse gear, the turning effect will be much stronger and with opposite direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Panamax Ports
A Panamax port is a deepwater port that can accommodate a fully laden Panamax ship. With the completion of the Panama Canal expansion project in 2016, this list will need to be significantly revised due to larger "post panamax" ships transiting Panama. Other lists are required for even bigger Valemax and Chinamax ships. Africa Mediterranean Sea * Djendjen ( Jijel), Algeria * Tanger-Med, Morocco Atlantic Ocean (from North to South) * Nouadhibou, Mauritania — iron ore terminal. * Nouakchott, Mauritania — proposed railhead for phosphate mine. * Port Kamsar, Guinea — bauxite loading port, origin of Kamsarmax ship type. * Monrovia, Liberia — proposed deepening to 20m for 200,000t vessels. * Sekondi-Takoradi, Ghana — built 1928 * Tema, Ghana — built 1961 * Cotonou — Benin * Lomé — Togo * Lekki Deep Sea Port, Nigeria Began operations in April 2023, it is currently the largest deep water port in Africa. Designed to welcome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
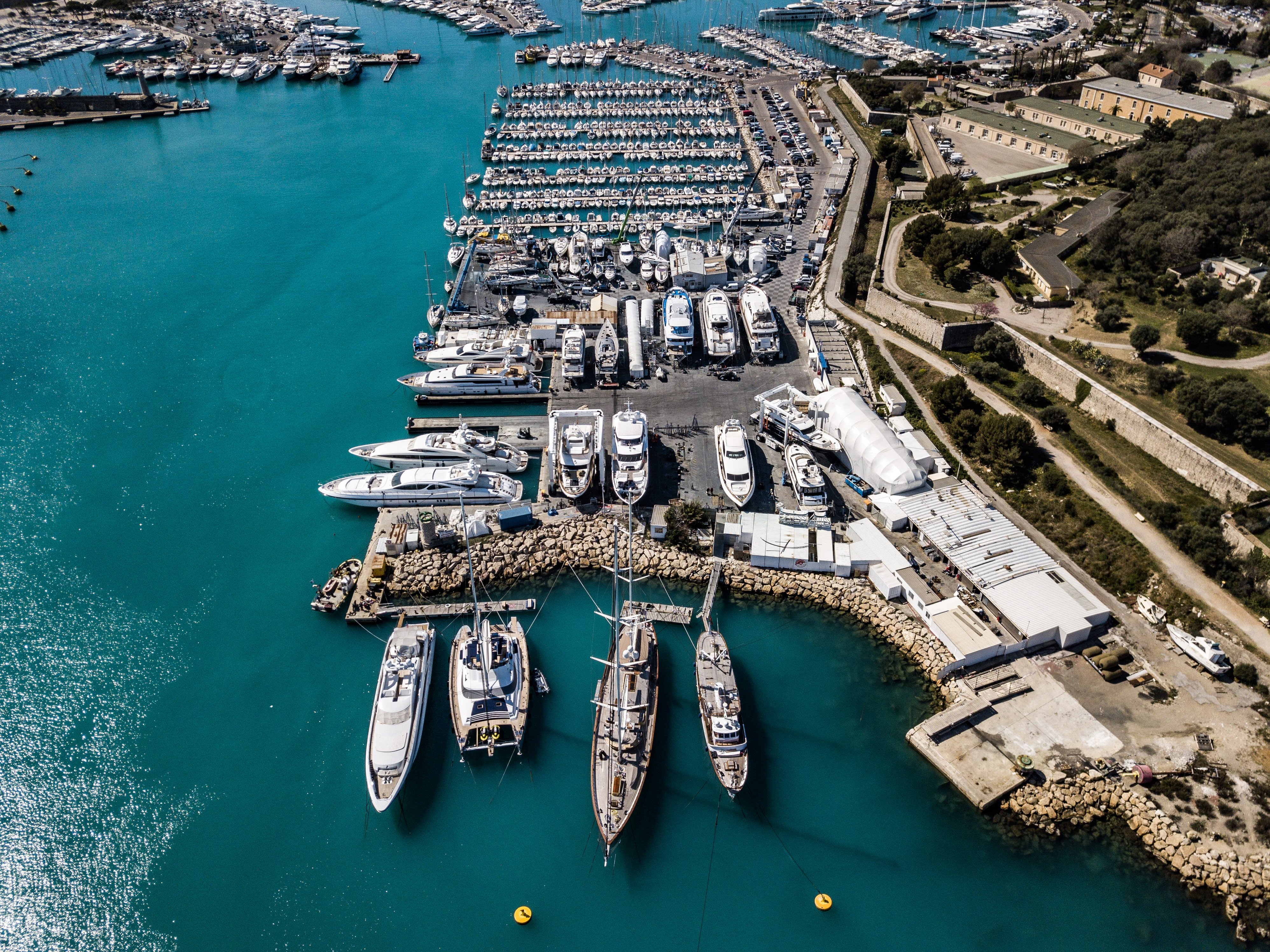
Shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are shipbuilding, built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes more involved with original construction, dockyards are sometimes more linked with maintenance and basing activities. The terms are routinely used interchangeably, in part because the Shipyard#History, evolution of dockyards and shipyards has often caused them to change or merge roles. Countries with large shipbuilding industries include Australia, Brazil, China, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, India, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, the Philippines, Poland, Romania, Russia, Singapore, South Korea, Sweden, Taiwan, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, the United States and Vietnam. The shipbuilding industry is more fragmented in Economy of Europe, Europe than in Econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
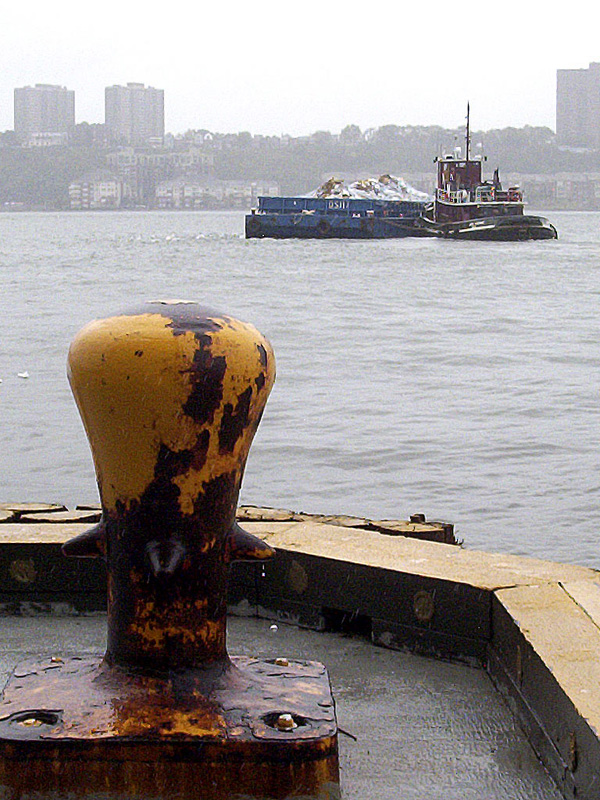
Bollard Pull Idealized-2
A bollard is a sturdy, short, vertical post (structural), post. The term originally referred to a post on a ship or wharf, quay used principally for mooring boats. In modern usage, it also refers to posts installed to road traffic control, control road traffic and posts designed to prevent automotive vehicles from traffic collision, colliding with pedestrians and structures. Etymology The term is probably related to Bole (botany), bole, meaning a tree trunk. The earliest citation given by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (referring to a maritime bollard) dates from 1844, although a reference in the ''Caledonian Mercury'' in 1817 describes bollards as huge posts. History Wooden posts were used for basic traffic management from at least the second half of the 17th century. One early well-documented case is that of the "postes and rales in ye King's highway for ye (safety) of all foot passengers" erected in 1671 in the High Street of Old Brentford, Middlesex (part of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |